AI for Production Line Balancing
In the Automotive sector, AI for Production Line Balancing refers to the application of artificial intelligence technologies to optimize the distribution of tasks across production lines. This concept encompasses various methodologies and tools designed to improve operational efficiency, reduce waste, and enhance overall productivity. As the automotive landscape increasingly leans towards automation and digitization, understanding this paradigm becomes essential for stakeholders aiming to stay competitive and align with broader trends in industrial transformation.
The significance of AI-driven practices in the Automotive ecosystem cannot be overstated. These technologies are transforming competitive dynamics by enabling faster innovation cycles and more agile stakeholder interactions. The integration of AI not only enhances efficiency but also empowers data-driven decision-making, shaping long-term strategic directions. However, while the opportunities for growth are substantial, challenges such as adoption barriers, integration complexities, and shifting expectations must be navigated carefully to realize the full potential of these advancements.
Transform Your Production Line with AI Strategies
Automotive manufacturers should strategically invest in AI-driven production line balancing technologies and forge partnerships with leading AI firms to enhance their capabilities. This approach promises significant ROI through streamlined operations, reduced waste, and improved product quality, providing a competitive edge in the automotive market.
Transforming Automotive Efficiency: The Role of AI in Production Line Balancing
Implementation Framework
Begin by analyzing current production processes to identify inefficiencies and bottlenecks. This assessment will guide AI implementation, optimize workflows, and enhance productivity across the automotive supply chain.
Industry Standards
Implement AI algorithms and machine learning models to analyze production data in real-time. This integration enhances decision-making, reduces downtime, and improves overall production efficiency in automotive manufacturing settings.
Technology Partners
Establish a monitoring system to track AI performance and production outcomes. Regularly adjust algorithms based on real-time data to ensure continuous improvement and alignment with production goals in automotive manufacturing.
Internal R&D
Develop training programs to equip employees with skills to effectively use AI tools. This investment in human capital fosters a culture of innovation, driving acceptance and maximizing AI benefits in production processes.
Industry Standards
Conduct regular evaluations of AI-driven changes on production metrics. Assess improvements in efficiency, cost reductions, and quality outputs to validate the effectiveness of AI initiatives in automotive line balancing.
Cloud Platform
Best Practices for Automotive Manufacturers
-
Impact : Reduces unexpected equipment failures
Example : Example: A leading automotive manufacturer implemented AI-based predictive maintenance, identifying potential equipment failures before they occurred, resulting in a 20% increase in production line uptime and significant cost savings.
-
Impact : Increases production line uptime
Example : Example: An automotive plant used predictive algorithms to schedule maintenance, reducing unplanned breakdowns by 30% and improving overall efficiency significantly without disrupting production schedules.
-
Impact : Enhances maintenance scheduling efficiency
Example : Example: By analyzing historical failure data, an OEM improved its maintenance scheduling, achieving a 25% reduction in downtime, allowing for smoother production flow and increased output.
-
Impact : Lowers overall maintenance costs
Example : Example: AI predictions enabled a major carmaker to allocate maintenance resources more effectively, resulting in a 15% reduction in maintenance costs while ensuring high production availability.
-
Impact : High initial investment for AI tools
Example : Example: An automotive manufacturer faced budget constraints when implementing AI, as initial investments in software and hardware exceeded projected costs, leading to delayed rollout and operational setbacks.
-
Impact : Integration with legacy systems
Example : Example: A legacy system in a car assembly line could not communicate with new AI tools, causing integration delays and increased costs as engineers worked to bridge the gap.
-
Impact : Dependence on accurate data inputs
Example : Example: During a shift to AI-driven maintenance, outdated sensors produced unreliable data, leading to erroneous predictions and subsequent production delays that impacted delivery schedules.
-
Impact : Change management resistance from staff
Example : Example: Employees resisted new AI systems, fearing job displacement, which slowed the adoption process and limited the potential benefits of the technology during the transition.
-
Impact : Improves immediate decision-making capabilities
Example : Example: An automotive plant integrated real-time monitoring AI, allowing managers to make timely adjustments during production, resulting in a 10% reduction in defects identified during final inspection stages.
-
Impact : Enhances quality control measures
Example : Example: Real-time monitoring systems enabled a major car manufacturer to address quality issues immediately on the production line, reducing defect rates by 15% and ensuring customer satisfaction.
-
Impact : Increases responsiveness to production issues
Example : Example: With real-time alerts from AI systems, a factory could respond to bottlenecks instantly, improving the assembly line flow and reducing idle time by 12% during peak hours.
-
Impact : Facilitates data-driven insights
Example : Example: Data-driven insights generated from live monitoring helped a car manufacturer forecast production trends, allowing for proactive adjustments and resulting in a 20% increase in operational efficiency.
-
Impact : Potential over-reliance on AI systems
Example : Example: An automotive plant became overly reliant on AI monitoring, leading to reduced human oversight, which caused missed anomalies that the AI system failed to detect, impacting quality control.
-
Impact : Data overload from excessive monitoring
Example : Example: A factory faced information overload from real-time data streams, complicating decision-making processes and causing delays in addressing production issues effectively.
-
Impact : Integration challenges with existing workflows
Example : Example: Integration of real-time monitoring with pre-existing workflows was challenging, requiring extensive retraining and causing temporary production disruptions during the transition.
-
Impact : High operational costs for real-time systems
Example : Example: The costs associated with maintaining and updating real-time monitoring systems escalated, leading management to reassess the budget allocated for AI innovations, causing potential delays in other projects.
-
Impact : Enhances employee adaptability to AI
Example : Example: Training sessions on AI tools empowered assembly line workers to adapt quickly, resulting in a 15% increase in productivity as they efficiently utilized AI insights for better output.
-
Impact : Increases overall productivity levels
Example : Example: By equipping employees with AI knowledge, an automotive plant reduced operational errors by 20%, significantly enhancing the quality of assembled vehicles and boosting customer trust.
-
Impact : Fosters a culture of innovation
Example : Example: Continuous training programs fostered an innovative mindset among employees, leading to the development of new production techniques that improved efficiency by 18% in a year.
-
Impact : Reduces operational errors significantly
Example : Example: A comprehensive AI training initiative resulted in a more agile workforce, enabling the plant to adapt quickly to changes in production demands without compromising quality standards.
-
Impact : Training costs can be substantial
Example : Example: An automotive manufacturer faced high expenses in rolling out extensive training programs on AI tools, straining the budget and delaying other initiatives aimed at enhancing production.
-
Impact : Resistance to change among employees
Example : Example: Employee resistance to adopting new AI systems led to a lack of engagement during training sessions, reducing the overall effectiveness of the initiative and prolonging the adjustment period.
-
Impact : Temporary productivity loss during training
Example : Example: Temporary productivity dips occurred during the training phase as workers adjusted to new AI tools, impacting production targets and highlighting the need for gradual implementation.
-
Impact : Limited understanding of AI capabilities
Example : Example: A lack of foundational knowledge about AI among staff led to confusion during training, emphasizing the necessity for tailored programs that address varying levels of understanding.
-
Impact : Optimizes inventory management processes
Example : Example: An automotive manufacturer integrated AI into its supply chain management, optimizing inventory levels and reducing excess stock by 25%, ultimately lowering carrying costs significantly.
-
Impact : Enhances supplier collaboration dynamics
Example : Example: AI tools improved collaboration with suppliers by providing data insights, resulting in a 15% reduction in lead times and enhancing overall production efficiency.
-
Impact : Improves demand forecasting accuracy
Example : Example: With AI-driven demand forecasting, a major automotive brand accurately predicted sales trends, reducing stockouts by 30%, ensuring production remained aligned with market demand.
-
Impact : Lowers supply chain operational costs
Example : Example: The integration of AI in supply chain management allowed an automotive manufacturer to cut operational costs by 10% through improved logistics and streamlined processes.
-
Impact : Potential disruptions in supplier relationships
Example : Example: Integrating AI in supply chain management strained relationships with some suppliers who were reluctant to adopt new technologies, creating friction in collaboration and affecting timely deliveries.
-
Impact : Initial integration complexities
Example : Example: Initial complexities during AI integration with existing supply chain systems delayed the rollout, causing temporary disruptions in inventory management and impacting production schedules.
-
Impact : Resistance from supply chain partners
Example : Example: Some supply chain partners resisted adopting AI tools due to fears of losing control over their processes, creating a barrier to effective collaboration and data sharing.
-
Impact : Data security concerns with shared information
Example : Example: Sharing sensitive data with AI systems raised security concerns among supply chain partners, leading to extensive negotiations around data privacy and protection protocols.
-
Impact : Fosters a culture of innovation
Example : Example: An automotive company adopted continuous improvement practices, leading to a 20% reduction in waste during production processes, enhancing both sustainability and profit margins.
-
Impact : Enhances operational efficiency continuously
Example : Example: By fostering a culture of innovation, the company empowered employees to suggest improvements, resulting in a 15% increase in operational efficiency across various production lines.
-
Impact : Reduces waste and inefficiencies
Example : Example: Continuous feedback loops allowed a major automotive manufacturer to identify inefficiencies quickly, reducing cycle times by 10% and increasing overall output.
-
Impact : Encourages employee engagement and feedback
Example : Example: Employee engagement increased significantly as staff felt valued in the continuous improvement process, leading to higher morale and productivity across the board.
-
Impact : Potential complacency over time
Example : Example: Over time, an automotive plant became complacent with their continuous improvement initiatives, resulting in stagnation and missed opportunities for innovation and efficiency gains.
-
Impact : Difficulty measuring improvement outcomes
Example : Example: Difficulty in measuring the outcomes of continuous improvement efforts led to frustration among management, as they struggled to quantify actual benefits against invested resources.
-
Impact : Resistance to new ideas from staff
Example : Example: Some employees resisted new ideas proposed during improvement sessions, leading to stagnation in innovation and limiting the potential for operational enhancements.
-
Impact : Short-term focus on immediate results
Example : Example: A focus on immediate results in continuous improvement efforts sidelined long-term strategic initiatives, ultimately undermining the overall effectiveness of the improvement culture.
AI is revolutionizing production line balancing, enabling manufacturers to optimize workflows and enhance efficiency like never before.
– Arjun SrinivasanCompliance Case Studies



Embrace AI-driven solutions for production line balancing and outpace your competition. Transform inefficiencies into streamlined success in the automotive industry today.
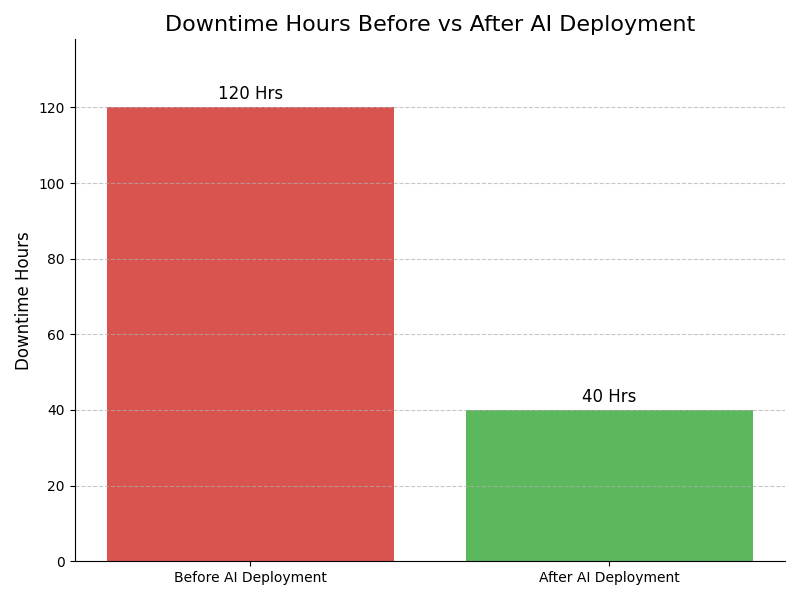
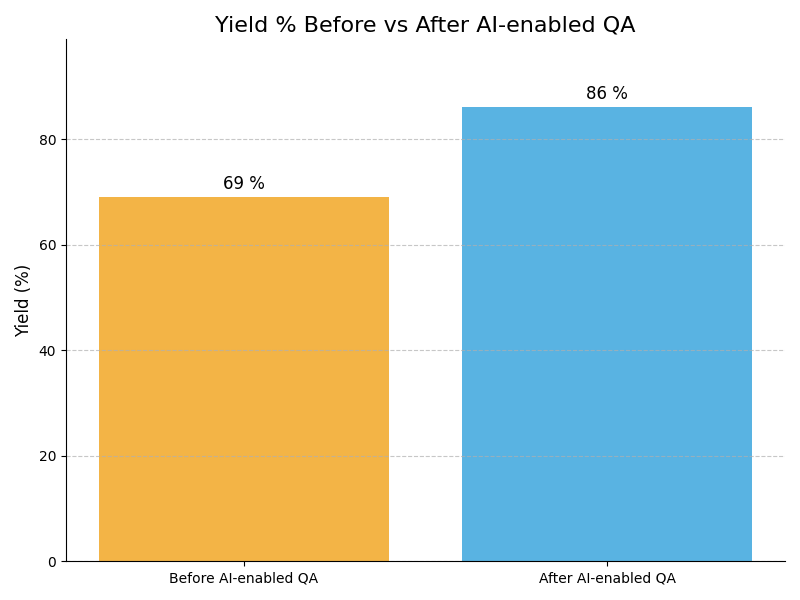
Leadership Challenges & Opportunities
Data Quality Issues
Utilize AI for Production Line Balancing to automate data cleansing and validation processes. Implement machine learning algorithms that learn from historical production data, ensuring high-quality inputs. This approach enhances decision-making accuracy, optimizes workflow efficiency, and minimizes production delays caused by data inconsistencies.
Change Resistance
Foster a culture of innovation by integrating AI for Production Line Balancing into existing workflows. Use change management strategies that emphasize transparent communication, employee involvement, and AI training programs. This boosts acceptance and engagement, ensuring smoother transitions to AI-driven processes within the Automotive sector.
Resource Allocation Challenges
Implement AI for Production Line Balancing to optimize resource allocation dynamically by analyzing real-time data. Leverage predictive analytics to forecast demand and adjust workforce and machine utilization accordingly. This maximizes efficiency, reduces idle time, and aligns production capabilities with market demands effectively.
Supplier Coordination Issues
Deploy AI for Production Line Balancing to enhance collaboration with suppliers through real-time data sharing and predictive analytics. Implement integrated platforms that facilitate transparent communication and streamline inventory management. This reduces lead times, enhances supply chain responsiveness, and ensures that production lines remain agile and efficient.
Assess how well your AI initiatives align with your business goals
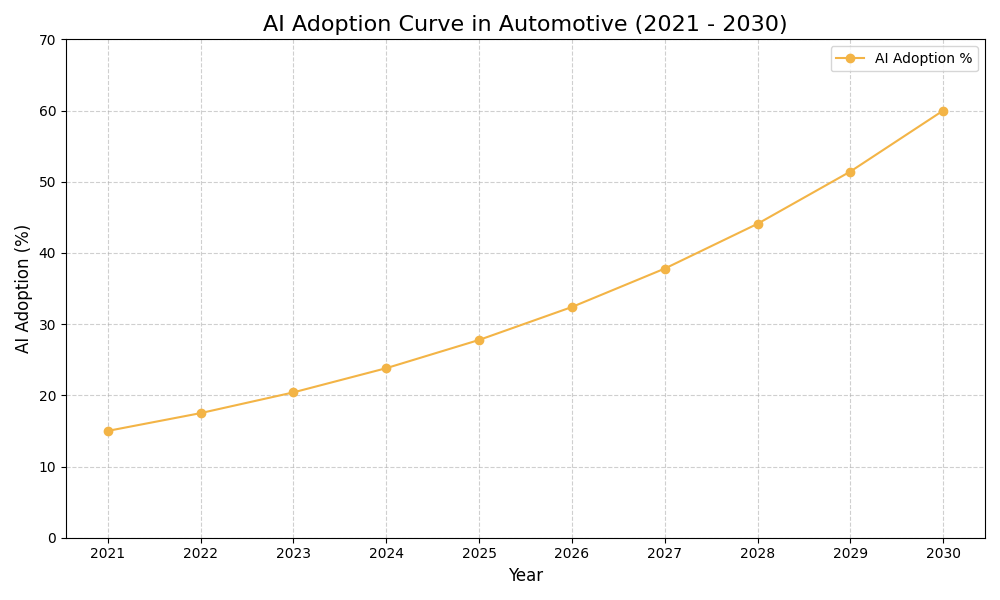
AI Use Case vs ROI Timeline
| AI Use Case | Description | Typical ROI Timeline | Expected ROI Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Predictive Maintenance Scheduling | AI can analyze machinery data to predict failures before they occur, leading to minimized downtime. For example, a car manufacturer uses AI to schedule maintenance on robotic arms based on historical performance data, improving production efficiency. | 6-12 months | High |
| Dynamic Resource Allocation | Leveraging AI, companies can dynamically allocate resources based on real-time demand and production rates. For example, an automotive plant uses AI to adjust workforce levels on the assembly line, increasing throughput during peak hours without compromising quality. | 12-18 months | Medium-High |
| Quality Control Automation | AI systems can inspect products for defects in real-time, ensuring quality standards are met. For example, an automotive manufacturer employs computer vision to automatically detect paint imperfections on vehicles, reducing rework rates and increasing customer satisfaction. | 6-9 months | High |
| Production Line Simulation | AI can simulate various production scenarios to optimize line configuration and workflows. For example, a manufacturer uses AI to model different layouts for an assembly line, resulting in a more efficient design that minimizes bottlenecks and maximizes output. | 12-18 months | Medium-High},{ |
Glossary
Work with Atomic Loops to architect your AI implementation roadmap — from PoC to enterprise scale.
Contact NowFrequently Asked Questions
- AI for Production Line Balancing optimizes workflows and enhances productivity in manufacturing.
- It reduces bottlenecks and improves resource allocation, leading to smoother operations.
- By leveraging real-time data, companies can make informed decisions quickly.
- AI also helps in maintaining consistent quality across production lines.
- Overall, it enhances competitiveness and responsiveness to market demands.
- Begin by assessing your current production processes for potential AI integration.
- Identify specific pain points that AI can address to enhance efficiency.
- Consider collaborating with technology providers for tailored AI solutions.
- Pilot projects can help validate concepts before full-scale implementation.
- Training staff on new technologies is crucial for successful adoption.
- AI can significantly enhance operational efficiency, reducing production cycle times.
- Companies often experience improved resource utilization and lower operational costs.
- Real-time data analytics lead to quicker decision-making and adaptations.
- Enhanced quality control reduces defects, improving customer satisfaction.
- Competitive advantages arise from faster innovation and responsiveness to changes.
- Resistance to change from employees can hinder successful implementation.
- Data quality and integration issues may complicate AI application.
- Lack of necessary technical skills can slow down the adoption process.
- Budget constraints can limit the scope of AI projects initially.
- Establishing clear objectives is essential to address these challenges effectively.
- Adoption should occur when current processes struggle to meet production demands.
- Consider implementing AI when aiming for significant efficiency improvements.
- If you're experiencing quality issues, AI can help identify root causes.
- Engagement with stakeholders is crucial to assess readiness for AI.
- Monitoring industry trends can provide insights on optimal timing for adoption.
- AI systems can automate compliance tracking, reducing human errors in reporting.
- Real-time monitoring ensures adherence to safety and quality regulations.
- Data analytics facilitates proactive identification of compliance risks.
- AI can help in maintaining detailed records for regulatory audits.
- Integrating AI fosters a culture of accountability within production teams.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) should include production efficiency rates.
- Monitor defect rates to assess improvements in quality control.
- Evaluate the reduction in cycle times as a measure of operational success.
- Cost savings associated with resource utilization should be tracked.
- Employee feedback can provide insights into the system's effectiveness and acceptance.
- Benchmarking against industry leaders can guide your AI implementation strategy.
- Standards for production efficiency and quality can be useful reference points.
- Collaboration with industry groups helps in sharing best practices and insights.
- Adopting recognized frameworks can streamline your implementation process.
- Regularly updating benchmarks is essential to stay competitive in a dynamic market.

