AI for Multi Plant Performance Optimization
In the Automotive sector, "AI for Multi Plant Performance Optimization" refers to the strategic application of artificial intelligence technologies to enhance the operational synchronization and efficiency of manufacturing plants. This approach leverages data analytics, machine learning, and automation to streamline processes, reduce waste, and improve overall production quality. As the automotive landscape evolves, stakeholders are increasingly recognizing the importance of AI in aligning their operational practices with emerging technological trends and market demands.
The integration of AI into multi-plant operations is reshaping the Automotive ecosystem by fostering innovation and redefining competitive advantages. AI-driven methodologies are enabling organizations to make data-informed decisions that enhance efficiency and responsiveness to market changes. This transformation not only influences how stakeholders interact but also sets the stage for new growth opportunities. However, companies must navigate challenges such as integration complexities and the shifting expectations of an increasingly tech-savvy workforce to fully realize the benefits of AI in optimizing plant performance.
Drive AI Excellence for Multi Plant Performance Optimization
Automotive leaders should strategically invest in partnerships focused on AI technologies to enhance Multi Plant Performance Optimization and streamline operations across facilities. By implementing AI-driven solutions, companies can expect substantial improvements in productivity, cost efficiency, and a stronger competitive edge in the market.
Transforming Automotive Efficiency: The Role of AI in Multi Plant Optimization
Implementation Framework
Begin by assessing current operations to identify inefficiencies in production and supply chain dynamics. This foundational step allows for targeted AI solutions, boosting efficiency and overall performance across multiple plants.
Internal R&D
Integrate data across multiple plants to create a centralized repository. This enables AI algorithms to analyze performance holistically, enhancing decision-making capabilities and streamlining operations throughout the automotive supply chain.
Technology Partners
Deploy AI algorithms tailored for performance optimization, focusing on predictive maintenance and quality control. This implementation enhances operational efficiency and reduces downtime, significantly impacting productivity in automotive manufacturing.
Industry Standards
Establish a monitoring framework to evaluate AI performance continuously. This feedback loop allows for real-time adjustments, ensuring AI solutions evolve with operational needs, driving sustained performance improvements across multiple automotive plants.
Cloud Platform
Invest in training programs to equip employees with the skills necessary to leverage AI technologies effectively. This enhances operational capabilities and fosters a culture of innovation, ensuring successful AI adoption across all plants.
Industry Standards
Best Practices for Automotive Manufacturers
-
Impact : Enhances defect detection accuracy significantly
Example : Example: In an automotive assembly line, a vision-based AI system flags microscopic paint defects in real time as car bodies pass under cameras, catching flaws human inspectors previously missed during night shifts.
-
Impact : Reduces production downtime and costs
Example : Example: A semiconductor factory uses AI to detect early soldering anomalies. The system stops the line immediately, preventing a full batch failure that would have caused hours of rework and shutdown.
-
Impact : Improves quality control standards
Example : Example: A food packaging plant uses AI image recognition to verify seal integrity on every packet, ensuring non-compliant packages are rejected instantly before shipping.
-
Impact : Boosts overall operational efficiency
Example : Example: AI dynamically adjusts inspection thresholds based on production speed, allowing the factory to increase output during peak demand without sacrificing quality.
-
Impact : High initial investment for implementation
Example : Example: A mid-sized electronics manufacturer delays AI rollout after realizing camera hardware, GPUs, and system integration push upfront costs beyond budget approvals.
-
Impact : Potential data privacy concerns
Example : Example: AI quality systems capturing worker activity unintentionally store employee facial data, triggering compliance issues with internal privacy policies.
-
Impact : Integration challenges with existing systems
Example : Example: AI software cannot communicate with a 15-year-old PLC controller, forcing engineers to manually export data and slowing decision-making.
-
Impact : Dependence on continuous data quality
Example : Example: Dust accumulation on camera lenses causes the AI to misclassify normal products as defective, leading to unnecessary scrap until recalibration.
-
Impact : Enables proactive maintenance strategies
Example : Example: An automotive manufacturer implements IoT devices to monitor machine health in real time. Predictive maintenance reduces unexpected breakdowns by 30%, enhancing overall equipment effectiveness.
-
Impact : Enhances supply chain responsiveness
Example : Example: Real-time data analytics allows a parts supplier to adjust inventory levels swiftly, minimizing stockouts and reducing excess holding costs by 15% during seasonal demand fluctuations.
-
Impact : Improves energy consumption tracking
Example : Example: An auto plant uses AI to monitor energy use across machinery, leading to a 20% reduction in utility costs after identifying areas for improvement with real-time insights.
-
Impact : Increases production line adaptability
Example : Example: AI systems adjust production schedules dynamically based on real-time order data, enabling the plant to respond to customer demands without delays, increasing customer satisfaction.
-
Impact : Over-reliance on automated systems
Example : Example: An automotive facility faced production halts when an AI monitoring system failed, causing reliance on automated alerts that missed critical anomalies, leading to delays in response time.
-
Impact : Data overload from constant monitoring
Example : Example: Real-time data streams overwhelmed analysts at an automotive plant, leading to missed opportunities for actionable insights due to information overload during high-production periods.
-
Impact : Potential for system failures during peak loads
Example : Example: During a system upgrade, an AI monitoring tool crashed during peak production hours, causing a temporary halt. Engineers scrambled to revert to manual processes, slowing down operations.
-
Impact : Insufficient staff training on new technologies
Example : Example: A workforce untrained in new AI technologies struggled to adapt, leading to misuse of monitoring tools and decreased productivity during the transition period.
-
Impact : Fosters a culture of continuous improvement
Example : Example: A major automotive manufacturer implemented regular AI training sessions, leading to a 40% increase in employee engagement scores, as staff felt equipped to handle new technologies confidently.
-
Impact : Enhances employee engagement and morale
Example : Example: Continuous training on AI tools at a manufacturing plant reduced resistance to technology changes, leading to smoother transitions and faster adoption of new processes by 25%.
-
Impact : Reduces resistance to technology adoption
Example : Example: Training programs enhanced operational knowledge, allowing cross-functional teams to collaborate more effectively, resulting in a 15% reduction in project completion times at an automotive facility.
-
Impact : Improves operational knowledge across teams
Example : Example: Increased employee familiarity with AI systems minimized errors during production, leading to a 10% improvement in overall product quality as teams adapted more quickly to new workflows.
-
Impact : Training costs may exceed budget
Example : Example: An automotive factory overestimated training budget needs, leading to financial strain after realizing costs for comprehensive AI training surpassed initial projections significantly.
-
Impact : Time away from production activities
Example : Example: Employees at a plant missed crucial production time during extensive training sessions, resulting in decreased output and tight deadlines that strained overall team performance.
-
Impact : Varying learning curves among employees
Example : Example: A wide disparity in tech-savviness among employees caused uneven adoption of AI tools, with some teams struggling significantly while others excelled, leading to inconsistent performance.
-
Impact : Potential knowledge gaps in technology updates
Example : Example: Lack of ongoing updates in training content left employees unaware of new AI features, creating knowledge gaps that hindered effective use of technology in production processes.
-
Impact : Enhances decision-making accuracy
Example : Example: An automotive production facility implemented AI-driven analytics, resulting in a 25% increase in decision-making accuracy regarding production schedules based on historical data trends.
-
Impact : Increases predictive maintenance effectiveness
Example : Example: Predictive maintenance powered by data analytics allowed an automotive plant to foresee equipment failures, reducing downtime by 30% and enhancing overall productivity significantly.
-
Impact : Improves supply chain forecasting
Example : Example: AI-enhanced supply chain forecasting led to a 20% reduction in excess inventory costs for an automotive supplier, as real-time data enabled more accurate demand predictions.
-
Impact : Facilitates better resource allocation
Example : Example: Using AI to analyze resource allocation data allowed an auto manufacturer to streamline processes, resulting in a 15% decrease in operational costs across multiple plants.
-
Impact : Data integrity issues may arise
Example : Example: An automotive manufacturer faced significant production delays due to data integrity issues, where inaccurate historical data led to faulty predictions and misaligned production schedules.
-
Impact : Challenges in data integration
Example : Example: An AI system's inability to integrate data from legacy systems caused delays in critical insights, forcing engineers to spend extra time manually consolidating information.
-
Impact : High costs of data storage solutions
Example : Example: A large automotive plant encountered escalating costs related to data storage solutions as they expanded their AI capabilities, straining financial resources and budgets.
-
Impact : Compliance risks with data regulations
Example : Example: Compliance risks emerged when an automotive company failed to properly anonymize customer data during AI analysis, leading to potential legal ramifications and fines.
-
Impact : Accommodates future growth needs
Example : Example: An automotive manufacturer adopted a modular AI system that easily scaled with production demands, resulting in a 20% increase in adaptability during peak seasons without major overhauls.
-
Impact : Enhances flexibility in operations
Example : Example: Scalable AI solutions at a plant allowed for seamless integration of additional machinery, leading to improved operational flexibility and a 15% increase in production output.
-
Impact : Reduces technology obsolescence risk
Example : Example: By investing in scalable technology, an automotive company reduced the risk of obsolescence, as upgrades could be implemented without complete system replacements, saving costs.
-
Impact : Facilitates easier upgrades and maintenance
Example : Example: Modular AI systems facilitated easier maintenance protocols, allowing teams to upgrade components without significant downtime, thus improving operational efficiency by 10%.
-
Impact : Potential compatibility issues with legacy systems
Example : Example: An automotive facility struggled with compatibility issues when integrating new AI systems with outdated machinery, resulting in production delays and additional costs for retrofitting.
-
Impact : Higher long-term costs for scalability
Example : Example: While scalable solutions offered long-term flexibility, an automotive manufacturer faced higher long-term costs due to underestimating the complexities involved in future expansions.
-
Impact : Complexity in managing multiple AI systems
Example : Example: Managing multiple AI systems increased operational complexity, leading to confusion among staff and eventual misalignment of production processes at an automotive plant.
-
Impact : Risk of over-engineering solutions
Example : Example: An over-engineered AI solution at a plant resulted in unnecessary features that complicated operations, leading to decreased efficiency and employee frustration.
AI is revolutionizing multi-plant operations, enabling unprecedented efficiency and performance across the automotive industry.
– Internal R&DCompliance Case Studies



Unlock unparalleled efficiency and gain a competitive edge with AI-driven solutions tailored for your automotive plants. Transform challenges into opportunities today!
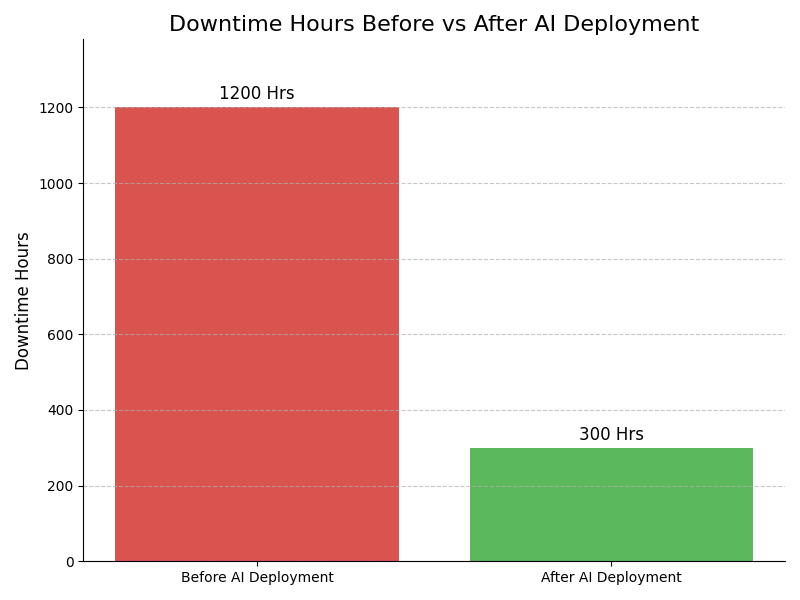

Leadership Challenges & Opportunities
Data Silos Across Plants
Utilize AI for Multi Plant Performance Optimization to integrate data across automotive plants through centralized platforms. Implement machine learning algorithms to analyze disparate datasets, enabling real-time insights. This enhances decision-making, reduces redundancy, and drives cohesive operations across multiple facilities.
Resistance to Change
Foster a culture of innovation by implementing AI for Multi Plant Performance Optimization in stages, with clear communication of benefits. Engage employees through workshops and pilot programs demonstrating immediate gains. This approach mitigates resistance and encourages collaborative adaptation to new technologies in the automotive sector.
High Initial Investment
Leverage AI for Multi Plant Performance Optimization using a phased investment approach, focusing on high-impact areas first. Adopt subscription-based models to spread costs over time. This strategy minimizes financial risk while demonstrating ROI, making it easier to justify further investment in advanced technologies.
Skill Shortages in AI
Address skill shortages by partnering with educational institutions and utilizing AI for Multi Plant Performance Optimization training modules. Implement mentorship programs and internship opportunities to build a skilled workforce. This proactive approach not only enhances internal capabilities but also fosters industry collaboration and innovation.
Assess how well your AI initiatives align with your business goals
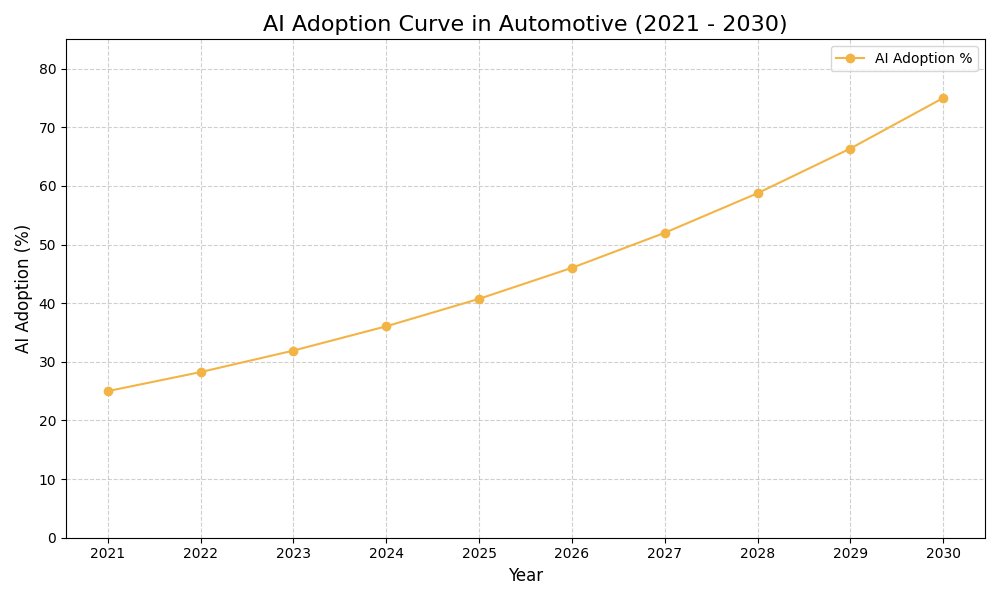
AI Use Case vs ROI Timeline
| AI Use Case | Description | Typical ROI Timeline | Expected ROI Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Predictive Maintenance Scheduling | AI algorithms analyze equipment data to predict failures before they occur. For example, in automotive manufacturing, sensors track machine performance to schedule timely maintenance, reducing downtime significantly. | 6-12 months | High |
| Quality Control Automation | AI systems inspect products for defects during production. For example, an automotive assembly line uses computer vision to identify paint imperfections, ensuring only flawless vehicles reach customers, enhancing brand reputation. | 6-12 months | Medium-High |
| Supply Chain Optimization | Machine learning models forecast demand and optimize inventory levels. For example, automotive plants adjust parts orders based on predictive analytics, reducing excess stock and associated costs while meeting production schedules efficiently. | 12-18 months | High |
| Energy Consumption Management | AI analyzes energy usage patterns to optimize consumption. For example, an automotive plant implements AI to adjust energy use during off-peak hours, leading to significant savings on energy bills and reduced carbon footprint. | 6-12 months | Medium-High |
Glossary
Work with Atomic Loops to architect your AI implementation roadmap — from PoC to enterprise scale.
Contact NowFrequently Asked Questions
- AI for Multi Plant Performance Optimization refers to using advanced algorithms to enhance operational efficiency.
- It enables real-time monitoring and data analysis to improve decision-making processes.
- Automotive companies can reduce waste and streamline production through predictive maintenance.
- AI helps in optimizing supply chain logistics and resource allocation effectively.
- The technology supports continuous improvement and innovation across multiple plants.
- Begin by assessing your current operational processes and identifying improvement areas.
- Engage key stakeholders to build a cross-functional team for the AI initiative.
- Pilot small-scale projects to validate AI solutions before a full rollout.
- Invest in necessary infrastructure and ensure team readiness for AI technologies.
- Document lessons learned to refine future implementations and scale effectively.
- AI enhances operational efficiency by automating repetitive tasks and reducing human errors.
- It provides actionable insights based on data analytics, improving decision-making accuracy.
- Companies can achieve significant cost savings through optimized resource utilization.
- AI-driven predictive maintenance minimizes downtime and enhances production reliability.
- The technology fosters innovation, enabling faster response to market changes and demands.
- Resistance to change from employees can hinder successful AI adoption in plants.
- Data quality and availability are crucial for effective AI implementation; poor data can lead to failures.
- Integrating AI with existing systems may present technical complexities and require additional resources.
- Ensuring compliance with industry regulations can be challenging during AI adoption.
- Continuous training and support are essential to overcome skill gaps within teams.
- Companies should evaluate their operational inefficiencies and readiness for digital transformation.
- Investment is timely when facing competitive pressures or significant market shifts.
- If existing systems are outdated, AI can provide essential upgrades for modernization.
- During product innovation phases, AI can accelerate development and production cycles.
- Regular assessment of emerging technologies can reveal opportune moments for AI investment.
- Key performance indicators include operational efficiency, production quality, and cost reduction.
- Monitoring downtime and maintenance frequency can indicate AI predictive capabilities.
- Employee productivity improvements signify effective AI integration in workflows.
- Customer satisfaction metrics can reflect enhanced product quality and delivery times.
- Compliance with regulatory standards can validate the effectiveness of AI solutions.
- AI is used for predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and optimizing equipment performance.
- Supply chain optimization through AI enhances logistics and inventory management processes.
- Quality control processes benefit from AI by identifying defects in real-time during production.
- AI-driven design simulations can accelerate product development and innovation timelines.
- Customer feedback analysis through AI helps tailor products to market demands effectively.
- Conduct thorough risk assessments to identify potential challenges before starting projects.
- Develop a robust change management strategy to support employees through transitions.
- Collaborate with technology partners to ensure best practices are followed during integration.
- Regular audits and performance reviews can help identify issues early in the process.
- Invest in continuous training to equip teams with necessary skills for managing AI technologies.

