AI in Ergonomics and Worker Efficiency
AI in Ergonomics and Worker Efficiency represents a pivotal intersection of technology and human-centered design within the Automotive sector. This concept encompasses the integration of artificial intelligence to enhance worker productivity, safety, and overall ergonomic practices. As the industry grapples with evolving operational priorities, the relevance of this approach is underscored by the need for innovative solutions that streamline processes and enhance worker satisfaction. By leveraging AI, stakeholders can foster environments that prioritize both efficiency and employee well-being.
The Automotive ecosystem is increasingly recognizing the transformative role of AI in reshaping ergonomics and worker efficiency. As organizations adopt these AI-driven practices, competitive dynamics shift, leading to accelerated innovation cycles and improved stakeholder collaboration. The influence of AI extends beyond mere operational enhancements; it equips decision-makers with actionable insights that can redefine long-term strategic directions. However, while the growth opportunities are significant, challenges such as integration complexity and evolving expectations must be navigated to fully realize the potential of this transformation.
Unlock AI Potential for Ergonomics and Worker Efficiency in Automotive
Automotive companies should strategically invest in AI technologies that enhance ergonomics and worker efficiency while forming partnerships with leading tech firms to harness innovative solutions. Implementing AI-driven strategies is expected to boost productivity, reduce workplace injuries, and create a safer environment, ultimately delivering significant ROI and competitive advantages.
How AI Transforms Ergonomics and Worker Efficiency in Automotive?
Implementation Framework
Conduct a thorough assessment of existing ergonomic practices, identifying areas for improvement. This analysis helps integrate AI solutions effectively, enhancing worker comfort and productivity while reducing injury risk, ultimately improving operational efficiency.
Internal R&D
Implement AI systems that monitor worker movements and provide real-time feedback to enhance ergonomic practices. This integration optimizes workflows, reduces fatigue, and increases overall worker efficiency and satisfaction within automotive operations.
Technology Partners
Develop training programs to educate employees about AI-driven ergonomic tools and their benefits. This knowledge empowers workers to utilize technology effectively, fostering a culture of safety and efficiency in automotive operations.
Industry Standards
Utilize AI analytics to continuously monitor the effectiveness of ergonomic interventions. This data-driven approach allows for timely adjustments, ensuring sustained improvements in worker efficiency and safety within the automotive sector.
Cloud Platform
Regularly evaluate the impact of AI solutions on worker ergonomics and efficiency. Gather feedback to refine strategies, ensuring continuous improvement and alignment with business goals while enhancing overall operational resilience.
Consulting Firms
Best Practices for Automotive Manufacturers
-
Impact : Enhances defect detection accuracy significantly
Example : Example: In an automotive assembly line, a vision-based AI system flags microscopic paint defects in real time as car bodies pass under cameras, catching flaws human inspectors previously missed during night shifts.
-
Impact : Reduces production downtime and costs
Example : Example: A semiconductor factory uses AI to detect early soldering anomalies. The system stops the line immediately, preventing a full batch failure that would have caused hours of rework and shutdown.
-
Impact : Improves quality control standards
Example : Example: A food packaging plant uses AI image recognition to verify seal integrity on every packet, ensuring non-compliant packages are rejected instantly before shipping.
-
Impact : Boosts overall operational efficiency
Example : Example: AI dynamically adjusts inspection thresholds based on production speed, allowing the factory to increase output during peak demand without sacrificing quality.
-
Impact : High initial investment for implementation
Example : Example: A mid-sized electronics manufacturer delays AI rollout after realizing camera hardware, GPUs, and system integration push upfront costs beyond budget approvals.
-
Impact : Potential data privacy concerns
Example : Example: AI quality systems capturing worker activity unintentionally store employee facial data, triggering compliance issues with internal privacy policies.
-
Impact : Integration challenges with existing systems
Example : Example: AI software cannot communicate with a 15-year-old PLC controller, forcing engineers to manually export data and slowing decision-making.
-
Impact : Dependence on continuous data quality
Example : Example: Dust accumulation on camera lenses causes the AI to misclassify normal products as defective, leading to unnecessary scrap until recalibration.
-
Impact : Enhances proactive maintenance scheduling
Example : Example: An automotive manufacturer employs AI to monitor machinery vibrations in real-time, enabling predictive maintenance that reduces unexpected breakdowns by 30% and minimizes production halts.
-
Impact : Improves worker safety and ergonomics
Example : Example: By integrating wearable AI technology, workers receive real-time feedback on posture, reducing fatigue-related injuries on the assembly line by 25%.
-
Impact : Increases productivity through data insights
Example : Example: Real-time monitoring of assembly speed and output helps management identify bottlenecks, leading to a 15% increase in productivity within a quarter.
-
Impact : Reduces overall operational costs
Example : Example: AI analyzes energy consumption patterns, allowing the plant to optimize machine schedules, resulting in a 20% reduction in energy costs.
-
Impact : Possible resistance from workforce
Example : Example: An automotive firm faces pushback from workers reluctant to adopt AI monitoring systems, fearing job loss, which delays implementation and hampers productivity.
-
Impact : Over-reliance on data analytics
Example : Example: A factory becomes overly reliant on AI for decision-making, leading to a failure to notice human errors, resulting in a costly production mishap.
-
Impact : Inaccurate data leading to wrong decisions
Example : Example: An AI system misinterprets sensor data due to calibration issues, leading management to make incorrect operational adjustments that disrupt workflow.
-
Impact : System failures causing operational delays
Example : Example: A critical software update leads to unexpected system downtime, causing a halt in operations and resulting in significant financial losses for the automotive plant.
-
Impact : Enhances employee engagement and morale
Example : Example: An automotive company regularly trains its workforce on AI tools, significantly boosting employee morale, as they feel equipped to handle new technologies with confidence.
-
Impact : Improves adaptability to new technologies
Example : Example: A plant implements a monthly training program that helps workers adapt quickly to new AI-driven processes, decreasing the learning curve by 40%.
-
Impact : Reduces training costs in the long run
Example : Example: Continuous training reduces the need for extensive onboarding sessions for new hires, saving the company 20% in training expenditures annually.
-
Impact : Increases overall production efficiency
Example : Example: Well-trained employees using AI tools increase production efficiency by 15%, allowing the company to meet rising market demands seamlessly.
-
Impact : Training may require significant time investment
Example : Example: A manufacturer allocates significant resources for AI training, but lengthy sessions disrupt production schedules, causing frustration among staff and management alike.
-
Impact : Potential for skill gaps among older workers
Example : Example: Older employees struggle with new AI tools, leading to skill gaps that affect overall productivity, prompting management to seek additional support.
-
Impact : Keeping training materials updated is challenging
Example : Example: Rapid advancements in AI technologies make it hard for training materials to stay current, causing discrepancies in knowledge among employees.
-
Impact : High turnover rates can affect training efficacy
Example : Example: High turnover rates result in frequent retraining needs, which increase costs and disrupt workflow as new employees need to be brought up to speed.
-
Impact : Reduces design cycle time significantly
Example : Example: An automotive company utilizes AI algorithms to simulate design variations, cutting the design cycle time by 40%, allowing faster product launches.
-
Impact : Enhances product ergonomics and usability
Example : Example: AI analyzes user feedback on vehicle ergonomics, leading to design changes that improve driver comfort ratings by 30% in new models.
-
Impact : Improves material efficiency and sustainability
Example : Example: By optimizing material use through AI simulations, a manufacturer reduces waste by 25%, aligning with sustainability goals while cutting costs.
-
Impact : Increases competitive advantage through innovation
Example : Example: Innovative AI-driven designs give the company a competitive edge, leading to a 15% increase in market share within the first year of launch.
-
Impact : Potential for design flaws if miscalibrated
Example : Example: An AI design optimization tool overlooks a critical safety feature, leading to product recalls that damage the brand's reputation and increase costs.
-
Impact : High dependency on accurate data input
Example : Example: A company realizes that inaccurate data inputs result in flawed designs, causing increased iterations and delays in time-to-market.
-
Impact : Resistance from traditional design teams
Example : Example: Traditional designers resist adapting to AI tools, fearing loss of creative control, which slows down the design process significantly.
-
Impact : Longer lead times for AI integration
Example : Example: Integrating AI tools into the design process takes longer than anticipated, causing delays that push back product launch schedules and impact revenue.
-
Impact : Enhances continuous improvement initiatives
Example : Example: An automotive plant implements feedback loops, allowing employees to report inefficiencies. This initiative boosts operational improvements, enhancing productivity by 20% within six months.
-
Impact : Boosts employee accountability and ownership
Example : Example: Regular feedback sessions empower workers to take ownership of processes, resulting in higher job satisfaction and a 15% decrease in staff turnover rates.
-
Impact : Increases customer satisfaction levels
Example : Example: Customer feedback integrated into production cycles leads to improved vehicle features, increasing satisfaction ratings by 25% and enhancing brand loyalty.
-
Impact : Improves product quality over time
Example : Example: Continuous product quality assessments through feedback loops result in a 30% reduction in defects, significantly improving market reputation.
-
Impact : Feedback may be ignored or undervalued
Example : Example: An automotive firm introduces feedback loops but finds that management often overlooks suggestions, leading to employee frustration and disengagement.
-
Impact : Requires ongoing commitment from leadership
Example : Example: Leadership fails to consistently participate in feedback sessions, resulting in a lack of direction and commitment to improvements within the team.
-
Impact : Can lead to information overload
Example : Example: The volume of feedback becomes overwhelming, leading to confusion and inaction as employees struggle to prioritize suggestions effectively.
-
Impact : Potential for conflicts among team members
Example : Example: Conflicting feedback from team members creates tension, resulting in stalled projects and inability to make timely improvements in processes.
-
Impact : Enhances worker comfort and productivity
Example : Example: An automotive assembly line integrates AI-driven ergonomics tools that adjust workstations in real-time based on individual worker preferences, enhancing comfort and productivity by 15%.
-
Impact : Reduces ergonomic-related injuries
Example : Example: AI analytics identify common ergonomic issues, leading to redesigns that reduce workplace injuries by 30%, significantly lowering healthcare costs for the company.
-
Impact : Improves employee retention rates
Example : Example: By focusing on ergonomic improvements, a plant sees an increase in employee retention rates by 20%, as workers feel valued and supported.
-
Impact : Optimizes workspace layouts effectively
Example : Example: AI optimizes workspace layouts based on workflow data, reducing unnecessary movements and increasing operational efficiency by 10%.
-
Impact : High setup costs for ergonomic assessments
Example : Example: An automotive company faces high costs when initially implementing AI-driven ergonomic assessments, impacting budget allocations for other projects.
-
Impact : Resistance to changes from workforce
Example : Example: Workers express resistance to changes in workstation layouts suggested by AI, leading to delays in implementation and frustration among management.
-
Impact : Potential for misinterpreted data
Example : Example: Misinterpretation of ergonomic data by AI tools results in ineffective adjustments to workstations that fail to improve comfort or productivity.
-
Impact : Need for continual adjustments over time
Example : Example: Continuous adjustments based on ergonomic data require ongoing investments in technology and training, straining operational budgets and resources.
AI is revolutionizing ergonomics in the automotive industry, enhancing worker efficiency and safety through intelligent design and real-time feedback.
– Megan LampinenCompliance Case Studies
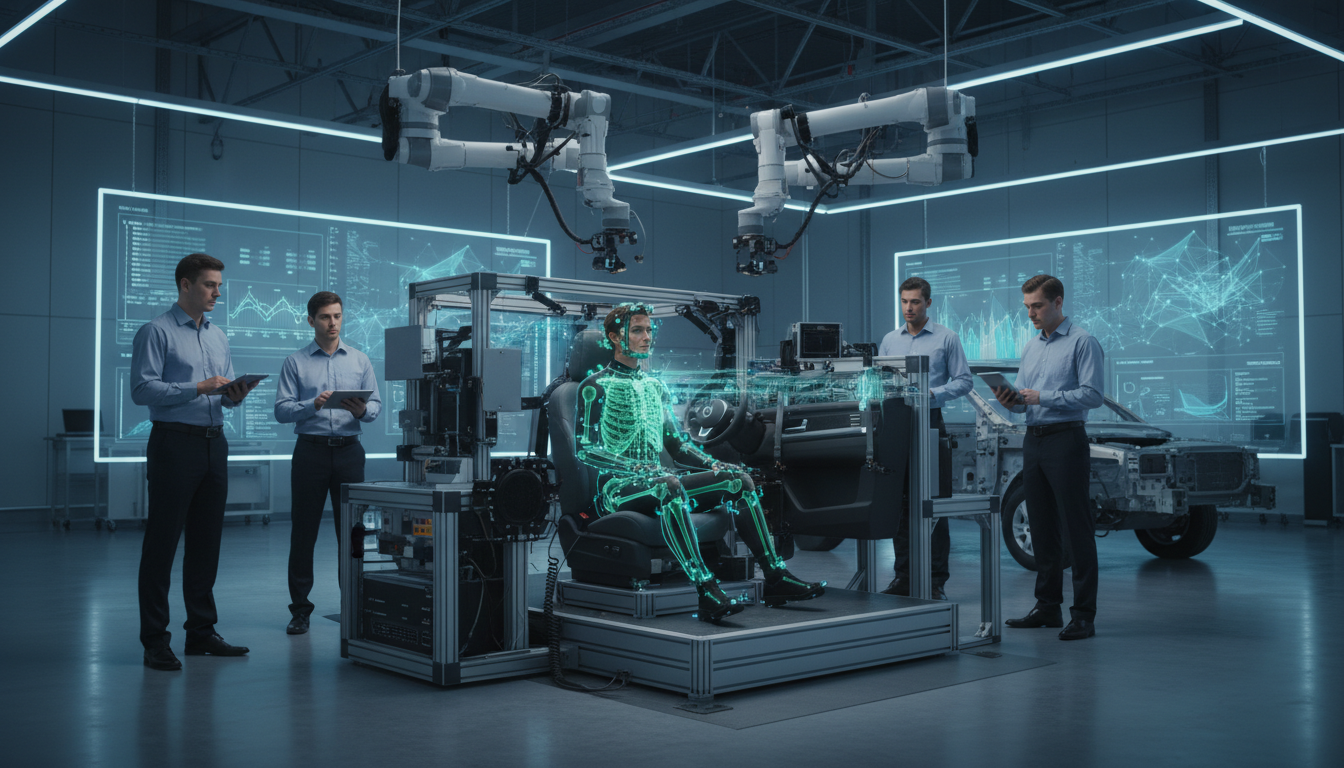




Embrace AI-driven ergonomics to enhance productivity and ensure worker safety. Stay ahead of the competition and unlock unprecedented operational excellence in the automotive industry.
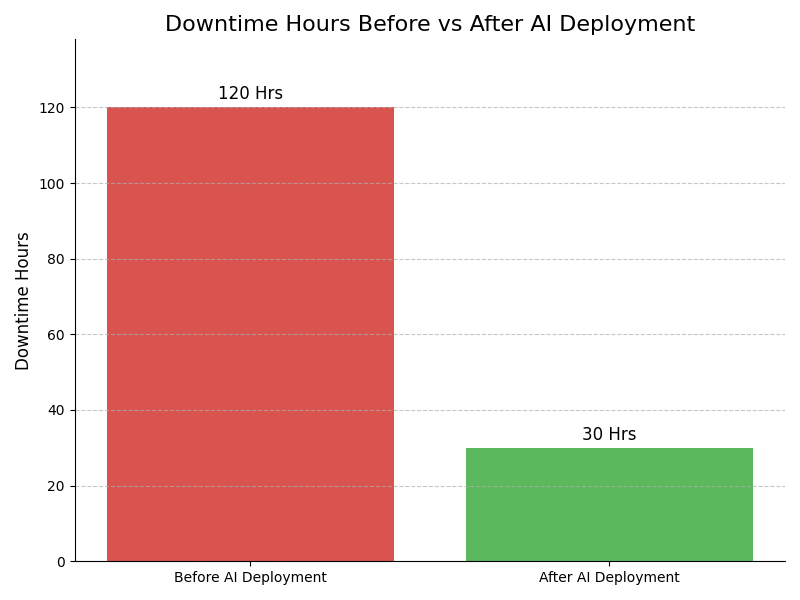
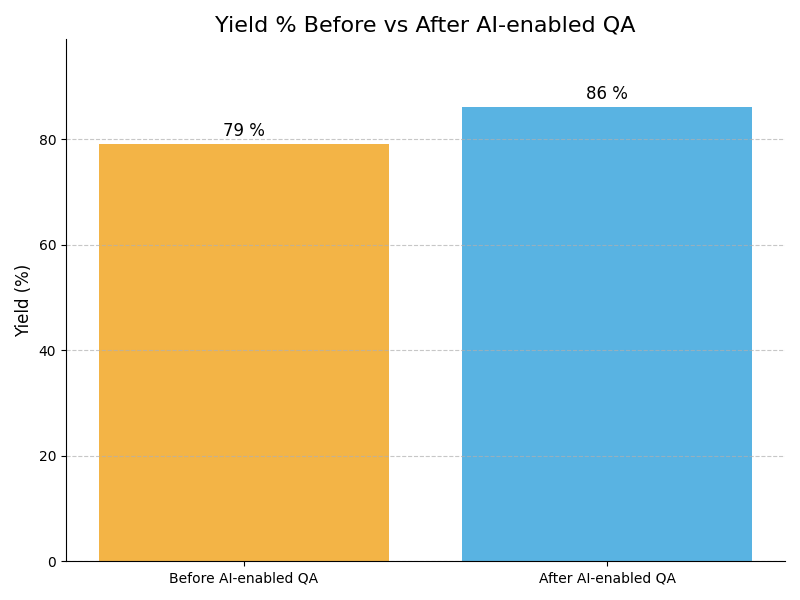
Leadership Challenges & Opportunities
Data Integration Challenges
Utilize AI in Ergonomics and Worker Efficiency to create interoperable data systems that aggregate information from various sources. Implement cloud-based platforms that facilitate real-time data sharing and analytics, enhancing decision-making and operational efficiency across the Automotive supply chain.
Resistance to Change
Foster an adaptive culture by integrating AI in Ergonomics and Worker Efficiency with change management strategies. Conduct workshops that demonstrate the benefits of AI tools, engage employees in feedback loops, and create champions within teams to facilitate a smoother transition to AI-driven workflows.
High Implementation Costs
Leverage AI in Ergonomics and Worker Efficiency with phased rollouts and pilot projects focusing on high-impact areas. This approach allows for gradual investment, demonstrating ROI early on, and securing further funding for broader deployment, making the transition financially manageable.
Compliance with Safety Standards
Integrate AI in Ergonomics and Worker Efficiency to automate compliance checks and enhance safety protocols in Automotive operations. Implement real-time monitoring systems that ensure adherence to safety regulations, reducing risks and improving worker safety through proactive data analytics and reporting.
Assess how well your AI initiatives align with your business goals
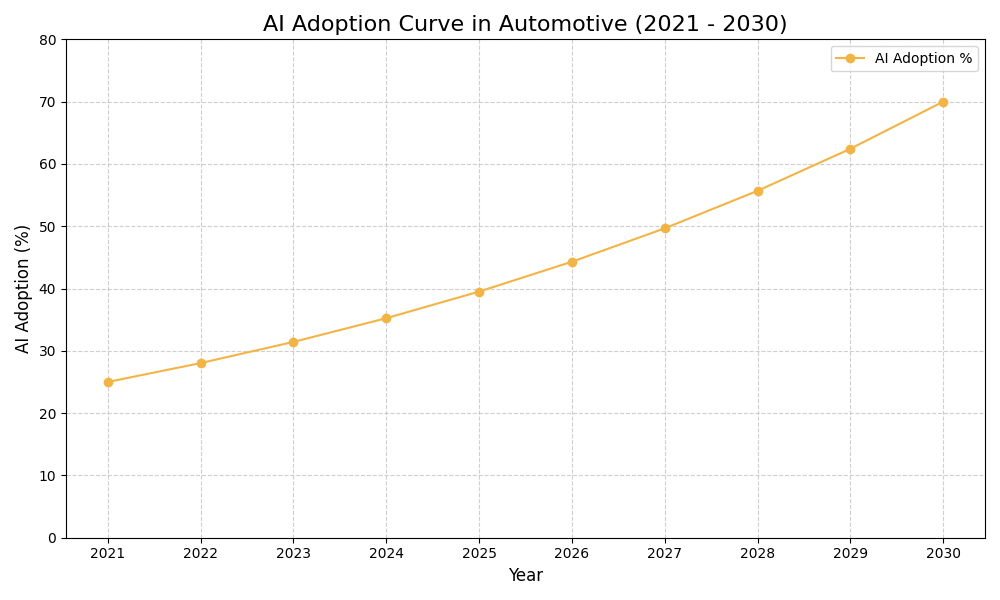
AI Use Case vs ROI Timeline
| AI Use Case | Description | Typical ROI Timeline | Expected ROI Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smart Workstation Design | AI analyzes employee movements and work patterns to optimize workstation layouts. For example, automotive assembly lines use AI to redesign stations, reducing unnecessary movements and increasing efficiency by 15%. | 6-12 months | High |
| Real-Time Ergonomic Feedback | Wearable devices equipped with AI provide real-time feedback on posture and movements. For example, factory workers receive alerts on posture adjustments, leading to a 20% reduction in musculoskeletal disorders. | 12-18 months | Medium-High |
| AI-Powered Training Simulations | AI creates personalized training programs based on worker performance data. For example, in automotive manufacturing, workers engage in virtual simulations that enhance their skills and reduce error rates by 25%. | 6-12 months | Medium-High |
| Predictive Maintenance for Ergonomics | AI predicts equipment failures that impact worker efficiency. For example, in automotive plants, predictive models alert maintenance teams before breakdowns occur, ensuring uninterrupted workflows and reducing downtime by 30%. | 12-18 months | High |
Glossary
Work with Atomic Loops to architect your AI implementation roadmap — from PoC to enterprise scale.
Contact NowFrequently Asked Questions
- AI leverages data analytics to enhance workplace ergonomics and productivity.
- It identifies potential hazards and optimizes workstations for better employee comfort.
- This technology can lead to reduced injury rates and increased worker satisfaction.
- By streamlining processes, AI improves overall operational efficiency in automotive settings.
- The implementation supports data-driven decisions, resulting in better resource allocation.
- Begin by assessing current ergonomics practices and identifying areas for improvement.
- Engage stakeholders to align on objectives and gather insights about existing challenges.
- Select an AI solution that integrates seamlessly with your current systems and processes.
- Start with pilot projects to validate technology effectiveness before full-scale implementation.
- Monitor results closely to ensure continuous improvement and refine your approach.
- AI can enhance productivity by automating repetitive tasks and reducing downtime.
- Improved ergonomics lead to fewer workplace injuries, minimizing healthcare costs.
- Organizations may experience higher employee morale and retention rates as a result.
- Data-driven insights provide a clearer understanding of operational efficiency metrics.
- These factors contribute to a stronger competitive position in the automotive market.
- Resistance to change from employees can hinder AI adoption efforts significantly.
- Integration with legacy systems may pose technical challenges and require additional resources.
- Data privacy and security concerns must be addressed to build trust among users.
- Lack of training can result in underutilization of AI tools and missed opportunities.
- Establishing clear goals helps mitigate these challenges and guides successful implementation.
- The best time to implement AI is when your organization is ready for digital transformation.
- Evaluate current operational inefficiencies and employee feedback for readiness indicators.
- Consider external market conditions and competitive pressures that may necessitate change.
- Align implementation with strategic goals to maximize benefits and impact.
- Continuous monitoring ensures that the timing remains relevant as conditions evolve.
- AI can optimize assembly line configurations to reduce worker strain and increase efficiency.
- Predictive analytics can foresee potential ergonomic hazards and recommend adjustments.
- Virtual reality training programs enhance employee understanding of ergonomic principles.
- AI-driven monitoring tools can assess real-time workstation performance and comfort levels.
- These applications ensure a safer, more efficient working environment in automotive manufacturing.
- Investing in AI solutions leads to enhanced worker safety and decreased injury rates.
- Improved ergonomics can result in significant cost savings on healthcare and worker compensation.
- AI tools enable better data collection and analysis for informed decision-making.
- These solutions foster a culture of innovation and continuous improvement within organizations.
- Ultimately, companies gain a competitive edge through optimized workforce efficiency.

