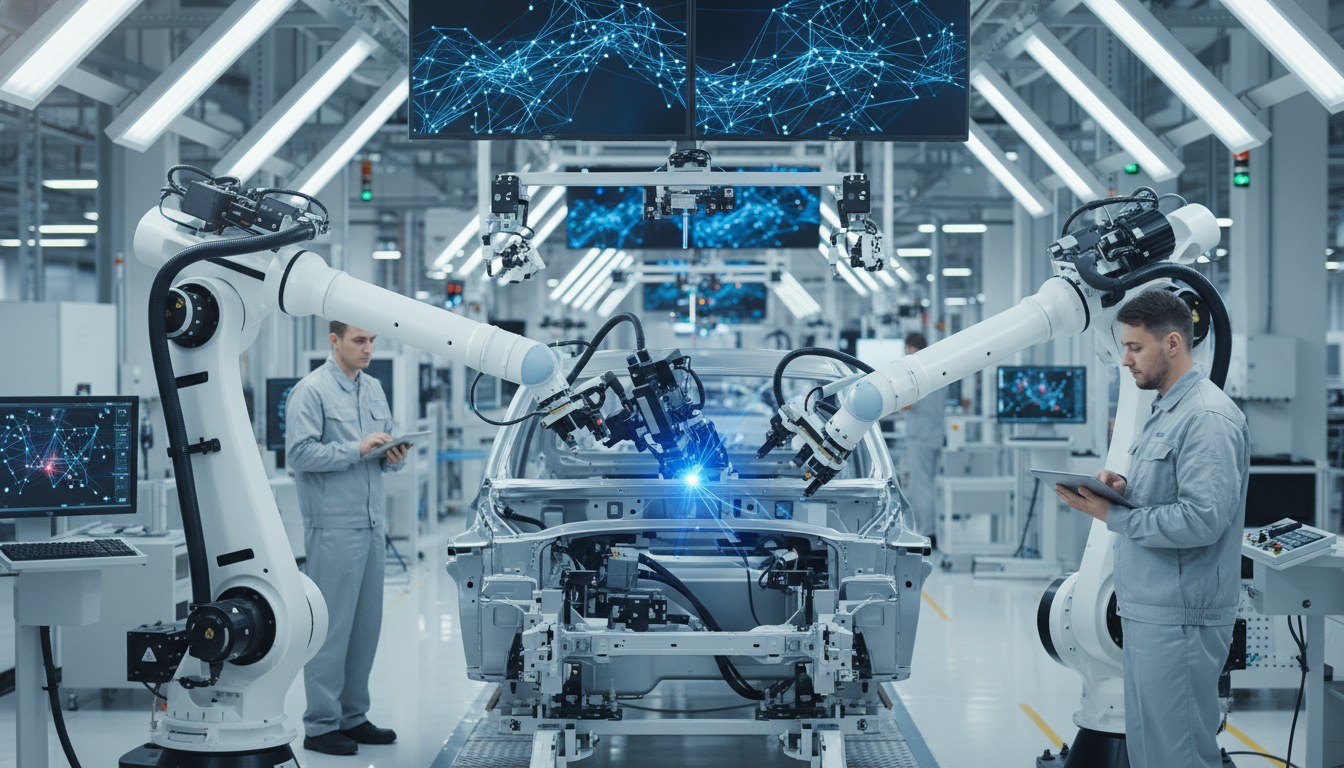
AI For Autonomous Quality Assurance
AI For Autonomous Quality Assurance represents a paradigm shift within the Automotive sector, where artificial intelligence technologies are leveraged to streamline and enhance quality assurance processes. This approach not only automates critical checks but also enables real-time monitoring and predictive analytics, ensuring that vehicles meet stringent safety and performance standards. As the automotive landscape evolves, this concept has become increasingly relevant, aligning with the broader trends of digital transformation and operational efficiency that stakeholders prioritize today.
The integration of AI into quality assurance processes is reshaping the entire Automotive ecosystem, fostering an environment of continuous innovation and heightened competitiveness. Organizations are experiencing enhanced decision-making capabilities and operational efficiencies, as AI tools facilitate faster, more accurate assessments of product quality. However, the journey towards full-scale adoption is not without challenges, including integration complexities and shifting stakeholder expectations. Despite these obstacles, the growth opportunities are significant, driven by the potential for improved quality, reduced costs, and better alignment with customer demands.

Accelerate AI Integration for Autonomous Quality Assurance
Automotive companies should strategically invest in AI technologies and forge partnerships with leading tech firms to enhance Autonomous Quality Assurance capabilities. By implementing these AI-driven solutions, organizations can significantly improve product quality, reduce operational costs, and gain a competitive edge in the market.
How AI is Transforming Quality Assurance in Automotive?
The Disruption Spectrum
Five Domains of AI Disruption in Automotive
Automate Production Flows
Enhance Generative Design
Optimize Simulation Testing
Revolutionize Supply Chains
Drive Sustainability Initiatives

Compliance Case Studies



| Opportunities | Threats |
|---|---|
| Enhance market differentiation through AI-driven quality assurance solutions. | Risk of workforce displacement due to increased automation reliance. |
| Strengthen supply chain resilience with predictive AI quality analytics. | High dependency on technology may lead to operational vulnerabilities. |
| Achieve automation breakthroughs for faster, error-free production processes. | Compliance and regulatory bottlenecks could hinder AI implementation efforts. |
Seize the future of automotive excellence with AI-driven quality assurance. Transform your processes, outperform competitors, and ensure unmatched quality today!
Risk Senarios & Mitigation
Neglecting Compliance Regulations
Legal penalties arise; regularly review compliance guidelines.
Overlooking Data Security Measures
Data breaches occur; enforce robust cybersecurity protocols.
Allowing Algorithmic Bias
Consumer trust erodes; conduct regular bias audits.
Experiencing System Operational Failures
Production halts; establish a failover system plan.
Assess how well your AI initiatives align with your business goals
Glossary
Work with Atomic Loops to architect your AI implementation roadmap — from PoC to enterprise scale.
Contact NowFrequently Asked Questions
- AI For Autonomous Quality Assurance utilizes machine learning to enhance quality control processes.
- It automates inspection tasks, reducing human error and increasing accuracy.
- The technology enables real-time monitoring, leading to faster issue resolution.
- Companies can ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations more effectively.
- Overall, it supports continuous improvement and innovation within the automotive landscape.
- Begin by assessing your current quality assurance processes for improvement opportunities.
- Identify specific use cases where AI can add value and drive efficiency gains.
- Engage cross-functional teams for insights and collaboration on AI projects.
- Pilot small-scale implementations to evaluate effectiveness before broader rollout.
- Develop a roadmap that includes timelines, resources, and integration strategies.
- AI enhances operational efficiency by automating repetitive quality checks and tasks.
- Companies can achieve higher accuracy rates, minimizing defects in production.
- It provides real-time data analytics for informed decision-making and faster responses.
- AI helps in lowering costs associated with manual inspections and rework.
- Overall, it fosters a culture of continuous improvement and innovation.
- Common challenges include resistance to change and lack of skilled personnel.
- Data quality and availability can hinder effective AI implementation.
- Integration with existing systems may present compatibility issues.
- Organizations should prioritize change management strategies to facilitate transition.
- Best practices include starting with pilot projects to demonstrate AI's value.
- Companies should adopt AI when they have established baseline quality processes.
- The readiness of technology infrastructure is critical for successful implementation.
- Timing is ideal when facing increasing pressure for quality and efficiency improvements.
- Identifying specific pain points can accelerate the decision to adopt AI solutions.
- Engaging stakeholders early helps in aligning goals and expectations for adoption.
- Compliance with automotive industry standards is crucial for AI applications.
- Data privacy regulations must be adhered to when using customer data for AI.
- Quality assurance processes should align with governmental and safety regulations.
- Documentation and accountability are essential for AI-driven decision-making.
- Regular audits can help ensure compliance and maintain industry standards.
- Improvements in defect rates can be quantified to demonstrate AI's effectiveness.
- Companies often see reduced inspection times, enhancing overall throughput.
- Customer satisfaction scores may increase due to higher quality products.
- Cost savings from reduced waste and rework can be tracked effectively.
- Data-driven insights can lead to strategic improvements in production processes.

