AI for Lean Manufacturing Automation
AI for Lean Manufacturing Automation represents a transformative approach within the Automotive sector, where artificial intelligence enhances operational efficiency and streamlines production processes. By integrating AI technologies, manufacturers can minimize waste, optimize resource allocation, and improve product quality. This concept is increasingly relevant as automotive stakeholders seek innovative solutions to meet evolving consumer demands and adapt to competitive pressures. As the industry embraces digital transformation, AI implementation is becoming a cornerstone of strategic initiatives aimed at driving operational excellence.
The Automotive ecosystem is significantly influenced by AI for Lean Manufacturing Automation, reshaping how companies interact with stakeholders and innovate. AI-driven practices are not only enhancing efficiency but also revolutionizing decision-making processes, thereby redefining competitive dynamics. As organizations adopt AI, they encounter opportunities for growth and improved stakeholder value, yet they must also navigate challenges such as integration complexities and shifting expectations. Balancing the benefits of AI adoption with these hurdles will be crucial for long-term success in this rapidly evolving landscape.
Transform Your Automotive Manufacturing with AI Now
Automotive companies should strategically invest in AI partnerships focused on Lean Manufacturing Automation to enhance efficiency and productivity. By implementing these AI-driven solutions, businesses can expect significant cost savings, improved quality control, and a strong competitive edge in the market.
How AI is Transforming Lean Manufacturing in Automotive?
Implementation Framework
Begin by assessing current manufacturing processes to identify inefficiencies. This evaluation utilizes AI analytics to pinpoint waste, enabling targeted improvements that enhance productivity and reduce operational costs in automotive production.
Industry Standards
Integrate AI systems into manufacturing workflows to automate repetitive tasks and optimize processes. Utilizing machine learning algorithms enhances decision-making speed, streamlining operations and boosting overall efficiency in automotive manufacturing environments.
Technology Partners
Provide comprehensive training to the workforce on AI tools and technologies. This investment in human capital ensures employees effectively utilize new systems, fostering adaptability and resilience in manufacturing processes within the automotive industry.
Internal R&D
Continuously monitor performance metrics post-AI integration to assess improvements and identify areas for further enhancement. Utilizing data analytics ensures sustained operational excellence and supports ongoing lean initiatives in automotive production environments.
Cloud Platform
Leverage AI insights to optimize supply chain operations, improving forecasting accuracy and inventory management. This strategic enhancement contributes to resilience and adaptability, crucial for automotive manufacturers facing market fluctuations and demand variability.
Industry Standards
Best Practices for Automotive Manufacturers
-
Impact : Enhances real-time decision-making capabilities
Example : Example: An automotive manufacturer integrates AI with its ERP system, enabling real-time adjustments to production schedules, which results in a 20% increase in on-time delivery rates.
-
Impact : Improves production scheduling accuracy
Example : Example: By implementing AI in its supply chain management, a car manufacturer achieves a 30% reduction in lead times, allowing for quicker adaptation to changing market demands.
-
Impact : Reduces manual errors in processes
Example : Example: A large automotive plant uses AI to automate inventory tracking, minimizing human errors and achieving a 25% decrease in stock discrepancies over six months.
-
Impact : Increases responsiveness to market changes
Example : Example: Implementing AI for predictive maintenance allows a manufacturer to respond to machinery issues proactively, reducing downtime by 15% during peak production times.
-
Impact : Requires comprehensive employee training programs
Example : Example: A leading automotive company invests in AI training for its workforce but faces challenges as many employees struggle to adapt, delaying the implementation timeline significantly.
-
Impact : Risk of technology obsolescence
Example : Example: After launching an AI-driven production line, a manufacturer realizes that the technology becomes outdated within two years, necessitating additional unplanned investments.
-
Impact : Integration complexity with legacy systems
Example : Example: Integrating AI with outdated machinery proves cumbersome, causing unexpected downtimes and requiring additional resources to bridge gaps between old and new systems.
-
Impact : Potential for over-reliance on automation
Example : Example: An automotive assembly line becomes overly reliant on AI-driven processes, resulting in production halts when the system encounters unexpected errors, highlighting the need for human oversight.
-
Impact : Forecasts maintenance needs accurately
Example : Example: Using AI predictive analytics, a car manufacturer identifies potential equipment failures before they occur, leading to a 40% reduction in unexpected breakdowns and maintenance costs.
-
Impact : Optimizes resource allocation effectively
Example : Example: An automotive plant employs predictive analytics to forecast labor needs, resulting in a 20% decrease in overtime hours and improved worker satisfaction.
-
Impact : Minimizes production disruptions
Example : Example: A leading automotive firm implements AI to predict supply chain disruptions, allowing for timely adjustments and a 15% reduction in production delays.
-
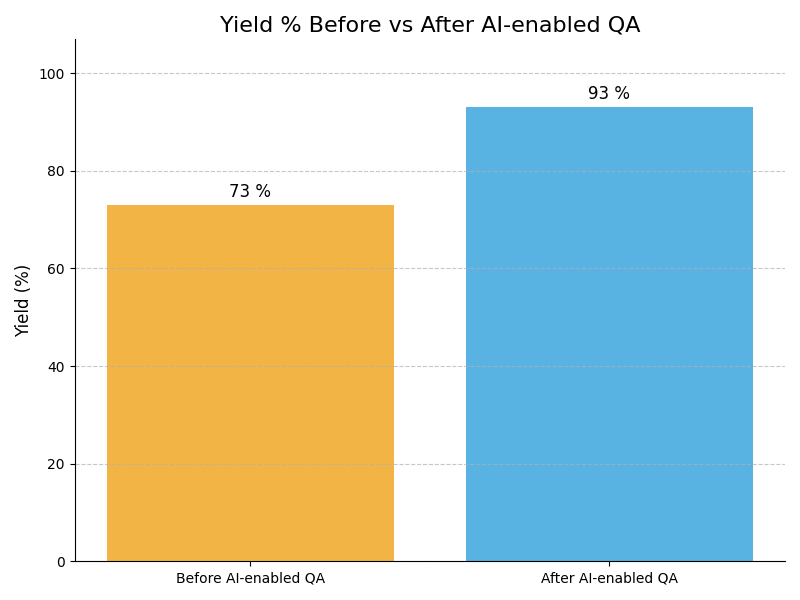
Impact : Enhances quality assurance processes
Example : Example: AI-driven quality assurance systems predict defects in the assembly process, improving overall product quality by 30% by catching issues early.
-
Impact : Dependence on historical data accuracy
Example : Example: A tire manufacturer relies on historical data for its AI models, but inaccuracies in past records lead to faulty predictions, causing a major production setback.
-
Impact : Potential for inaccurate forecasting
Example : Example: An automotive company faces production issues when its AI system miscalculates demand forecasts, resulting in overproduction and excess inventory costs.
-
Impact : Challenge of data integration
Example : Example: Integrating data from multiple sources proves challenging, as discrepancies in formats lead to delays in AI system effectiveness and decision-making.
-
Impact : Need for ongoing algorithm adjustments
Example : Example: An AI system requires frequent recalibrations as production processes evolve, illustrating the need for continuous monitoring and adjustments to maintain accuracy.
-
Impact : Enhances operational transparency
Example : Example: A major automotive manufacturer installs AI-driven real-time monitoring systems across its assembly line, achieving a 25% increase in operational visibility and quicker issue resolution.
-
Impact : Facilitates immediate corrective actions
Example : Example: By leveraging real-time data analytics, a plant can immediately identify quality issues, leading to a 50% reduction in defective units during peak production.
-
Impact : Improves employee accountability
Example : Example: Real-time monitoring increases employee accountability by providing instant feedback on performance metrics, resulting in a 15% boost in productivity across shifts.
-
Impact : Boosts overall equipment effectiveness
Example : Example: An automotive facility utilizes AI to track equipment performance, enhancing overall equipment effectiveness by 20% and minimizing downtime.
-
Impact : High costs of system upgrades
Example : Example: A large automotive company faces significant costs upgrading its monitoring systems, delaying the implementation of AI technologies for several quarters due to budget constraints.
-
Impact : Infrastructure requirements may be substantial
Example : Example: Installing new AI sensors requires extensive infrastructure changes, leading to production halts and increased project timelines for an automotive plant.
-
Impact : Potential data overload from sensors
Example : Example: The influx of data from real-time sensors overwhelms the existing analytics systems, causing delays in actionable insights and frustrating management.
-
Impact : Integration issues with existing software
Example : Example: Integration of AI monitoring systems with legacy software results in data inconsistencies, necessitating additional work to align systems before effective use.
-
Impact : Enhances supplier collaboration
Example : Example: An automotive company utilizes AI to improve communication with its suppliers, leading to a 30% reduction in lead times and enhanced collaboration on new models.
-
Impact : Reduces logistics costs significantly
Example : Example: By optimizing logistics routes using AI, a manufacturer cuts transportation costs by 25%, significantly impacting overall operational efficiency.
-
Impact : Improves inventory turnover rates
Example : Example: AI-driven inventory management allows a leading automotive firm to achieve a 40% increase in inventory turnover, reducing holding costs significantly.
-
Impact : Increases visibility across the supply chain
Example : Example: Implementing AI tools gives visibility into the supply chain, allowing for better demand forecasting and a 20% reduction in stockouts in automotive parts.
-
Impact : Potential supply chain disruptions
Example : Example: A global automotive manufacturer experiences supply chain disruptions when a key AI system fails, demonstrating the risks of over-reliance on technology without contingency planning.
-
Impact : Over-dependence on AI algorithms
Example : Example: An automotive firm becomes too dependent on AI for sourcing decisions, leading to missed opportunities when human insights could have provided better context.
-
Impact : Risk of data silos
Example : Example: Data silos develop when different departments use separate AI systems, resulting in inefficiencies and lack of communication among supply chain teams.
-
Impact : Vulnerability to cyber threats
Example : Example: Cyber threats targeting AI systems expose critical supply chain data, prompting a major automotive company to rethink its cybersecurity measures and protocols.
-
Impact : Builds a culture of innovation
Example : Example: A leading automotive company invests in AI training programs for its workforce, resulting in a culture of innovation and a 20% increase in employee engagement scores.
-
Impact : Improves job satisfaction levels
Example : Example: After comprehensive AI training, employees express higher job satisfaction, leading to a 15% decrease in turnover rates within the automotive manufacturing sector.
-
Impact : Enhances skill sets for future needs
Example : Example: An automotive plant enhances its workforce's skills through regular training, preparing them for future technology integration and increasing productivity by 25%.
-
Impact : Increases productivity among teams
Example : Example: Providing ongoing AI education enables teams to leverage new technologies effectively, resulting in a 30% improvement in overall production efficiency.
-
Impact : Requires significant investment in training
Example : Example: An automotive company struggles to justify the costs of extensive training programs, causing delays in AI integration and limiting workforce readiness for new technologies.
-
Impact : Resistance to change among employees
Example : Example: Employees resist adopting new AI tools due to fears of job displacement, hindering the integration process and leading to friction within teams in an automotive plant.
-
Impact : Time-consuming to implement effectively
Example : Example: A rushed implementation of AI training results in incomplete understanding among employees, leading to ongoing skill gaps and inefficiencies in the manufacturing process.
-
Impact : Potential skill gaps remain unresolved
Example : Example: After training, some employees still struggle with AI applications, revealing persistent skill gaps that require additional resources to address within the automotive sector.
-
Impact : Uncovers hidden operational inefficiencies
Example : Example: A prominent automotive manufacturer uses data analytics to identify bottlenecks in production, leading to an overall 15% increase in operational efficiency after adjustments.
-
Impact : Improves customer satisfaction metrics
Example : Example: By analyzing customer feedback data, an automotive company enhances its product offerings, resulting in a 20% improvement in customer satisfaction ratings.
-
Impact : Enables data-driven decision-making
Example : Example: Leveraging data analytics empowers management to make informed decisions, achieving a 30% reduction in operational costs through targeted interventions.
-
Impact : Fosters a proactive management approach
Example : Example: An automotive assembly line adopts a proactive management approach using data insights, resulting in a 25% decrease in rework and scrap rates, boosting profitability.
-
Impact : Requires robust data governance frameworks
Example : Example: A car manufacturer faces challenges in implementing data governance, leading to inconsistencies in analytics outputs and delayed decision-making processes.
-
Impact : Data privacy regulations can complicate use
Example : Example: Compliance with data privacy regulations complicates the use of customer data, causing delays in a manufacturer’s efforts to personalize offerings based on insights.
-
Impact : Need for continuous data quality assurance
Example : Example: An automotive plant discovers data quality issues after analytics implementation, highlighting the need for ongoing assurance processes to maintain accuracy and reliability.
-
Impact : Risk of inadequate data interpretation
Example : Example: Inadequate interpretation of data analytics leads to misguided strategic decisions, causing an automotive manufacturer to invest in ineffective process improvements.
Automakers and suppliers have a unique opportunity to move ahead by embedding digital collaboration, automation, and AI across their operations.
– Björn Noack, Partner at Bain & CompanyCompliance Case Studies




Embrace AI-driven lean manufacturing solutions to boost efficiency and stay ahead in the competitive automotive landscape. Transform your operations and drive impressive results today!

Leadership Challenges & Opportunities
Data Silos in Operations
Utilize AI for Lean Manufacturing Automation to integrate disparate data sources across Automotive production lines. Implement data lakes and real-time analytics to ensure a unified view of operations. This enables informed decision-making, enhances operational efficiency, and reduces downtime caused by miscommunication.
Resistance to Change Culture
Foster a culture of innovation by leveraging AI for Lean Manufacturing Automation to demonstrate quick wins in productivity. Initiate pilot projects that showcase tangible benefits, thereby encouraging employee buy-in. Regular training and updates will help ease transitions and promote a proactive approach to adopting new technologies.
High Initial Investment Costs
Mitigate high upfront costs of AI for Lean Manufacturing Automation by adopting modular solutions that allow for phased implementation. Focus on integrating high-impact areas first, which can yield immediate ROI, enabling reinvestment into further automation. This strategic approach minimizes financial strain while maximizing efficiency gains.
Compliance with Industry Standards
Implement AI for Lean Manufacturing Automation systems that incorporate real-time compliance monitoring and reporting features tailored to Automotive regulations. Utilize predictive analytics to foresee compliance issues, thus allowing preemptive actions. This not only streamlines adherence processes but also reduces the risk of costly penalties.
Assess how well your AI initiatives align with your business goals

AI Use Case vs ROI Timeline
| AI Use Case | Description | Typical ROI Timeline | Expected ROI Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Predictive Maintenance Scheduling | Utilizing AI to predict equipment failures before they occur. For example, automotive manufacturers can analyze sensor data to schedule maintenance, reducing downtime and costs. This ensures production lines remain operational, increasing overall efficiency. | 6-12 months | High |
| Quality Control Automation | Implementing AI-driven vision systems for quality inspection. For example, automotive plants can automate the detection of defects on the assembly line, significantly reducing error rates and rework costs. | 6-9 months | Medium-High |
| Supply Chain Optimization | Leveraging AI algorithms to improve inventory management. For example, automotive suppliers can predict demand more accurately, ensuring optimal stock levels, reducing excess inventory costs and stockouts. | 12-18 months | Medium-High |
| Production Line Optimization | Using AI to streamline production processes. For example, automotive manufacturers can analyze workflow data to identify bottlenecks, leading to enhanced throughput and reduced cycle times. | 6-12 months | High},{ |
Glossary
Work with Atomic Loops to architect your AI implementation roadmap — from PoC to enterprise scale.
Contact NowFrequently Asked Questions
- AI for Lean Manufacturing Automation enhances efficiency by automating repetitive tasks in production.
- It helps identify waste and streamline processes through data analysis and machine learning.
- Companies benefit from improved quality control and reduced error rates in manufacturing.
- The technology supports real-time monitoring, allowing for proactive decision-making.
- Overall, it drives innovation and competitiveness in the automotive sector.
- Begin by assessing current operations to identify areas where AI can add value.
- Develop a clear strategy outlining objectives, resources, and timeline for implementation.
- Engage cross-functional teams to ensure integration with existing manufacturing processes.
- Consider starting with pilot projects to evaluate AI effectiveness before full-scale deployment.
- Continuous training and support for staff are essential for smooth adoption and success.
- AI enhances operational efficiency by reducing waste and optimizing resource allocation.
- Companies experience improved product quality and faster production times as a result.
- Data-driven insights lead to informed decision-making and strategic planning.
- Automation reduces labor costs and minimizes human error in manufacturing processes.
- Organizations gain a competitive edge through enhanced agility and innovation capabilities.
- Common obstacles include resistance to change and lack of technical expertise among staff.
- Integration with existing systems can be complex and require careful planning.
- Data quality issues can hinder the effectiveness of AI solutions and insights.
- It's crucial to establish clear governance and compliance measures to mitigate risks.
- Best practices include iterative testing and involving stakeholders throughout the process.
- The right timing often aligns with organizational readiness and digital transformation goals.
- Companies should assess their current operational challenges and market conditions.
- Early adoption can be advantageous in rapidly changing automotive markets.
- Consider industry trends and competitor actions when planning your timeline.
- Phased implementation can allow for gradual adaptation and learning opportunities.
- AI can optimize supply chain logistics by predicting demand and managing inventory.
- Predictive maintenance helps reduce downtime by anticipating equipment failures.
- Robotics and automation streamline assembly lines, increasing speed and precision.
- Quality control processes can be enhanced through AI-driven visual inspection technologies.
- These applications lead to greater efficiencies and cost savings across manufacturing operations.
- Start by establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) relevant to your operations.
- Measure improvements in efficiency, quality, and cost reductions post-implementation.
- Analyze productivity gains and compare them against initial investment costs.
- Regularly review performance data to assess ongoing AI effectiveness over time.
- Communicate results to stakeholders to highlight the value added by AI initiatives.
- Conduct thorough risk assessments to identify potential challenges early in the process.
- Implement robust data governance policies to ensure compliance and security.
- Establish contingency plans to address unforeseen issues during implementation.
- Regular training and updates for staff can minimize operational risks and errors.
- Engage experts and partners to provide guidance throughout the AI adoption journey.