Advanced AI for Casting and Forging
Advanced AI for Casting and Forging represents a significant leap in the Automotive sector, where artificial intelligence is harnessed to enhance the processes of casting and forging. This innovative approach integrates advanced algorithms and data analytics to optimize production efficiencies, material usage, and operational workflows. As stakeholders increasingly seek to improve quality and reduce costs, the relevance of AI in these processes has become paramount, aligning with the broader trends of digital transformation and operational excellence in the automotive landscape.
The impact of Advanced AI in the Automotive ecosystem is profound, reshaping competitive dynamics and fostering innovation. By adopting AI-driven practices, companies are experiencing enhanced decision-making capabilities and streamlined operations that drive strategic initiatives. However, the journey towards full AI integration is not without hurdles, including challenges related to technology adoption, integration complexity, and evolving stakeholder expectations. Yet, as organizations navigate these challenges, opportunities for growth and enhanced stakeholder value continue to emerge, positioning AI as a cornerstone of future advancements in manufacturing practices.
Elevate Your Automotive Production with Advanced AI Strategies
Automotive leaders should strategically invest in Advanced AI for Casting and Forging, forming partnerships with tech innovators to unlock transformative potential. Implementing AI can drive significant operational efficiencies, enhance product quality, and create a competitive edge in the fast-evolving market landscape.
Transforming Automotive Manufacturing: The Role of Advanced AI in Casting and Forging
Implementation Framework
Conduct a thorough assessment of existing technologies and processes to identify gaps and opportunities for AI integration in casting and forging operations, ensuring alignment with business goals and long-term strategy.
Internal R&D
Identify and select AI technologies that best fit the needs of casting and forging processes, focusing on predictive analytics and machine learning to enhance efficiency and reduce operational costs.
Technology Partners
Initiate pilot projects to apply selected AI technologies in controlled environments, allowing for the assessment of effectiveness, scalability, and integration into existing workflows while gathering valuable insights for full-scale deployment.
Industry Standards
Develop comprehensive training programs to equip employees with the necessary skills and knowledge to effectively leverage AI technologies in their daily operations, fostering a culture of innovation and continuous improvement.
Cloud Platform
Establish ongoing monitoring mechanisms to evaluate the performance of AI systems in casting and forging, allowing for continuous optimization and adaptation to changing market conditions and operational demands.
Industry Standards
Best Practices for Automotive Manufacturers
-
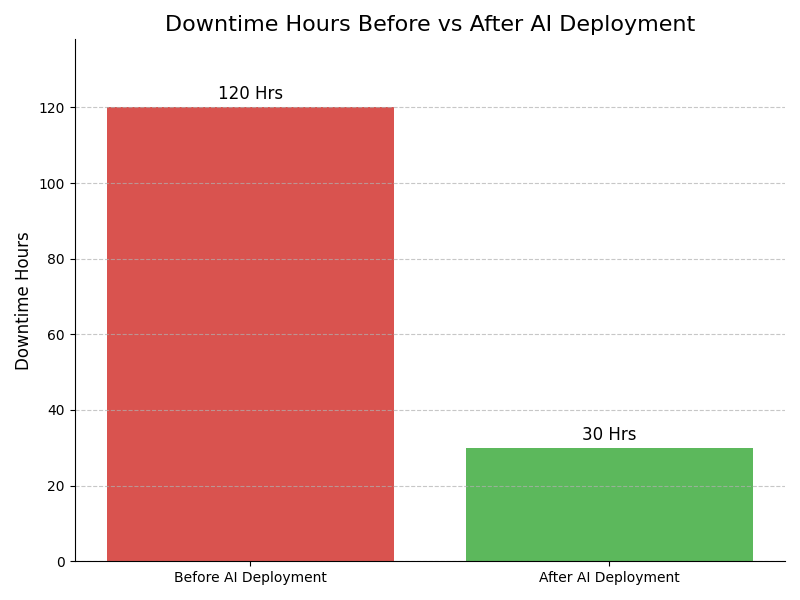
Impact : Reduces unexpected machinery failures
Example : Example: An automotive plant implements AI-driven predictive maintenance, which forecasts machinery failures, reducing unexpected downtime by 30%, leading to a significant cost saving in emergency repairs and lost production time.
-
Impact : Extends equipment lifespan significantly
Example : Example: AI algorithms analyze historical machine data to predict wear and tear, allowing maintenance schedules to be adjusted ahead of time, extending equipment lifespan by an estimated 20%.
-
Impact : Optimizes maintenance scheduling
Example : Example: By using AI for predictive maintenance, a factory optimizes its maintenance scheduling, which decreases unplanned downtime from 15% to 5%, resulting in smoother production flows.
-
Impact : Decreases operational downtime costs
Example : Example: An automotive manufacturer reduces unplanned machine failures by 40% through AI predictive maintenance, translating into significant savings on repair costs and enhanced productivity.
-
Impact : High costs of AI technology deployment
Example : Example: A major automotive manufacturer faces budget overruns during AI deployment due to unexpected costs associated with necessary infrastructure upgrades, delaying ROI on the investment.
-
Impact : Complex integration with legacy systems
Example : Example: A factory struggles to integrate AI solutions with outdated legacy systems, leading to inefficiencies and data silos that hinder effective decision-making.
-
Impact : Data dependency leading to potential failures
Example : Example: A sudden failure in data collection systems causes the AI to provide inaccurate predictions, leading to unplanned downtime and costly production delays.
-
Impact : Resistance from workforce adapting to AI
Example : Example: Workers resist the adoption of AI technologies, fearing job loss, which creates friction and slows down the implementation process, ultimately affecting productivity.
-
Impact : Improves accuracy of data insights
Example : Example: By enhancing data collection processes, an automotive company improves the accuracy of its production data, allowing for more reliable insights that drive operational improvements and product quality.
-
Impact : Facilitates real-time decision-making
Example : Example: Real-time data collection enables an automotive manufacturer to make informed decisions quickly, leading to a 20% increase in production efficiency and responsiveness to market demands.
-
Impact : Supports advanced AI training
Example : Example: Advanced data collection techniques support AI training, which enhances the system's ability to detect defects in casting processes, improving overall product quality and reducing waste.
-
Impact : Enables better quality control
Example : Example: A company implements IoT devices for real-time monitoring, allowing for immediate detection of quality issues, which significantly reduces the number of defective parts reaching customers.
-
Impact : Costly upgrades for data infrastructure
Example : Example: An automotive manufacturer incurs high costs when upgrading its data infrastructure to accommodate new AI systems, straining its budget and delaying project timelines.
-
Impact : Data quality issues affecting AI outcomes
Example : Example: Inconsistent data quality leads to AI misinterpretations, causing increased scrap rates in casting processes and undermining the value of the AI investment.
-
Impact : Security vulnerabilities in data systems
Example : Example: Security vulnerabilities in the newly implemented data systems expose sensitive production data to cyber-attacks, posing significant risks to the company’s reputation and operations.
-
Impact : Potential non-compliance with data regulations
Example : Example: A company faces regulatory scrutiny after failing to comply with data protection regulations during the implementation of its new data collection systems, resulting in hefty fines.
-
Impact : Boosts employee confidence and skill
Example : Example: An automotive manufacturer invests in training programs for its workforce on AI tools, resulting in increased employee confidence and a 25% boost in productivity in production lines.
-
Impact : Enhances collaboration between AI and humans
Example : Example: Training employees on AI tools fosters better collaboration between human operators and AI systems, enhancing overall operational efficiency and reducing errors by 15%.
-
Impact : Improves operational efficiency
Example : Example: By providing comprehensive training, a company facilitates smoother transitions to AI-driven technologies, minimizing disruptions and maintaining production levels during the changeover.
-
Impact : Facilitates smoother technology transitions
Example : Example: Employees become adept at using AI tools, leading to improved operational efficiency and a more innovative workplace culture that embraces continuous improvement.
-
Impact : Training costs may exceed budget
Example : Example: An automotive company underestimates training costs, which exceed the budget as advanced AI tools require specialized knowledge, delaying implementation timelines.
-
Impact : Employee resistance to new technologies
Example : Example: Workforce resistance to adopting new technologies hampers the effectiveness of AI tools, leading to reduced productivity and missed opportunities for operational improvements.
-
Impact : Knowledge gaps in AI application
Example : Example: Some employees lack the necessary knowledge to apply AI tools effectively, resulting in inefficiencies and a failure to realize anticipated benefits from the technology.
-
Impact : Time-consuming training processes
Example : Example: Lengthy training processes create temporary gaps in production capabilities, affecting output and profitability while employees learn to navigate new AI systems.
-
Impact : Enhances operational responsiveness
Example : Example: Real-time monitoring systems in automotive casting processes enable immediate detection of anomalies, allowing teams to respond faster and improve overall operational responsiveness by 30%.
-
Impact : Improves production quality
Example : Example: An automotive plant employs real-time monitoring to track quality metrics, significantly reducing defects and ensuring higher production quality, leading to enhanced customer satisfaction.
-
Impact : Facilitates timely decision-making
Example : Example: By utilizing real-time data, decision-makers can promptly address issues in production lines, reducing delays and enhancing productivity, which ultimately boosts overall profitability.
-
Impact : Reduces waste in manufacturing
Example : Example: Implementing real-time monitoring reduces waste significantly, as the system identifies inefficiencies in the manufacturing process that can be corrected immediately, saving costs.
-
Impact : High costs for monitoring technology
Example : Example: An automotive manufacturer finds that installing real-time monitoring technology incurs high costs, straining its budget and delaying other critical upgrades needed in the facility.
-
Impact : Integration issues with existing systems
Example : Example: Integration issues arise when real-time monitoring systems fail to communicate with existing machinery, causing delays in data flow and impacting overall productivity.
-
Impact : Dependence on consistent data streams
Example : Example: The production team experiences data overload from real-time monitoring systems, leading to confusion and difficulty in prioritizing critical issues, ultimately hindering operations.
-
Impact : Potential for information overload
Example : Example: A factory's reliance on consistent data streams for real-time monitoring exposes it to risks when data interruptions occur, leading to potential operational failures and quality issues.
-
Impact : Improves accuracy of predictions
Example : Example: Regular optimization of AI algorithms in a casting facility leads to improved accuracy of defect predictions, decreasing scrap rates by 25% and enhancing overall production quality.
-
Impact : Increases adaptability to new challenges
Example : Example: By updating AI algorithms, an automotive company increases its adaptability to new production challenges, allowing for seamless adjustments in workflows and maintaining efficiency.
-
Impact : Enhances efficiency of production processes
Example : Example: Efficient AI algorithms streamline production processes, resulting in a 15% reduction in cycle times and significantly enhancing throughput in high-demand periods.
-
Impact : Boosts return on investment in AI
Example : Example: Regular algorithm optimizations lead to better investment returns, as improved performance directly correlates with reduced operational costs and increased output levels.
-
Impact : Continuous monitoring required for algorithms
Example : Example: An automotive manufacturer realizes that continuous monitoring of AI algorithms incurs ongoing costs, straining resources and complicating budget management over time.
-
Impact : High costs for algorithm updates
Example : Example: High costs associated with regular algorithm updates lead to delays in improvements, as financial constraints limit the company’s ability to maintain cutting-edge AI performance.
-
Impact : Potential for algorithmic bias
Example : Example: A company faces challenges when unintended algorithmic biases emerge, leading to product quality issues and potential reputational damage in the market.
-
Impact : Need for specialized talent for optimization
Example : Example: The need for specialized talent to optimize AI algorithms creates hiring challenges, as the automotive industry competes with tech firms for skilled professionals, delaying improvements.
AI is fundamentally transforming the automotive industry, enhancing efficiency and precision in casting and forging processes.
– Randy BeanCompliance Case Studies



Embrace the future of automotive manufacturing with Advanced AI solutions. Secure your competitive edge and transform your operations for unparalleled efficiency and quality.

Leadership Challenges & Opportunities
Data Quality Issues
Utilize Advanced AI for Casting and Forging to enhance data collection and validation processes. Implement machine learning algorithms that automatically cleanse and enrich data, ensuring high-quality inputs for production. This leads to improved decision-making and optimized manufacturing outcomes in the Automotive sector.
Change Resistance in Teams
Foster an innovation-driven culture by integrating Advanced AI for Casting and Forging through collaborative workshops and pilot projects. Engage teams in the AI implementation process to demonstrate value. By showcasing tangible results, you can build trust and enthusiasm for new technologies within the organization.
Talent Acquisition Challenges
Address talent shortages by partnering with educational institutions to create specialized training programs focused on Advanced AI for Casting and Forging. Promote internships and co-op opportunities to attract skilled candidates. This proactive approach ensures a pipeline of talent ready to navigate the complexities of modern automotive manufacturing.
High Implementation Costs
Adopt a phased implementation of Advanced AI for Casting and Forging to distribute costs over time. Start with small-scale projects that deliver measurable ROI, allowing organizations to reinvest savings into broader AI initiatives. This strategic approach mitigates financial risks while demonstrating the technology's value.
Assess how well your AI initiatives align with your business goals
AI Use Case vs ROI Timeline
| AI Use Case | Description | Typical ROI Timeline | Expected ROI Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Predictive Maintenance for Equipment | AI can predict equipment failures in casting and forging processes by analyzing historical data and sensor information. For example, implementing AI algorithms at a forging plant reduced downtime by predicting machine failures before they occurred. | 6-12 months | High |
| Quality Control Automation | Utilizing AI in quality control can enhance defect detection during casting and forging. For example, an automotive manufacturer used AI vision systems to inspect parts, resulting in a 30% reduction in defective products. | 12-18 months | Medium-High |
| Supply Chain Optimization | AI algorithms can optimize raw material supply and inventory levels in casting and forging industries. For example, an AI-driven system helped an automotive supplier reduce excess inventory by 20%, enhancing cash flow and efficiency. | 6-12 months | Medium |
| Process Parameter Optimization | AI can optimize parameters in casting and forging processes to improve yield and reduce waste. For example, a forging company used AI to adjust parameters dynamically, leading to a 15% increase in material yield. | 12-18 months | High |
Glossary
Work with Atomic Loops to architect your AI implementation roadmap — from PoC to enterprise scale.
Contact NowFrequently Asked Questions
- Advanced AI for Casting and Forging enhances manufacturing processes through intelligent automation.
- It utilizes machine learning to optimize material usage and reduce waste effectively.
- The technology provides real-time data analysis for improved decision-making and efficiency.
- AI-driven simulations improve design accuracy and product quality in manufacturing.
- Companies can achieve faster production times and better resource management overall.
- Integration involves assessing current systems for compatibility with AI technologies.
- Collaboration with AI vendors ensures tailored solutions for specific manufacturing needs.
- Data from legacy systems must be migrated to train AI models effectively.
- Phased implementation allows gradual adaptation without disrupting ongoing operations.
- Training staff on new technologies is crucial for successful integration and adoption.
- AI improves product quality by minimizing defects through predictive analytics.
- Operational efficiency increases, leading to reduced production costs and cycle times.
- Companies can achieve higher throughput rates with optimized manufacturing processes.
- AI enables enhanced data analytics for better forecasting and inventory management.
- Overall, businesses gain a competitive edge in a rapidly evolving market landscape.
- Common challenges include resistance to change from employees and management.
- Data quality and availability can hinder effective AI model training and deployment.
- Integration complexities with legacy systems may require significant resources.
- Establishing clear objectives and KPIs is essential for measuring success.
- Ongoing support and training are vital to overcome obstacles and ensure longevity.
- Organizations should assess their digital maturity before considering AI adoption.
- Identifying specific pain points can highlight the urgency for AI solutions.
- Market competition can dictate the need for faster, more efficient processes.
- Pilot projects can help gauge readiness before a full-scale rollout.
- Regular reviews of technological advancements indicate optimal timing for investment.
- Compliance with industry standards is crucial for technology deployment in manufacturing.
- Data privacy regulations must be adhered to when handling sensitive information.
- Organizations should ensure AI algorithms are transparent and explainable.
- Regular audits can help maintain compliance with evolving regulations.
- Staying informed about legal frameworks will mitigate potential risks and liabilities.
- AI can optimize mold design processes, enhancing product quality and efficiency.
- Predictive maintenance helps reduce downtime by forecasting equipment failures.
- Quality control processes benefit from AI through real-time defect detection.
- Supply chain optimization ensures timely delivery of materials and components.
- AI-driven simulations enable faster prototyping and testing of new designs.
- Investing in AI leads to significant cost savings through improved efficiency.
- It fosters innovation, enabling companies to stay competitive in the market.
- AI enhances product quality, leading to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Long-term investments in AI provide measurable ROI through data-driven insights.
- Embracing AI prepares organizations for future challenges and technological advancements.