AI for Sustainability in Automotive Plants
In the context of the Automotive sector, "AI for Sustainability in Automotive Plants" refers to the integration of artificial intelligence technologies to enhance environmental stewardship, resource efficiency, and operational effectiveness within manufacturing facilities. This approach not only optimizes production processes but also aligns with the sector's growing commitment to sustainability. As stakeholders increasingly prioritize eco-friendly practices, AI emerges as a pivotal tool that supports strategic goals, encouraging innovation and operational excellence in a rapidly evolving landscape.
The Automotive ecosystem is undergoing a profound transformation influenced by the adoption of AI-driven practices aimed at sustainability. These innovations reshape competitive dynamics, redefine innovation cycles, and enhance interactions among stakeholders. By leveraging AI, companies can significantly improve operational efficiency, streamline decision-making processes, and chart more sustainable strategic directions. However, the journey towards comprehensive integration presents challenges, including barriers to adoption and the complexities of implementation, necessitating a careful balance between pursuing growth opportunities and addressing realistic operational hurdles.
Drive AI Innovation for Sustainable Automotive Manufacturing
Automotive companies should invest in strategic partnerships with AI technology providers and prioritize the integration of AI-driven sustainability initiatives in their operations. Leveraging AI can lead to reduced waste, enhanced energy efficiency, and a significant boost in competitive advantage within the market.
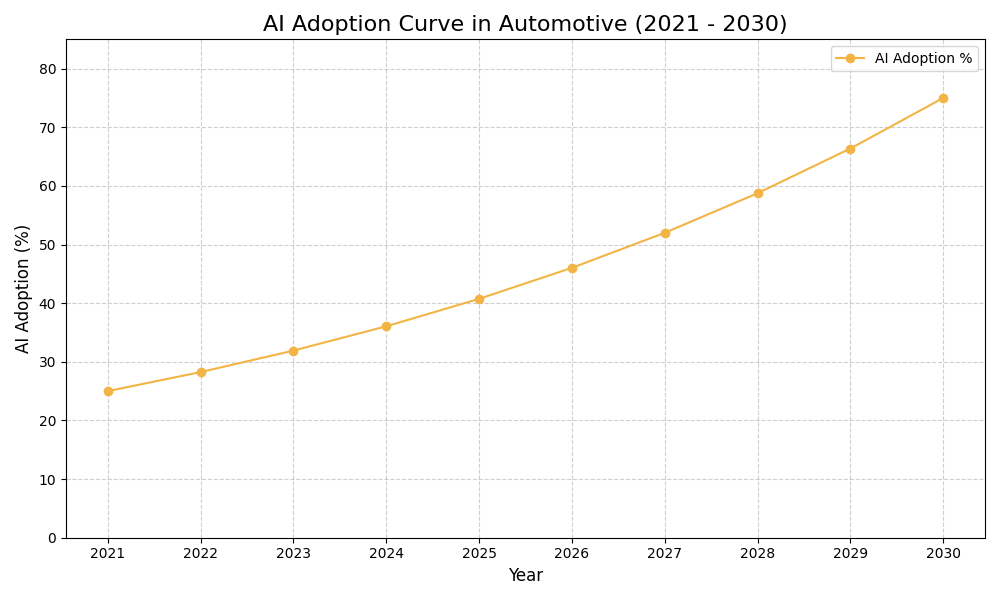
How AI is Transforming Sustainability in Automotive Plants?
Implementation Framework
Conduct a thorough assessment of current operations to identify specific areas where AI can enhance efficiency and sustainability, optimizing resource usage and reducing emissions across the automotive manufacturing process.
McKinsey & Company
Build and train AI models specifically designed for the automotive sector, focusing on predictive maintenance and supply chain optimization to reduce waste, improve efficiency, and enhance production sustainability.
Deloitte Insights
Integrate AI technologies into existing manufacturing systems, ensuring seamless collaboration between AI-driven analytics and human operators to enhance decision-making and operational efficiency while promoting sustainable practices.
Gartner
Establish a robust framework for continuously monitoring AI system performance, allowing for ongoing optimization and adjustments based on real-time data to ensure sustained improvements in sustainability metrics.
Forrester Research
Develop strategies to scale successful AI applications across multiple plants, facilitating broader adoption of sustainable practices and maximizing the overall impact of AI on the automotive supply chain.
PwC
Best Practices for Automotive Manufacturers
-
Impact : Reduces energy costs significantly
Example : Example: An automotive plant employs AI to optimize energy usage during off-peak hours, resulting in a 30% reduction in energy costs and a noticeable drop in carbon emissions.
-
Impact : Minimizes carbon emissions
Example : Example: By analyzing energy consumption patterns, AI systems identify wasteful practices, leading to a 20% increase in overall operational efficiency and sustainability ratings.
-
Impact : Enhances operational efficiency
Example : Example: AI-driven predictive maintenance of machinery helps avoid energy spikes during peak usage, saving costs and reducing the carbon footprint by 15%.
-
Impact : Improves sustainability metrics
Example : Example: A factory's AI model adjusts HVAC settings based on real-time occupancy, leading to a significant reduction in energy consumption and enhanced sustainability reporting.
-
Impact : High initial investment for implementation
Example : Example: A large automotive manufacturer hesitates to implement AI solutions due to the upfront costs of technology and training, delaying potential energy savings for over a year.
-
Impact : Resistance to change from workers
Example : Example: Employees resist AI adoption, fearing job loss, which leads to stalled projects and inefficient energy management processes that could have improved sustainability efforts.
-
Impact : Potential system integration issues
Example : Example: A legacy system fails to integrate with new AI tools, causing delays in energy optimization initiatives and resulting in higher energy bills during the transition period.
-
Impact : Dependence on accurate data inputs
Example : Example: AI tools dependent on inaccurate data inputs miscalculate energy savings, leading to wasted resources and skepticism about the technology's effectiveness.
-
Impact : Reduces unplanned downtime significantly
Example : Example: An automotive plant uses AI for predictive maintenance, reducing unplanned downtime by 40% and ensuring continuous production flow, which boosts quarterly earnings.
-
Impact : Extends equipment lifespan
Example : Example: By employing AI to predict machinery failures, a plant extends equipment lifespan by 25%, saving costs on replacements and repairs in the long run.
-
Impact : Improves resource allocation
Example : Example: AI analytics help managers allocate resources more effectively, ensuring that maintenance teams address issues before they escalate, thus improving overall operational efficiency.
-
Impact : Enhances safety protocols
Example : Example: AI-driven alerts on potential machinery failures enhance safety protocols, reducing workplace accidents by 30% and promoting a culture of safety in the plant.
-
Impact : High complexity of AI models
Example : Example: A major automotive manufacturer faces difficulties with complex AI models that require specialized knowledge, leading to delays in predictive maintenance implementation and missed opportunities.
-
Impact : Potential over-reliance on technology
Example : Example: Over-reliance on AI predictions causes operators to overlook manual checks, resulting in an unexpected machinery failure that halts production and incurs costs.
-
Impact : Initial training requirements for staff
Example : Example: Staff struggles to adapt to new AI tools during initial training, causing a temporary dip in productivity as teams navigate the learning curve.
-
Impact : Integration with legacy systems
Example : Example: Legacy systems complicate the integration of predictive maintenance AI, causing disruptions and requiring costly adjustments to existing processes.
-
Impact : Enhances visibility into operations
Example : Example: An automotive plant implements real-time monitoring, providing managers with instant visibility into production processes, leading to quicker decisions and optimized operations.
-
Impact : Enables quick decision-making
Example : Example: With real-time data analytics, quality control teams can immediately address defects, improving overall production quality by 20% and reducing waste.
-
Impact : Improves production quality
Example : Example: AI systems analyze real-time data to identify bottlenecks, enabling production managers to make adjustments that enhance throughput and operational efficiency.
-
Impact : Facilitates continuous improvement
Example : Example: Continuous monitoring allows for immediate feedback on production processes, facilitating a culture of continuous improvement and innovation in manufacturing operations.
-
Impact : High data storage requirements
Example : Example: A factory's real-time monitoring system generates massive amounts of data, leading to high storage costs and challenges in data management and analysis.
-
Impact : Potential cybersecurity vulnerabilities
Example : Example: Cybersecurity vulnerabilities in real-time monitoring systems expose sensitive production data, prompting concerns about potential breaches and loss of competitive advantage.
-
Impact : Dependence on stable internet connectivity
Example : Example: An automotive plant experiences disruptions when internet connectivity issues impede access to real-time monitoring tools, causing delays in decision-making.
-
Impact : Risk of information overload
Example : Example: Operators face information overload from excessive data streams, making it difficult to identify actionable insights and slowing down response times to operational issues.
-
Impact : Boosts employee engagement and morale
Example : Example: An automotive manufacturer invests in comprehensive AI training for employees, leading to higher engagement and morale as staff feel more competent and valued in their roles.
-
Impact : Improves operational efficiency
Example : Example: Improved training programs result in a 30% increase in operational efficiency, as employees become adept at using AI tools to enhance production processes.
-
Impact : Facilitates successful AI adoption
Example : Example: By focusing on AI skills training, a plant successfully adopts new technologies, minimizing resistance and ensuring smoother transitions during AI rollouts.
-
Impact : Reduces skill gaps in workforce
Example : Example: Targeted training reduces skill gaps, enabling the workforce to leverage AI tools effectively, thus enhancing overall productivity and competitiveness in the market.
-
Impact : Training costs can be substantial
Example : Example: A large automotive company faces substantial training costs, leading to budgetary constraints that delay AI integration initiatives and hinder progress.
-
Impact : Employee turnover may affect training
Example : Example: High employee turnover results in loss of trained staff, forcing the company to repeatedly invest in training, which disrupts ongoing projects and initiatives.
-
Impact : Inconsistent training quality
Example : Example: Inconsistent training quality leads to confusion among employees, causing operational inefficiencies as staff apply different methods to AI tools and systems.
-
Impact : Time constraints on training schedules
Example : Example: Time constraints on training schedules limit the depth of AI education, resulting in employees feeling unprepared to utilize new systems effectively.
-
Impact : Reduces supplier lead times
Example : Example: By integrating AI-driven supply chain optimization, an automotive plant reduces supplier lead times by 25%, improving production schedules and customer satisfaction.
-
Impact : Enhances inventory management
Example : Example: AI tools enhance inventory management, allowing a plant to maintain optimal stock levels, which minimizes waste and reduces carrying costs by 15% annually.
-
Impact : Minimizes waste and overstock
Example : Example: The use of AI in demand forecasting minimizes overstock situations, thereby reducing waste and freeing up capital for reinvestment in sustainable practices.
-
Impact : Improves collaboration among partners
Example : Example: AI systems improve collaboration among supply chain partners by providing real-time data, leading to better decision-making and more responsive production strategies.
-
Impact : Complexity of supply chain systems
Example : Example: An automotive company struggles with the complexity of its supply chain systems, making it difficult to implement AI solutions effectively, leading to project delays.
-
Impact : Potential vendor lock-in issues
Example : Example: Vendor lock-in with specific AI solutions limits the automotive plant's flexibility, preventing it from adapting to changing market conditions and technologies.
-
Impact : Resistance from supply chain partners
Example : Example: Resistance from supply chain partners to adopt AI technologies hampers optimization efforts, resulting in continued inefficiencies and missed opportunities.
-
Impact : Data sharing challenges
Example : Example: Data sharing challenges among supply chain partners slow down AI implementation, limiting the potential benefits of real-time analytics and collaboration.
AI is the key to unlocking sustainable practices in automotive manufacturing, enabling us to reduce waste and enhance efficiency.
– Pete MayCompliance Case Studies




Embrace AI solutions to transform your automotive plant’s sustainability efforts. Don’t fall behind—seize the opportunity to lead in eco-friendly innovation today!


Leadership Challenges & Opportunities
Data Privacy Concerns
Implement AI for Sustainability in Automotive Plants with robust encryption and access control protocols to safeguard sensitive data. Regular audits and compliance checks can ensure data integrity while leveraging AI-driven analytics for informed decision-making. This approach balances innovation with necessary privacy protections.
Supply Chain Transparency
Utilize AI for Sustainability in Automotive Plants to enhance supply chain visibility through real-time monitoring and predictive analytics. Implement blockchain technology in tandem to ensure traceability and accountability, leading to reduced waste and improved sustainability outcomes across the production process.
Change Management Resistance
Address organizational resistance by integrating AI for Sustainability in Automotive Plants with change management frameworks that involve stakeholder engagement and training. Foster a culture of innovation by showcasing successful AI applications, thus aligning employee goals with sustainability objectives and ensuring smoother transitions.
High Implementation Costs
Mitigate financial constraints by adopting AI for Sustainability in Automotive Plants using phased implementations and pilot testing. Focus on areas with the highest impact for initial investments. Leverage governmental incentives and partnerships with tech firms to offset costs and maximize resource allocation effectively.
Assess how well your AI initiatives align with your business goals
AI Use Case vs ROI Timeline
| AI Use Case | Description | Typical ROI Timeline | Expected ROI Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Predictive Maintenance for Equipment | AI analyzes sensor data from machinery to predict failures before they occur. For example, using machine learning algorithms, a plant can schedule maintenance only when necessary, reducing downtime and costs significantly. | 6-12 months | High |
| Energy Consumption Optimization | AI algorithms optimize energy usage by analyzing real-time data. For example, an automotive plant can adjust energy consumption based on production schedules, resulting in significant cost savings and reduced carbon footprint. | 12-18 months | Medium-High |
| Supply Chain Resource Allocation | AI helps in optimizing resource allocation throughout the supply chain. For example, using predictive analytics, a plant can forecast material needs accurately, reducing waste and ensuring timely production. | 6-12 months | Medium |
| Waste Reduction through AI Analytics | AI analyzes production processes to identify waste sources. For example, by implementing AI-driven analytics, an automotive plant can minimize scrap material, leading to lower disposal costs and improved sustainability. | 12-18 months | Medium-High |
Glossary
Work with Atomic Loops to architect your AI implementation roadmap — from PoC to enterprise scale.
Contact NowFrequently Asked Questions
- AI for Sustainability optimizes processes, reducing waste and enhancing resource efficiency.
- It facilitates real-time monitoring, leading to informed decision-making based on data.
- Sustainability initiatives improve brand reputation and customer loyalty in the automotive sector.
- The technology supports compliance with increasing regulatory standards for environmental impact.
- Ultimately, AI drives long-term profitability while addressing environmental concerns.
- Begin with assessing your current systems and identifying specific sustainability goals.
- Engage stakeholders to understand their needs and build a collaborative plan.
- Select pilot projects that demonstrate quick wins to gain organizational buy-in.
- Invest in training staff to ensure they understand AI tools and their applications.
- Evaluate results regularly to refine strategies and expand AI adoption across operations.
- AI enhances operational efficiency, leading to significant cost savings over time.
- It reduces energy consumption and waste, aligning business practices with sustainability goals.
- Companies gain a competitive edge by innovating faster and improving product quality.
- Data-driven insights enable proactive management of resources and supply chains.
- Implementing AI fosters a culture of sustainability that resonates with consumers.
- Resistance to change from employees can hinder the adoption of AI technologies.
- Data integration issues may arise when combining new AI systems with legacy systems.
- Initial costs for AI deployment can be a barrier for some organizations.
- Ensuring data privacy and security is critical to avoid compliance issues.
- Lack of expertise in AI can lead to ineffective implementation; training is essential.
- Organizations should consider AI when aiming to enhance efficiency and reduce costs.
- Implementing AI during a major operational review can provide valuable insights.
- The growing regulatory pressure for sustainability makes this a timely initiative.
- Strategic planning should align AI implementation with long-term business goals.
- Assessing market trends can signal when to adopt AI solutions for competitive advantage.
- AI can optimize supply chain logistics, reducing carbon footprints through efficiency.
- Predictive maintenance minimizes downtime and enhances equipment lifespan in plants.
- Quality control processes can leverage AI to reduce defects and minimize waste.
- Sustainability reporting can be automated, ensuring compliance with regulations.
- Energy management systems can be enhanced by AI to monitor and reduce consumption.
- Establish baseline metrics for operational efficiency and resource consumption before implementation.
- Track improvements in cost savings and productivity post-AI deployment for comparison.
- Customer satisfaction metrics can indicate the impact of sustainability on brand perception.
- Regular audits can assess compliance and sustainability impact against industry benchmarks.
- Engaging stakeholders in feedback loops ensures continuous improvement and value realization.
- Start with small, manageable projects to demonstrate quick wins and build momentum.
- Involve cross-functional teams to ensure diverse perspectives and expertise are considered.
- Maintain clear communication throughout the organization to address concerns and expectations.
- Regularly review and adapt AI strategies based on performance and evolving business needs.
- Invest in ongoing training to keep staff updated on AI advancements and applications.

