AI for Electrification Component Manufacturing
AI for Electrification Component Manufacturing represents a transformative approach within the Automotive sector, where artificial intelligence is leveraged to enhance the production and efficiency of electrification components. This concept encompasses a range of applications, from optimizing supply chains to improving quality control in manufacturing processes. As stakeholders navigate the shift towards electrification, the integration of AI becomes essential for addressing new operational challenges and aligning with strategic goals centered around sustainability and innovation.
The significance of this sector lies in its dynamic interplay with technological advancements, shaping competitive landscapes and fostering innovation. AI-driven practices are redefining traditional workflows, enhancing decision-making processes, and cultivating closer interactions among stakeholders. While the potential for increased efficiency and strategic agility is promising, organizations must also contend with challenges such as adoption barriers and integration complexities. Balancing these opportunities with the realities of a rapidly evolving environment will be crucial for sustained growth in this transformative landscape.
Accelerate AI Adoption for Electrification in Automotive Manufacturing
Automotive companies should strategically invest in partnerships focused on AI innovations for Electrification Component Manufacturing, enhancing their production capabilities. Implementing these AI strategies is expected to drive operational efficiencies, reduce costs, and create a competitive edge in the rapidly evolving automotive landscape.
How AI is Revolutionizing Electrification in Automotive Manufacturing
Implementation Framework
Conduct a comprehensive analysis of current manufacturing processes to identify areas for AI integration, focusing on efficiency and productivity improvements to enhance competitiveness in electrification components.
Industry Standards
Develop a scalable data infrastructure that supports the collection, storage, and analysis of manufacturing data, enabling effective AI model training and insights that drive decision-making and operational improvements.
Cloud Platform
Integrate advanced AI tools into manufacturing workflows, focusing on automation and predictive analytics to optimize production schedules and reduce downtime, thereby improving overall operational efficiency and responsiveness.
Technology Partners
Continuously monitor key performance indicators to evaluate the effectiveness of AI implementations, ensuring alignment with operational goals and allowing for adjustments that enhance productivity and quality in component manufacturing.
Internal R&D
Identify and scale successful AI initiatives throughout manufacturing processes, fostering a culture of innovation and continuous improvement that strengthens competitiveness and operational resilience in the automotive electrification sector.
Industry Standards
Best Practices for Automotive Manufacturers
-
Impact : Enhances defect detection accuracy significantly
Example : Example: In an automotive assembly line, a vision-based AI system flags microscopic paint defects in real time as car bodies pass under cameras, catching flaws human inspectors previously missed during night shifts.
-
Impact : Reduces production downtime and costs
Example : Example: A semiconductor factory uses AI to detect early soldering anomalies. The system stops the line immediately, preventing a full batch failure that would have caused hours of rework and shutdown.
-
Impact : Improves quality control standards
Example : Example: A food packaging plant uses AI image recognition to verify seal integrity on every packet, ensuring non-compliant packages are rejected instantly before shipping.
-
Impact : Boosts overall operational efficiency
Example : Example: AI dynamically adjusts inspection thresholds based on production speed, allowing the factory to increase output during peak demand without sacrificing quality.
-
Impact : High initial investment for implementation
Example : Example: A mid-sized electronics manufacturer delays AI rollout after realizing camera hardware, GPUs, and system integration push upfront costs beyond budget approvals.
-
Impact : Potential data privacy concerns
Example : Example: AI quality systems capturing worker activity unintentionally store employee facial data, triggering compliance issues with internal privacy policies.
-
Impact : Integration challenges with existing systems
Example : Example: AI software cannot communicate with a 15-year-old PLC controller, forcing engineers to manually export data and slowing decision-making.
-
Impact : Dependence on continuous data quality
Example : Example: Dust accumulation on camera lenses causes the AI to misclassify normal products as defective, leading to unnecessary scrap until recalibration.
-
Impact : Increases predictive maintenance capabilities
Example : Example: A major automotive plant implements real-time sensor data to predict machine failures, allowing for scheduled maintenance that reduces unplanned downtimes by 30% over six months.
-
Impact : Enhances supply chain responsiveness
Example : Example: An electric vehicle manufacturer enhances supply chain visibility through real-time tracking, allowing proactive adjustments to orders, which reduced lead times by 20% and improved production flow.
-
Impact : Improves resource allocation efficiency
Example : Example: Using AI-driven analytics, a parts manufacturer optimizes workforce allocation based on real-time demand, increasing efficiency by reallocating resources to high-need areas immediately.
-
Impact : Minimizes operational bottlenecks
Example : Example: Real-time AI dashboards monitor workflow, identifying bottlenecks instantly and enabling quick adjustments, resulting in a 15% boost in overall productivity within a quarter.
-
Impact : Requires reliable data connectivity
Example : Example: A vehicle assembly plant experiences connectivity issues on the production floor, causing real-time monitoring systems to fail, leading to delays and miscommunication among teams.
-
Impact : Potential for over-reliance on technology
Example : Example: A manufacturer becomes overly reliant on AI predictions, neglecting human oversight, which results in critical errors when the AI misjudges a production requirement.
-
Impact : Challenges in staff training and adaptation
Example : Example: Employees struggle to adapt to an AI-driven monitoring system, resulting in inefficiencies and increased error rates until adequate training programs are implemented.
-
Impact : Risk of system overload during peak periods
Example : Example: During peak production times, the influx of real-time data overwhelms the system, causing slowdowns and inaccurate reporting, ultimately affecting delivery schedules.
-
Impact : Boosts AI adoption and efficacy
Example : Example: An automotive manufacturing firm implements a monthly AI training workshop, resulting in a 40% increase in employee engagement with new technologies and improved productivity metrics.
-
Impact : Fosters a culture of innovation
Example : Example: A company encourages innovation by regularly training employees on AI tools, leading to multiple new process improvements and a 25% increase in operational efficiency over the year.
-
Impact : Reduces resistance to change
Example : Example: By offering ongoing training sessions, a manufacturer successfully reduces employee resistance to AI implementations, achieving smoother transitions in processes and an increase in collaboration.
-
Impact : Enhances employee skill sets
Example : Example: Regular skill enhancement programs on AI technologies enable employees to become proficient, resulting in a 30% reduction in error rates during production.
-
Impact : Training may incur significant costs
Example : Example: A large automotive manufacturer faces budget overruns as the costs for extensive AI training programs exceed initial estimates, causing financial strain on other departments.
-
Impact : Varied employee learning curves
Example : Example: Employees show differing levels of aptitude in AI training programs, leading to uneven skill development and potential knowledge gaps in crucial areas of the production process.
-
Impact : Potential knowledge gaps in teams
Example : Example: A company neglects to update its AI training materials, resulting in employees using outdated practices that hinder productivity and efficiency in the long term.
-
Impact : Risk of outdated training materials
Example : Example: When training is inconsistent, teams miss critical updates on AI applications, leading to operational inefficiencies and increased errors on the production line.
-
Impact : Informs strategic decision-making
Example : Example: An electric vehicle manufacturer uses data analytics to assess consumer trends, leading to the launch of a new model that captures a 15% market share within the first year.
-
Impact : Identifies new market opportunities
Example : Example: By analyzing production data, a manufacturer identifies inefficiencies in their component supply chain, resulting in a 20% reduction in costs and improved delivery times.
-
Impact : Enhances product development processes
Example : Example: Data analytics helps an automotive company refine its product development timeline, shortening it by three months through better resource management and planning.
-
Impact : Optimizes supply chain logistics
Example : Example: A parts supplier utilizes analytics to optimize logistics routes, decreasing transportation costs by 12% while maintaining delivery schedules.
-
Impact : Data interpretation may lead to errors
Example : Example: An automotive company misinterprets analytics insights, leading to poor production decisions that result in increased costs and delayed timelines.
-
Impact : Overwhelming amounts of data
Example : Example: A manufacturer struggles to manage vast amounts of data generated, making it difficult for teams to identify actionable insights, causing missed opportunities for improvement.
-
Impact : Requires skilled data analysts
Example : Example: The company faces challenges in hiring skilled data analysts, leading to gaps in data-driven decision-making and suboptimal production outcomes.
-
Impact : Potential biases in data sets
Example : Example: Bias in historical data leads to skewed analytics results, causing a manufacturer to overlook emerging market trends that could have driven innovation.
-
Impact : Cultivates a proactive innovation culture
Example : Example: A major automotive manufacturer adopts a continuous improvement framework, resulting in a 50% reduction in production errors and fostering a culture of innovation among staff.
-
Impact : Encourages feedback-driven enhancements
Example : Example: By encouraging feedback loops, a company identifies and resolves equipment issues faster, leading to a 30% decrease in downtime across its production lines.
-
Impact : Facilitates rapid problem resolution
Example : Example: Regular team meetings focused on continuous improvement enable rapid problem resolution, ensuring that production targets are consistently met or exceeded.
-
Impact : Aligns teams toward common goals
Example : Example: Aligning teams around shared improvement goals enhances collaboration, resulting in a 25% increase in project completion rates across departments.
-
Impact : Resistance to change from employees
Example : Example: Employees resist adopting continuous improvement practices, leading to stalled initiatives and a decline in productivity during the transition period.
-
Impact : Requires ongoing commitment and resources
Example : Example: A manufacturer finds that continuous improvement efforts require significant ongoing resources, straining budgets and diverting attention from other crucial operations.
-
Impact : May lead to temporary performance dips
Example : Example: During initial implementation phases, a company experiences performance dips as teams adjust to new practices, affecting overall production targets temporarily.
-
Impact : Challenges in measuring improvement effectiveness
Example : Example: Measuring the effectiveness of continuous improvement initiatives proves challenging, complicating efforts to demonstrate value and secure future investment.
-
Impact : Increases production speed and efficiency
Example : Example: An automotive parts manufacturer integrates AI-driven automation on the assembly line, achieving a 40% increase in production speed while maintaining quality standards.
-
Impact : Reduces labor costs significantly
Example : Example: AI automation in a factory setting reduces labor costs by 30% as routine tasks are delegated to robots, allowing human workers to focus on complex tasks.
-
Impact : Enhances safety in manufacturing processes
Example : Example: Implementing AI-driven robotics enhances safety on the production floor, reducing accidents by 50% and creating a safer work environment for all employees.
-
Impact : Improves precision in component assembly
Example : Example: Automation technology improves the precision of component assembly, reducing error rates by 25% and increasing customer satisfaction with product quality.
-
Impact : High upfront costs for automation technologies
Example : Example: A manufacturer faces high upfront costs when installing AI-driven automation systems, leading to budget reallocations and financial strain in other project areas.
-
Impact : Job displacement concerns among workers
Example : Example: Concerns about job displacement arise among workers in an automotive assembly plant, creating tension and resistance against the adoption of AI technologies.
-
Impact : Integration complexities with existing systems
Example : Example: Integration issues with legacy systems delay the implementation of new automation technologies, causing frustration and missed deadlines for production goals.
-
Impact : Maintenance challenges for automated systems
Example : Example: Automated systems require specialized maintenance, and a lack of skilled technicians leads to increased downtime and production disruptions when issues arise.
AI is the catalyst for a new era in automotive electrification, driving efficiency and innovation in component manufacturing.
– Internal R&DCompliance Case Studies



Embrace AI-driven solutions to optimize your manufacturing processes, boost efficiency, and stay ahead in the competitive automotive landscape. Transform today for a brighter future.
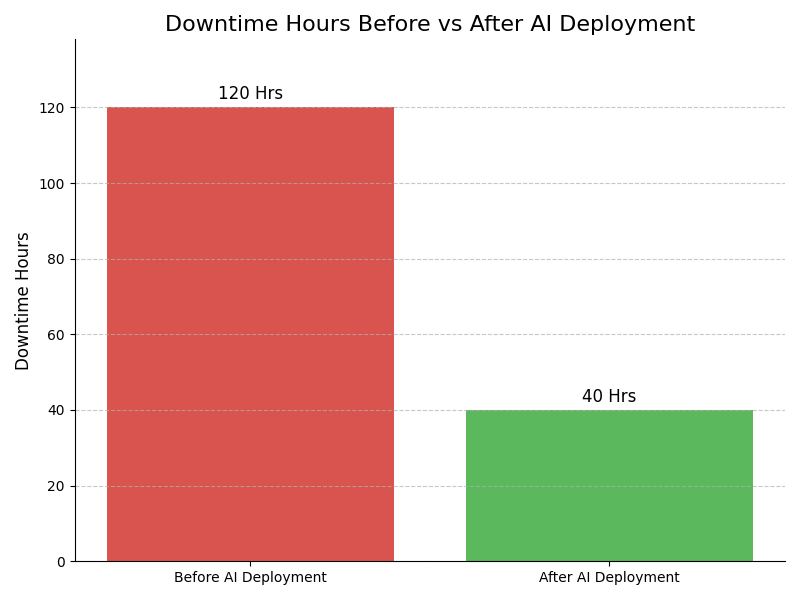

Leadership Challenges & Opportunities
Data Integration Challenges
Utilize AI for Electrification Component Manufacturing to enhance data integration across diverse Automotive systems. Implement machine learning algorithms that automate data cleansing and consolidation, ensuring accurate insights. This approach enables real-time analytics, optimizing production processes and decision-making efficiency.
Supply Chain Disruptions
Leverage AI for Electrification Component Manufacturing to predict and mitigate supply chain disruptions through advanced analytics. Implement predictive modeling to assess risks and optimize inventory management. This proactive strategy enhances resilience, ensuring timely availability of critical components in the Automotive sector.
Talent Acquisition Issues
Address talent acquisition challenges by employing AI for Electrification Component Manufacturing to streamline recruitment processes. Utilize AI-driven platforms for candidate screening and skill assessment, ensuring a better match for roles. This approach accelerates hiring and enhances workforce quality in the competitive Automotive landscape.
Regulatory Compliance Complexity
Implement AI for Electrification Component Manufacturing solutions with integrated compliance frameworks to navigate complex Automotive regulations. Use AI-driven monitoring tools that automatically update compliance status and generate reports. This proactive approach reduces legal risks and ensures adherence to evolving industry standards.
Assess how well your AI initiatives align with your business goals
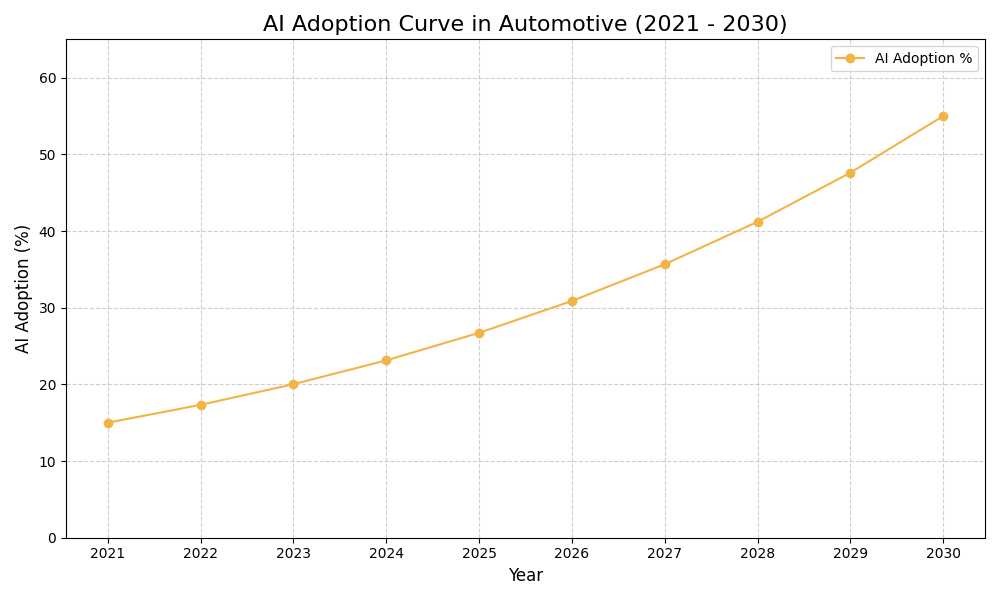
AI Use Case vs ROI Timeline
| AI Use Case | Description | Typical ROI Timeline | Expected ROI Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Predictive Maintenance Using AI | AI algorithms analyze equipment health data to predict failures before they occur. For example, sensors on manufacturing lines can trigger maintenance alerts, reducing downtime. This proactive approach enhances productivity in electric component production. | 6-12 months | High |
| Quality Control Automation | AI-driven visual inspection systems identify defects in components during production. For example, cameras equipped with AI can detect inconsistencies in battery cells, ensuring high-quality standards and reducing waste. | 12-18 months | Medium-High |
| Supply Chain Optimization | AI tools analyze supply chain data to optimize inventory levels and reduce costs. For example, predictive analytics can forecast demand for electric vehicle parts, enabling better stock management and minimizing excess inventory. | 6-12 months | Medium-High |
| Energy Consumption Forecasting | AI models predict energy usage patterns in manufacturing processes, allowing for better energy management. For example, adjusting machine operations based on predicted peaks can lower energy costs significantly. | 12-18 months | Medium-High |
Glossary
Work with Atomic Loops to architect your AI implementation roadmap — from PoC to enterprise scale.
Contact NowFrequently Asked Questions
- AI enhances electrification component manufacturing by optimizing design and production processes.
- It improves accuracy in quality control through real-time monitoring and data analysis.
- This technology reduces lead times by automating repetitive tasks and workflows.
- AI-driven insights enable better decision-making in resource allocation and production scheduling.
- Ultimately, it fosters innovation and competitiveness in the rapidly evolving automotive market.
- Begin with a comprehensive assessment of your current manufacturing processes and needs.
- Identify specific areas where AI can optimize efficiency and reduce costs effectively.
- Engage stakeholders to secure buy-in and establish a clear implementation roadmap.
- Consider pilot projects to test AI solutions before full-scale integration.
- Utilize partnerships with AI experts to navigate technology selection and integration.
- AI significantly enhances operational efficiency, leading to reduced production costs over time.
- It provides actionable insights that improve product quality and customer satisfaction metrics.
- Companies can achieve faster time-to-market for new electrification solutions and products.
- AI fosters data-driven decision-making, optimizing supply chain and inventory management.
- Organizations gain a competitive edge by leveraging advanced technologies to innovate rapidly.
- Data quality and availability can hinder effective AI implementation and outcomes.
- Resistance from employees can slow down the adoption of AI technologies and processes.
- Integration with legacy systems often presents technical challenges that need addressing.
- Ensuring compliance with industry regulations is critical to successful AI deployment.
- Organizations should anticipate ongoing training needs to maximize AI utilization and benefits.
- Timing should align with organizational readiness for digital transformation initiatives.
- It’s best to implement AI during product development cycles for maximum impact.
- Assess market trends and competitive pressures to identify urgency in adoption.
- Organizations should be prepared to invest in infrastructure ahead of implementation.
- Continuous evaluation of technological advancements can guide optimal timing for AI integration.
- AI can optimize battery management systems, enhancing performance and lifespan.
- Predictive maintenance enables timely interventions, reducing downtime and costs.
- Quality assurance processes benefit from AI through automated defect detection.
- Supply chain optimization is improved with AI for demand forecasting and logistics.
- AI supports regulatory compliance by ensuring adherence to safety and environmental standards.
- Establish clear KPIs before implementation to measure success against predefined goals.
- Monitor cost reductions in production and operational efficiencies over time.
- Evaluate improvements in product quality and customer satisfaction metrics regularly.
- Assess time-to-market reductions for new electrification components as a critical metric.
- Conduct regular audits to analyze performance against initial ROI projections and expectations.
- Start with pilot projects to validate AI solutions before large-scale deployment.
- Engage cross-functional teams to foster collaboration and knowledge sharing throughout implementation.
- Invest in comprehensive training programs to equip employees with necessary AI skills.
- Continuously monitor and adjust AI models to ensure optimal performance and adaptability.
- Maintain a focus on data integrity and governance to support effective AI outcomes.

