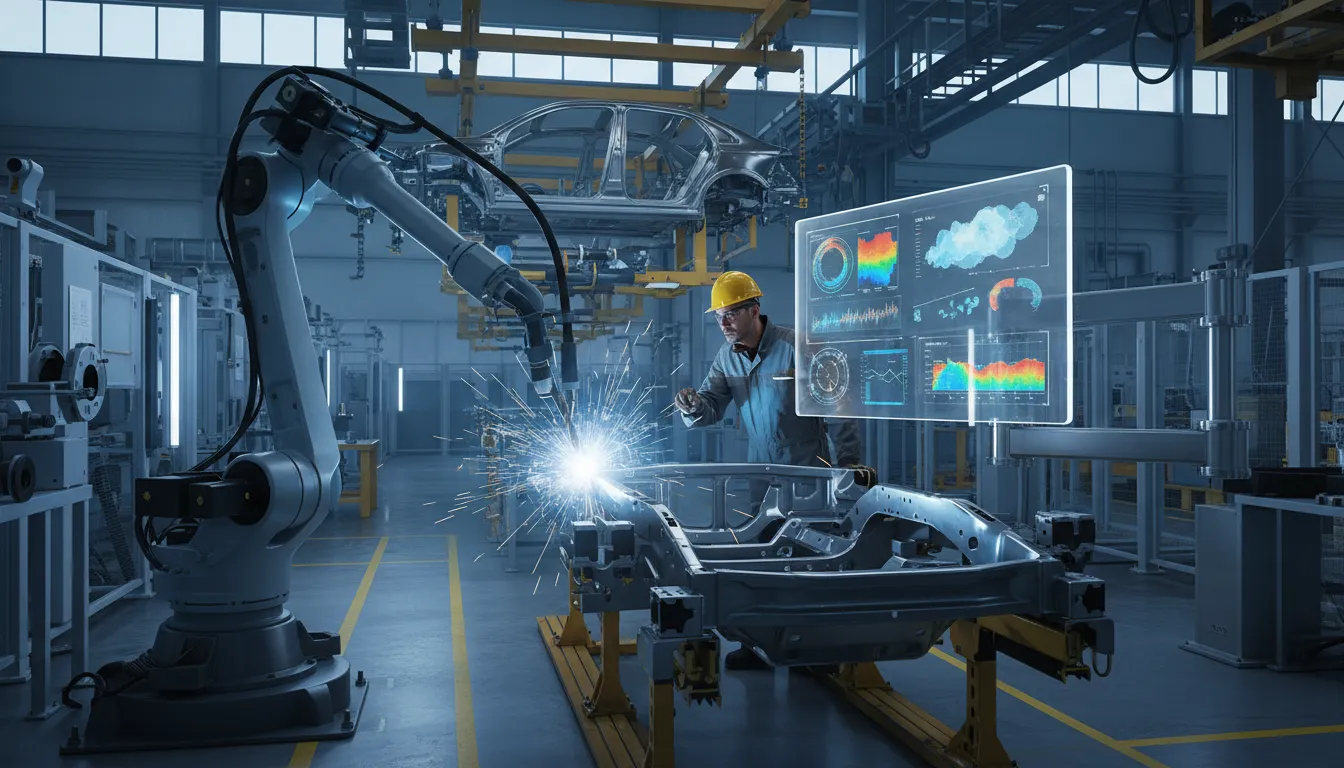
AI for Welding Defect Prediction
AI for Welding Defect Prediction represents a transformative approach within the Automotive sector, focusing on utilizing artificial intelligence to identify and mitigate welding defects during production. This core concept is crucial as it enhances quality assurance processes, ensuring that vehicles meet stringent safety and performance standards. The relevance of this technology is underscored by the ongoing shift towards automation and intelligent manufacturing practices, which are becoming essential to meet evolving consumer expectations and regulatory requirements.
The integration of AI in welding defect prediction is reshaping the Automotive landscape by driving innovation and intensifying competition among manufacturers. These AI-driven practices not only enhance operational efficiency but also enable more informed decision-making at various organizational levels. As stakeholders increasingly adopt these technologies, they encounter both significant growth opportunities and challenges, such as the complexity of integration and shifting workforce expectations. The path forward requires balancing optimism for AI's potential with a strategic approach to overcoming barriers to implementation.
Unlock AI-Driven Welding Excellence for Automotive Leaders
Automotive companies should strategically invest in partnerships with AI technology firms focused on welding defect prediction to enhance manufacturing precision and reduce costs. Implementing AI solutions is expected to significantly improve defect detection rates, driving efficiency and fostering competitive advantages in the automotive sector.
Revolutionizing Quality: The Role of AI in Welding Defect Prediction for Automotive
Implementation Framework
Begin by evaluating existing data sources to determine what additional data is needed for effective AI-driven welding defect prediction, enhancing operational efficiency and ensuring quality control in automotive manufacturing processes.
Industry Standards
Deploy machine learning algorithms that utilize historical welding data to predict potential defects, thereby enabling proactive adjustments in the production process, which reduces waste and improves product quality across automotive manufacturing.
Technology Partners
Establish real-time monitoring systems using AI to continuously analyze welding processes, allowing for immediate detection and correction of defects, which optimizes production efficiency and maintains high quality in automotive outputs.
Cloud Platform
Conduct training sessions for operational staff on AI tools and predictive analytics, ensuring that teams effectively utilize technology for welding defect predictions, fostering a culture of continuous improvement and innovation within the automotive industry.
Internal R&D
Regularly review the performance of AI systems used for welding defect prediction, analyzing data accuracy and operational impact to refine algorithms, thus ensuring continuous improvement and sustained competitive advantage in automotive manufacturing.
Industry Standards
Best Practices for Automotive Manufacturers
-
Impact : Enhances defect detection accuracy significantly
Example : Example: In an automotive assembly line, a vision-based AI system flags microscopic paint defects in real time as car bodies pass under cameras, catching flaws human inspectors previously missed during night shifts.
-
Impact : Reduces production downtime and costs
Example : Example: A semiconductor factory uses AI to detect early soldering anomalies. The system stops the line immediately, preventing a full batch failure that would have caused hours of rework and shutdown.
-
Impact : Improves quality control standards
Example : Example: A food packaging plant uses AI image recognition to verify seal integrity on every packet, ensuring non-compliant packages are rejected instantly before shipping.
-
Impact : Boosts overall operational efficiency
Example : Example: AI dynamically adjusts inspection thresholds based on production speed, allowing the factory to increase output during peak demand without sacrificing quality.
-
Impact : High initial investment for implementation
Example : Example: A mid-sized electronics manufacturer delays AI rollout after realizing camera hardware, GPUs, and system integration push upfront costs beyond budget approvals.
-
Impact : Potential data privacy concerns
Example : Example: AI quality systems capturing worker activity unintentionally store employee facial data, triggering compliance issues with internal privacy policies.
-
Impact : Integration challenges with existing systems
Example : Example: AI software cannot communicate with a 15-year-old PLC controller, forcing engineers to manually export data and slowing decision-making.
-
Impact : Dependence on continuous data quality
Example : Example: Dust accumulation on camera lenses causes the AI to misclassify normal products as defective, leading to unnecessary scrap until recalibration.
-
Impact : Facilitates immediate defect detection
Example : Example: An automotive manufacturer implements real-time AI monitoring, which instantly identifies welding defects on chassis as they occur, allowing immediate adjustments to prevent flawed assemblies from proceeding down the line.
-
Impact : Enables proactive quality management
Example : Example: A car assembly plant uses AI-driven sensors to monitor welding temperatures. This instant feedback loop helps operators adjust processes, ensuring consistent quality and reducing the risk of overheating.
-
Impact : Improves production line responsiveness
Example : Example: AI systems analyze welding processes in real-time, alerting technicians to anomalies. This proactive approach prevents defects, reducing the need for extensive post-production inspections.
-
Impact : Reduces waste and rework costs
Example : Example: By utilizing AI for instant defect identification, a manufacturer reduces scrap rates by 30%, significantly cutting costs associated with rework and waste disposal.
-
Impact : Requires extensive training for staff
Example : Example: A leading automotive firm struggles to train staff on new AI monitoring systems. Insufficient training leads to confusion, resulting in missed alerts for defects that escalate into major quality issues.
-
Impact : Potential over-reliance on technology
Example : Example: An automotive assembly line becomes overly reliant on AI, ignoring operator insights. This dependency leads to missed defects that the AI fails to detect, resulting in costly recalls.
-
Impact : Risk of false positives in detection
Example : Example: High false positive rates in AI detection cause excessive downtime as workers halt production to investigate non-existent defects, frustrating staff and leading to decreased morale.
-
Impact : Challenges in system scalability
Example : Example: As production scales, an AI system struggles to process increased data volume, leading to system slowdowns and missed defect alerts during peak production hours.
-
Impact : Enhances employee skill sets continuously
Example : Example: An automotive manufacturer invests in AI training programs for welders, resulting in a 25% improvement in defect identification accuracy, as employees learn to leverage AI tools effectively in their workflows.
-
Impact : Increases acceptance of AI solutions
Example : Example: After implementing AI systems, a company conducts regular workshops. Employee engagement increases, leading to smoother integration of AI into daily operations and higher productivity levels.
-
Impact : Improves collaboration between human and AI
Example : Example: Training sessions on AI tools help operators understand their role in the automation process, fostering a partnership that enhances defect detection capabilities and reduces errors in production.
-
Impact : Reduces resistance to technological changes
Example : Example: A structured training program leads to a 40% reduction in operator resistance to AI, significantly enhancing the overall effectiveness and acceptance of the integrated systems on the assembly line.
-
Impact : Training programs can be time-consuming
Example : Example: An automotive plant faces delays in production due to extensive AI training programs, causing temporary disruptions and impacting quarterly output targets during the transition phase.
-
Impact : Initial resistance from long-term employees
Example : Example: Long-term employees resist new AI systems, leading to friction in the workplace. This resistance delays implementation and diminishes the potential benefits of AI integration.
-
Impact : Costs associated with continuous education
Example : Example: Continuous training incurs significant costs, leading management to question the return on investment, especially when immediate improvements in defect detection are not clearly visible.
-
Impact : Difficulty measuring training effectiveness
Example : Example: A manufacturer struggles to assess the effectiveness of its training programs. Lack of measurable outcomes leads to uncertainty about whether the investment in employee education is yielding expected results.
-
Impact : Identifies potential defects before they occur
Example : Example: By leveraging predictive analytics, an automotive manufacturer predicts welding defects based on historical data, allowing adjustments to be made proactively before defects occur during production.
-
Impact : Optimizes maintenance schedules effectively
Example : Example: An automotive firm utilizes predictive maintenance analytics to schedule machine checks before predicted failures, minimizing unexpected downtime and reducing repair costs by up to 20%.
-
Impact : Enhances resource allocation and planning
Example : Example: AI-driven analytics enhances resource allocation by predicting peak production times, ensuring that the right number of technicians and systems are available, thus avoiding bottlenecks.
-
Impact : Improves overall production quality
Example : Example: Predictive analytics identifies trends in defect occurrences, allowing engineers to implement corrective measures in the welding process, resulting in a 15% increase in overall production quality.
-
Impact : Requires high-quality historical data
Example : Example: An automotive manufacturer struggles to implement predictive analytics due to insufficient historical data, resulting in unreliable predictions and ineffective quality control measures during production.
-
Impact : Potential for inaccurate predictions
Example : Example: An AI model developed for defect prediction produces inaccurate forecasts due to flawed algorithms, leading to incorrect preventive actions and increased defects in the final assembly.
-
Impact : Complexity in model development
Example : Example: Developing predictive models requires specialized expertise that the existing workforce lacks, leading to delays in implementation and additional costs for external consultants or training.
-
Impact : Can lead to overconfidence in data
Example : Example: Over-reliance on predictive analytics causes an automotive plant to overlook manual inspection processes, which results in a spike in undetected defects during a critical production run.
-
Impact : Creates continuous improvement culture
Example : Example: An automotive manufacturer integrates feedback loops into their AI systems, enabling real-time adjustments based on defect data, resulting in a 50% reduction in response time to quality issues on the assembly line.
-
Impact : Enhances system learning and adaptation
Example : Example: Monthly feedback sessions among teams discussing AI performance lead to valuable insights, which enhance the AI's learning capabilities and improve defect detection accuracy over time.
-
Impact : Improves defect resolution times
Example : Example: Establishing a feedback loop allows operators to report AI inaccuracies, which are quickly addressed. This process creates a culture of continuous improvement that benefits the entire production line.
-
Impact : Strengthens team communication and coordination
Example : Example: Feedback mechanisms improve communication between AI systems and human operators, allowing them to collaborate more effectively, thereby minimizing defects and enhancing overall productivity.
-
Impact : Requires commitment from all levels
Example : Example: An automotive plant struggles to maintain commitment to feedback loops among management, resulting in inconsistent implementation and missed opportunities for system enhancements and defect reductions.
-
Impact : Feedback processes can become cumbersome
Example : Example: Feedback collection becomes cumbersome, leading to delays in implementing necessary changes, which ultimately prolongs defect resolution times on the production line.
-
Impact : Risk of ignoring valuable insights
Example : Example: Valuable insights from operators regarding AI performance are sometimes overlooked, causing missed opportunities for improvement and resulting in persistent defects that could have been avoided.
-
Impact : May lead to analysis paralysis
Example : Example: Over-analysis of feedback data leads to confusion among teams, causing significant delays in decision-making and ultimately hindering the ability to address defects in a timely manner.
-
Impact : Ensures ongoing quality assurance
Example : Example: An automotive manufacturer implements continuous testing strategies throughout the welding process, ensuring defects are identified and resolved before large-scale production begins, significantly reducing recall rates.
-
Impact : Identifies issues before mass production
Example : Example: By integrating continuous testing into their AI systems, a company detects issues early in the production cycle, allowing teams to make iterative improvements that enhance overall quality.
-
Impact : Facilitates iterative improvements
Example : Example: Regular testing in the AI system helps identify flaws in defect detection algorithms, enabling timely adjustments that improve accuracy and reduce defects during mass production.
-
Impact : Enhances stakeholder confidence
Example : Example: Continuous testing builds stakeholder confidence by demonstrating a commitment to quality assurance, ultimately leading to increased customer satisfaction and brand loyalty.
-
Impact : Increased operational complexity
Example : Example: An automotive plant faces increased operational complexity due to continuous testing, leading to potential slowdowns in production as more resources are diverted to quality checks and validations.
-
Impact : Potential for resource strain
Example : Example: Continuous testing places a strain on existing resources, leading to delays in production schedules and increased pressure on teams to meet output targets while maintaining quality standards.
-
Impact : Requires dedicated testing personnel
Example : Example: The need for dedicated personnel for continuous testing takes away valuable resources from production roles, resulting in a temporary decline in workforce efficiency and productivity.
-
Impact : Risk of diminishing returns
Example : Example: Over time, continuous testing yields diminishing returns as the initial improvements plateau, prompting management to question the ongoing investment in such strategies.
AI is revolutionizing welding by predicting defects before they occur, transforming quality control from reactive to proactive.
– Engrity Group Inc.Compliance Case Studies



Seize the opportunity to enhance quality and efficiency in your automotive production. Leverage AI for Welding Defect Prediction and stay ahead of the competition.
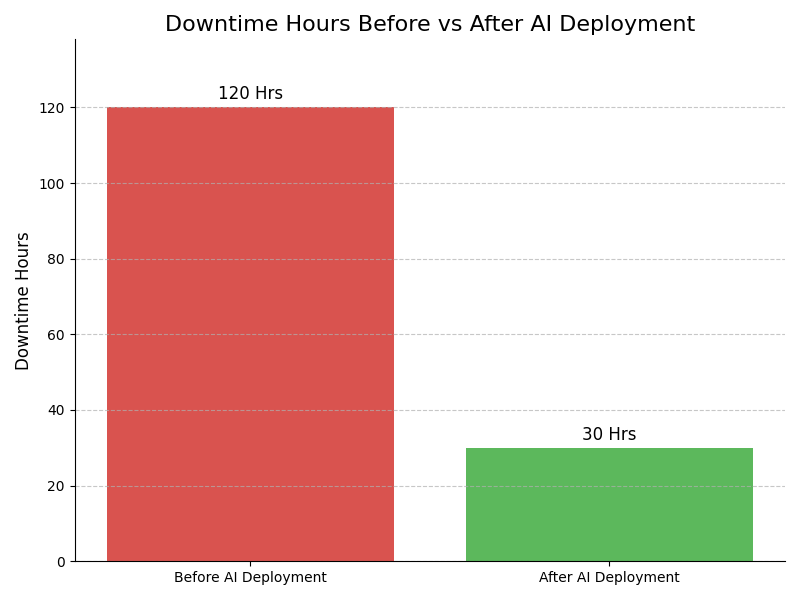
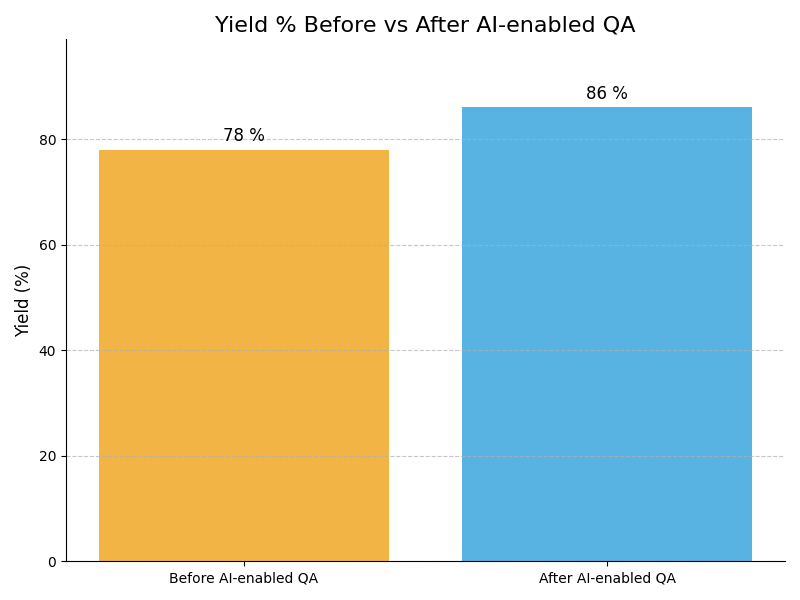
Leadership Challenges & Opportunities
Data Integration Challenges
Utilize AI for Welding Defect Prediction to streamline data integration from various sources within Automotive operations. Implement a centralized data management system with real-time analytics, enabling seamless communication between production lines and predictive maintenance, thus enhancing operational efficiency and decision-making.
Resistance to Change
Cultivate a culture of innovation by showcasing successful AI for Welding Defect Prediction implementations. Foster collaboration between teams and leadership, providing workshops to demonstrate tangible benefits. This approach encourages employee buy-in and mitigates resistance, ensuring smoother transitions to advanced predictive technologies.
High Implementation Costs
Leverage AI for Welding Defect Prediction through phased rollouts that prioritize high-impact areas within the Automotive sector. Secure funding through pilot projects that highlight immediate cost savings and efficiency gains, allowing for reinvestment into broader AI initiatives while minimizing financial risk.
Talent Acquisition Issues
Develop partnerships with educational institutions to create specialized training programs in AI and welding technologies. Use AI for Welding Defect Prediction to enhance learning outcomes with practical applications, ensuring a skilled workforce that meets industry demands while fostering internal talent development.
Assess how well your AI initiatives align with your business goals
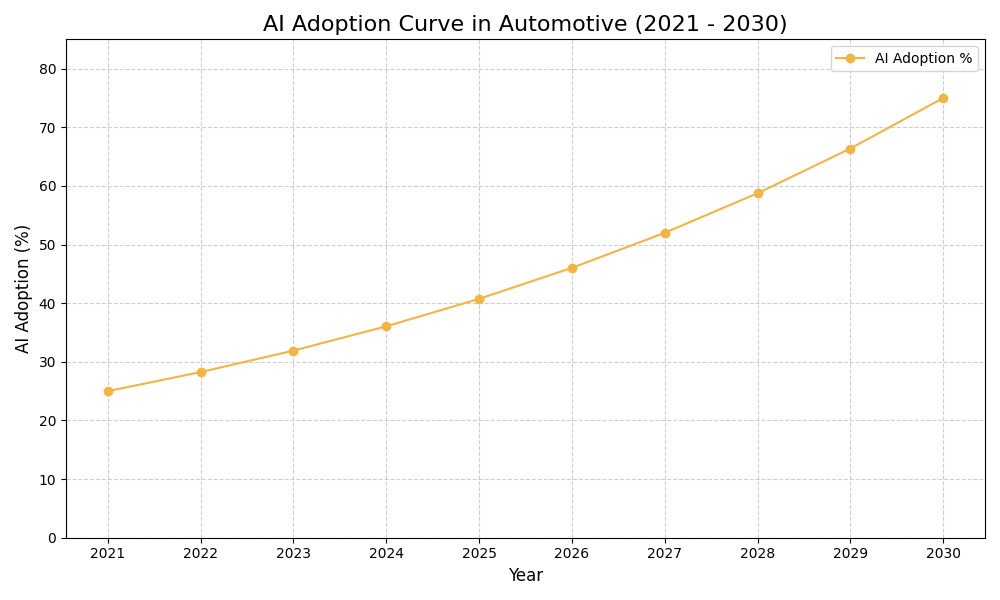
AI Use Case vs ROI Timeline
| AI Use Case | Description | Typical ROI Timeline | Expected ROI Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Predictive Maintenance for Welding Equipment | AI predicts equipment failures by analyzing real-time sensor data. For example, sensors monitoring welding machines can alert operators before a failure occurs, reducing downtime and maintenance costs significantly. | 6-12 months | High |
| Welding Quality Assurance | AI monitors welding processes to ensure quality standards. For example, computer vision systems can detect defects in real-time, allowing immediate corrective action that minimizes rework and scrap rates. | 12-18 months | Medium-High |
| Automated Defect Classification | AI classifies welding defects using image recognition. For example, an AI system can analyze images of welds and categorize defects, enabling faster decision-making and targeted improvements. | 6-12 months | Medium |
| Process Optimization through Data Analysis | AI analyzes historical welding data to optimize parameters. For example, it can recommend optimal heat settings based on past successful welds, enhancing overall production efficiency. | 12-18 months | Medium-High |
Glossary
Work with Atomic Loops to architect your AI implementation roadmap — from PoC to enterprise scale.
Contact NowFrequently Asked Questions
- AI for Welding Defect Prediction utilizes machine learning algorithms to analyze welding data.
- The technology identifies patterns that indicate potential defects in welds before they occur.
- It enhances quality control by providing real-time alerts and insights for quick action.
- This predictive capability helps reduce rework and scrap costs significantly.
- Ultimately, it fosters a culture of continuous improvement in manufacturing processes.
- Begin by assessing your current welding processes and data collection methods.
- Engage stakeholders to identify specific goals and desired outcomes for AI implementation.
- Consider partnering with AI experts to define a tailored strategy and roadmap.
- Allocate resources for necessary technology upgrades and staff training initiatives.
- Starting with pilot projects can validate the approach before full-scale deployment.
- AI can significantly enhance operational efficiency by minimizing defect rates in welding.
- It allows for more informed decision-making based on data-driven insights and analytics.
- Implementing this technology often results in cost savings through reduced waste and rework.
- Organizations leveraging AI gain a competitive edge through improved product quality and reliability.
- Ultimately, this leads to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty in the market.
- Resistance to change from employees can hinder successful AI adoption within the organization.
- Data quality issues may arise, affecting the accuracy of AI predictions and insights.
- Integration with existing systems can present technical challenges that require careful planning.
- Ensuring adequate training for staff is essential to maximize the benefits of the technology.
- Developing a clear risk mitigation strategy is vital to address potential implementation pitfalls.
- Evaluate your current operational challenges to determine if AI can address them effectively.
- Industry trends may signal an urgent need for innovation and quality improvements.
- Consider adopting AI when you have sufficient historical data for training machine learning models.
- The right timing often aligns with organizational readiness to embrace technological changes.
- Regularly reviewing performance metrics can help identify optimal moments for implementation.
- AI can monitor welding parameters in real-time to detect anomalies during production.
- It predicts potential defects based on historical data and current operational conditions.
- The technology can optimize welding process settings to enhance quality and consistency.
- AI solutions can automate reporting and compliance checks for regulatory standards.
- Ultimately, this leads to streamlined operations and improved overall production efficiency.
- Adherence to industry standards and regulations is crucial for AI implementation success.
- Ensure that AI solutions comply with safety and quality control regulations applicable to welding.
- Documented processes and transparency are essential for regulatory audits and inspections.
- Engaging with legal experts can help navigate compliance requirements effectively.
- Continuous monitoring of regulatory changes ensures ongoing alignment with industry expectations.

