AI for Worker Safety and Compliance
In the Automotive sector, "AI for Worker Safety and Compliance" encompasses the integration of artificial intelligence technologies to enhance workplace safety and ensure regulatory compliance. This approach not only focuses on mitigating risks associated with vehicle manufacturing and maintenance processes but also aligns with the industry's shifting priorities towards automation and digital transformation. By leveraging AI, organizations can proactively identify hazards, streamline compliance workflows, and foster a culture of safety that is both innovative and responsive to regulatory demands.
The impact of AI in this context is profound, as it reshapes how companies operate and compete within the Automotive ecosystem. AI-driven practices are enabling organizations to improve operational efficiency, enhance decision-making processes, and adapt to evolving safety standards. Stakeholder interactions are increasingly influenced by AI capabilities, promoting collaboration and transparency. However, while the potential for growth is significant, companies must navigate challenges such as adoption barriers, integration complexities, and shifting expectations from both employees and regulators. Addressing these challenges head-on will be crucial for realizing the full benefits of AI in enhancing worker safety and compliance.
Elevate Worker Safety with AI-Driven Solutions
Automotive companies should strategically invest in AI technologies focused on worker safety and compliance, forming partnerships with leading tech firms to harness innovative solutions. Implementing these AI strategies is expected to enhance operational efficiency, reduce workplace incidents, and create a safer environment, ultimately driving competitive advantage in the market.
How AI is Transforming Worker Safety in Automotive Manufacturing?
Implementation Framework
Conduct a thorough analysis of current worker safety and compliance systems to identify gaps. This enables targeted AI integration, enhancing overall safety measures and operational efficiency in the automotive sector.
Industry Standards
Integrate AI-driven tools for real-time safety monitoring and compliance tracking. This technology can predict potential risks, thereby enhancing worker safety and ensuring adherence to regulations in the automotive industry.
Technology Partners
Develop comprehensive training programs for employees on new AI tools and compliance protocols. Educating the workforce ensures effective utilization of AI technology, promoting a culture of safety and compliance throughout the organization.
Internal R&D
Establish metrics to monitor the performance of AI safety tools and compliance processes, allowing for ongoing evaluation and adjustments. This ensures continuous improvement and alignment with safety objectives in the automotive industry.
Industry Standards
Utilize advanced data analytics to interpret safety data collected by AI systems. This provides actionable insights, enabling proactive measures to prevent incidents and optimize compliance within automotive operations.
Cloud Platform
Best Practices for Automotive Manufacturers
-
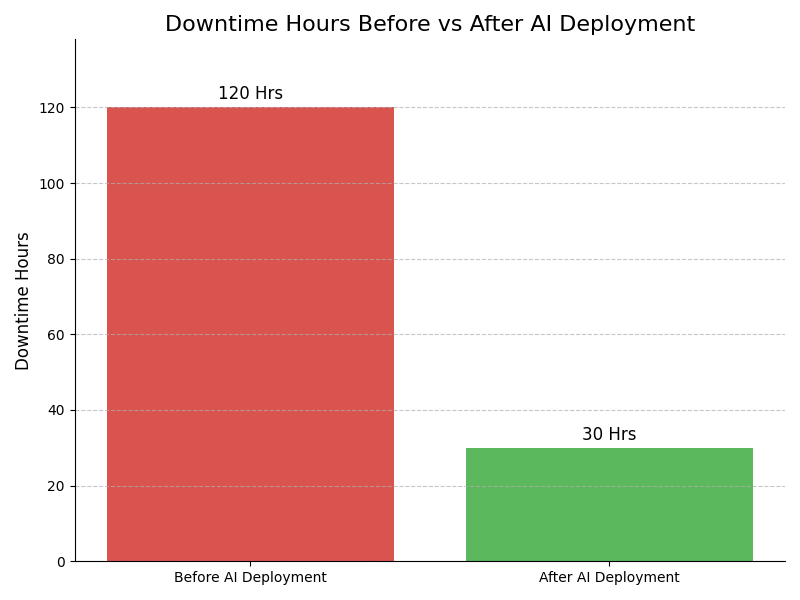
Impact : Reduces workplace accidents significantly
Example : Example: A major automotive manufacturer leverages predictive analytics to foresee potential safety hazards, reducing workplace accidents by 30% over two years, and fostering a culture of safety awareness among employees.
-
Impact : Improves compliance with safety regulations
Example : Example: By analyzing historical incident data, a car assembly plant ensures compliance with safety regulations, achieving a 95% adherence rate during audits, which positively impacts insurance premiums.
-
Impact : Enhances operational efficiency and productivity
Example : Example: Predictive analytics in a vehicle assembly line identifies patterns leading to machinery failures, enhancing productivity by reducing downtime by 20%, allowing for smoother operations.
-
Impact : Promotes proactive safety culture among workers
Example : Example: An automotive supplier utilizes predictive tools to forecast safety issues, leading to a proactive safety culture that has resulted in a 40% decrease in near-miss incidents.
-
Impact : Requires skilled personnel for analytics interpretation
Example : Example: A leading car manufacturer struggles to interpret complex predictive analytics data, causing delays in safety improvements and misallocating resources to non-critical safety issues, impacting overall operational efficiency.
-
Impact : Potential over-reliance on predictive models
Example : Example: A plant overly relies on predictive models, neglecting manual safety checks, which leads to a workplace accident that could have been prevented, ultimately damaging the company's safety reputation.
-
Impact : Integration may disrupt existing workflows
Example : Example: Integrating predictive analytics disrupts existing workflows at an automotive assembly plant, causing confusion among staff and temporary drops in productivity as employees adapt to the new system.
-
Impact : Data inaccuracies can lead to false predictions
Example : Example: Inaccurate data inputs into predictive models at a large auto supplier lead to false predictions, resulting in unnecessary safety measures that waste resources and frustrate employees.
-
Impact : Enhances immediate response to hazards
Example : Example: A leading automotive plant uses real-time monitoring systems to detect gas leaks instantly, allowing for immediate evacuation and reducing potential exposure, enhancing worker safety.
-
Impact : Improves safety compliance tracking
Example : Example: Real-time compliance tracking in a vehicle manufacturing facility enables managers to address safety issues immediately, achieving a compliance rate of 98% during inspections and reducing penalties.
-
Impact : Increases worker engagement in safety
Example : Example: Workers at an automotive assembly line engage with real-time safety dashboards, leading to a 25% increase in reported safety concerns, fostering a more aware and proactive culture.
-
Impact : Facilitates rapid data-driven decisions
Example : Example: AI-driven monitoring allows managers at a major automotive factory to make rapid decisions regarding equipment failures, significantly reducing downtime and enhancing safety protocols on the floor.
-
Impact : High costs for advanced monitoring systems
Example : Example: A well-known automotive company faces budget overruns when implementing advanced real-time monitoring systems, leading to a temporary halt in production while financial issues are resolved.
-
Impact : Potential technical glitches during operation
Example : Example: A new monitoring system at an assembly line experiences technical glitches, leading to false alarms that disrupt operations and create confusion among workers, impacting morale.
-
Impact : Requires robust IT support and maintenance
Example : Example: An automotive plant's real-time monitoring system requires ongoing IT support, straining resources and leading to delays in addressing urgent safety issues due to maintenance backlog.
-
Impact : Worker resistance to new monitoring technologies
Example : Example: Employees resist new monitoring technologies believing they infringe on privacy, leading to decreased morale and reluctance to fully engage with the safety protocols aimed at protecting them.
-
Impact : Boosts employee confidence in safety protocols
Example : Example: A global automotive manufacturer implements quarterly training sessions on AI safety protocols, resulting in a 60% reduction in human errors over six months, significantly improving workplace safety.
-
Impact : Enhances knowledge of AI systems
Example : Example: Regular training increases employees' confidence in using AI systems for safety checks, leading to a 30% rise in accurate hazard reporting on the factory floor.
-
Impact : Reduces human error in operations
Example : Example: An automotive plant enhances knowledge of AI systems through frequent workshops, empowering workers to utilize technology better, resulting in a noticeable decline in safety incidents.
-
Impact : Strengthens safety communication channels
Example : Example: Strengthening communication channels through training at a car manufacturing facility leads to clearer safety guidelines and a 40% increase in safety reporting among staff.
-
Impact : Training sessions can be time-consuming
Example : Example: A busy automotive assembly line struggles with time management, causing training sessions to be postponed frequently, ultimately leading to safety protocol gaps and increased incidents.
-
Impact : Inconsistent engagement from employees
Example : Example: An automotive plant experiences inconsistent engagement during training sessions, resulting in a divide between informed and uninformed employees, which compromises overall safety effectiveness.
-
Impact : Potential for misinformation during sessions
Example : Example: Miscommunication during training leads to misinformation about safety protocols, causing confusion among employees and increasing the risk of accidents on the production floor.
-
Impact : Costs associated with training materials
Example : Example: High costs associated with training materials for new AI safety systems strain the budget of a mid-sized automotive manufacturer, delaying necessary updates and improvements to safety measures.
-
Impact : Improves hazard detection capabilities
Example : Example: Implementing AI-driven safety tools in a car manufacturing plant leads to a 50% improvement in hazard detection capabilities, allowing for quicker responses to potential safety threats and reducing incidents.
-
Impact : Enhances compliance with regulations
Example : Example: An automotive company adopts AI safety tools, achieving 100% compliance with safety regulations during their audits, which lowers insurance costs and mitigates risks associated with violations.
-
Impact : Reduces costs related to accidents
Example : Example: AI-driven tools help an automotive assembly line reduce costs related to accidents by 40%, allowing resources to be reallocated toward innovation and development.
-
Impact : Increases overall productivity levels
Example : Example: The integration of AI safety tools increases productivity levels by minimizing downtime related to safety incidents, resulting in a 20% boost in output within the first year.
-
Impact : High initial implementation costs
Example : Example: A large automotive manufacturer faces high initial costs when implementing AI-driven safety tools, leading to a delay in deployment as the finance department seeks budget approvals.
-
Impact : Potential for over-reliance on AI
Example : Example: Over-reliance on AI tools in an assembly plant leads to complacency among workers, resulting in missed manual safety checks and incidents that could have been avoided.
-
Impact : Integration with legacy systems can falter
Example : Example: Legacy systems struggle to integrate with new AI-driven safety tools, causing disruptions in operations and requiring additional resources to resolve technical issues in the automotive plant.
-
Impact : Requires continuous updates and training
Example : Example: Continuous updates and training for AI systems at a vehicle manufacturing plant strain resources, causing delays in the implementation of necessary safety improvements.
-
Impact : Enhances safety reporting accuracy
Example : Example: An automotive company implements feedback mechanisms for safety reporting, resulting in a 40% increase in accurate incident reporting and fostering a culture of transparency and accountability.
-
Impact : Fosters a culture of continuous improvement
Example : Example: By incorporating employee feedback, a vehicle manufacturer fosters a culture of continuous improvement, leading to the successful implementation of new safety measures that reduce incidents by 30%.
-
Impact : Encourages employee participation in safety
Example : Example: Encouraging employee participation in safety discussions at an automotive plant results in innovative solutions, boosting overall safety compliance and engagement among workers.
-
Impact : Improves decision-making processes
Example : Example: Feedback mechanisms improve decision-making processes by allowing management at an automotive factory to quickly address safety concerns, resulting in a safer work environment and increased productivity.
-
Impact : Feedback may be ignored by management
Example : Example: Management at an automotive facility occasionally ignores feedback from employees, leading to unresolved safety concerns and a growing sense of frustration amongst staff regarding safety protocols.
-
Impact : Potential for biased reporting
Example : Example: Employees at a car manufacturing plant report biased safety concerns, leading to misallocated resources and a failure to address real hazards, putting workers at risk.
-
Impact : Requires ongoing evaluation and adjustment
Example : Example: Ongoing evaluation of feedback mechanisms at an automotive company requires constant adjustments, which can lead to resource strain and delays in implementing effective safety measures.
-
Impact : Employee fatigue from constant surveys
Example : Example: Constant safety surveys fatigue employees in a vehicle assembly line, leading to reduced participation and inaccurate reporting, ultimately undermining safety improvement efforts.
AI will surpass the seatbelt in vehicle safety, fundamentally transforming how we protect workers and ensure compliance in the automotive industry.
– Internal R&DCompliance Case Studies




Embrace AI solutions to enhance worker safety and compliance in your automotive operations. Stay ahead of the competition and drive transformative results now!

Leadership Challenges & Opportunities
Legacy Data Integration
Implement AI for Worker Safety and Compliance by utilizing data lakes to consolidate legacy information from various Automotive systems. Use machine learning algorithms to cleanse and analyze this data, enabling predictive analytics for safety measures and compliance, thus enhancing decision-making accuracy.
Cultural Resistance to Change
Employ change management strategies alongside AI for Worker Safety and Compliance adoption. Foster a culture of safety by involving employees in the implementation process, using AI-driven insights to demonstrate benefits, and providing training that highlights improved safety measures and compliance.
Cost of Implementation
Utilize AI for Worker Safety and Compliance through phased implementation strategies that focus on high-impact areas first. Leverage cloud solutions to reduce upfront costs and use data-driven insights to justify investments by demonstrating ROI through decreased incident rates and improved compliance.
Evolving Regulatory Landscape
Leverage AI for Worker Safety and Compliance to automate tracking of regulatory changes in the Automotive industry. Implement AI systems that provide real-time alerts and updates, ensuring compliance processes adapt swiftly, thus minimizing risk and maintaining operational integrity.
Assess how well your AI initiatives align with your business goals
AI Use Case vs ROI Timeline
| AI Use Case | Description | Typical ROI Timeline | Expected ROI Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Predictive Maintenance Alerts | AI systems analyze equipment data to predict failures before they occur. For example, sensors on production lines alert managers about potential machinery issues, enabling proactive maintenance that minimizes downtime and enhances worker safety. | 6-12 months | High |
| Real-Time Hazard Detection | AI-powered cameras monitor work environments for potential hazards and alert workers immediately. For example, in an automotive assembly plant, cameras detect spills and notify staff to prevent accidents, ensuring compliance with safety regulations. | 12-18 months | Medium-High |
| Automated Safety Training | AI platforms deliver personalized training modules based on worker performance and safety records. For example, a virtual reality training program simulates hazardous situations in an automotive factory, improving employee preparedness and safety compliance. | 6-9 months | Medium |
| Incident Reporting Automation | AI tools streamline the incident reporting process by using natural language processing to categorize and log reports. For example, workers can verbally report incidents through an app, which automatically organizes data for compliance audits. | 6-12 months | Medium-High |
Glossary
Work with Atomic Loops to architect your AI implementation roadmap — from PoC to enterprise scale.
Contact NowFrequently Asked Questions
- AI for Worker Safety and Compliance leverages advanced technologies to enhance workplace safety.
- It automates safety monitoring through real-time data analysis and risk assessment.
- Organizations can predict potential hazards, minimizing incidents and improving compliance.
- The technology integrates seamlessly with existing safety protocols and systems.
- Overall, it fosters a proactive safety culture within automotive organizations.
- Begin with a comprehensive assessment of current safety processes and needs.
- Identify key areas where AI can drive improvements and reduce risks.
- Allocate necessary resources and establish a dedicated implementation team.
- Pilot projects can help validate approaches before full-scale implementation.
- Ensure ongoing training and support for staff to maximize AI usage.
- AI-driven solutions lead to a significant reduction in workplace accidents and injuries.
- Organizations can see improved compliance with safety regulations and standards.
- Enhanced data analytics provide actionable insights for continuous improvement.
- Cost savings result from reduced downtime and lower insurance premiums.
- AI fosters a culture of safety that can enhance employee morale and retention.
- Resistance to change from employees can hinder successful implementation efforts.
- Integration with legacy systems may pose technical challenges and delays.
- Data quality and availability are crucial for effective AI-driven solutions.
- Training staff on new technologies is essential for maximizing benefits.
- Establishing clear communication can mitigate misunderstandings and build trust.
- Evaluate your current safety performance and identify gaps requiring attention.
- Adopting AI is timely when facing increased regulatory scrutiny or compliance pressures.
- Organizations should consider AI when seeking to enhance operational efficiency.
- Early adoption can provide a competitive edge in safety management.
- Regularly review technological advancements to stay ahead in safety innovations.
- AI can enhance ergonomics by analyzing worker movements and suggesting improvements.
- Predictive maintenance powered by AI can reduce equipment-related accidents.
- Automated monitoring systems help track compliance in real-time across production lines.
- AI-driven simulations can train employees on safety protocols effectively.
- Customization of AI tools is essential to meet specific automotive safety needs.
- Ensuring data privacy and security is paramount when implementing AI solutions.
- Regulatory compliance must be maintained throughout the AI implementation process.
- Organizations should regularly audit AI systems to ensure ongoing compliance.
- Documentation of AI decisions is crucial for transparency and accountability.
- Engagement with legal and compliance teams can strengthen AI initiatives.
- Establish clear objectives and KPIs to guide the implementation process.
- Involve cross-functional teams to gain diverse perspectives and buy-in.
- Focus on continuous training and support to enhance user adoption.
- Regularly review and refine AI tools based on performance feedback.
- Maintain open communication throughout the organization to foster collaboration.

