AI Powered Maintenance Scheduling
AI Powered Maintenance Scheduling represents a transformative approach in the Automotive sector, leveraging advanced algorithms and real-time data analytics to optimize vehicle maintenance. By automating scheduling processes, this technology not only enhances operational efficiency but also aligns with the broader trend of AI-driven innovation. Stakeholders in this space are increasingly recognizing the relevance of proactive maintenance strategies, which can lead to improved vehicle performance and reduced downtime.
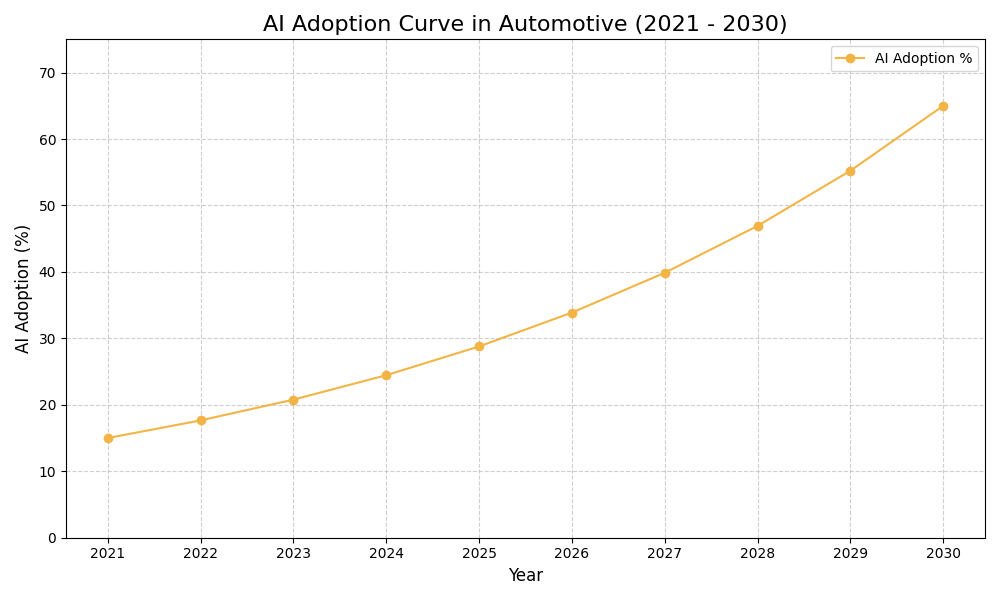
The Automotive ecosystem is witnessing a significant shift as AI-powered practices redefine competitive dynamics and foster rapid innovation. By integrating AI into maintenance scheduling, companies can enhance decision-making processes, streamline operations, and ultimately drive strategic growth. However, the journey toward widespread adoption is not without challenges, as organizations must navigate integration complexities and evolving customer expectations. As they do so, the potential for increased efficiency and value creation remains substantial, paving the way for long-term success in an increasingly competitive landscape.
Optimize Your Maintenance Strategy with AI Innovations
Automotive leaders should strategically invest in AI-powered maintenance scheduling solutions and form partnerships with technology providers to enhance operational efficiency. Leveraging AI can lead to reduced downtime, improved resource allocation, and a significant competitive edge in the automotive market.
How is AI Transforming Maintenance Scheduling in the Automotive Sector?
Implementation Framework
Conduct a comprehensive assessment of existing maintenance systems to determine AI readiness, identifying data sources and integration capabilities crucial for effective scheduling and predictive maintenance. This lays the groundwork for advanced AI adoption.
Internal R&D
Establish robust data collection frameworks using IoT sensors and telemetry to gather real-time vehicle performance data. This data is essential for training AI models to enhance decision-making in maintenance scheduling and efficiency.
Technology Partners
Utilize machine learning techniques to develop predictive maintenance models that analyze historical data, enabling proactive scheduling. This significantly reduces unplanned downtimes and optimizes resource allocation in automotive operations.
Industry Standards
Seamlessly integrate AI-driven maintenance solutions into current workflows, ensuring compatibility with legacy systems. This facilitates real-time data analysis, streamlining operations and empowering staff with AI-enhanced insights for better decision-making.
Cloud Platform
Establish a continuous feedback loop to monitor AI system performance, using analytics to refine algorithms and operational processes. This ongoing optimization leads to improved maintenance outcomes and sustained AI effectiveness in the automotive sector.
Internal R&D
Best Practices for Automotive Manufacturers
-
Impact : Reduces unexpected equipment failures
Example : Example: A major automotive manufacturer uses predictive analytics to foresee engine failures, allowing timely interventions that reduce unplanned downtime by 30%, ultimately saving significant repair costs.
-
Impact : Enhances resource allocation efficiency
Example : Example: By analyzing historical maintenance data, a car plant optimizes labor allocation, reducing maintenance staff hours by 20%, which reallocates resources to production lines.
-
Impact : Improves maintenance scheduling accuracy
Example : Example: An automotive supplier employs predictive models to optimize maintenance schedules based on usage patterns, improving on-time performance by 25% and enhancing customer satisfaction.
-
Impact : Lowers overall operational costs
Example : Example: Predictive analytics allows a truck assembly line to schedule maintenance during non-peak hours, decreasing operational costs significantly and enhancing overall productivity.
-
Impact : Dependence on quality data inputs
Example : Example: An automotive company faces challenges as their predictive system relies on poor quality data from outdated sensors, leading to inaccurate maintenance predictions and increased downtime.
-
Impact : Resistance to technology adoption
Example : Example: Employees resist using the new predictive analytics tools, resulting in underutilization that hampers efficiency improvements and leads to prolonged equipment failures.
-
Impact : Initial integration complexity
Example : Example: Integrating predictive analytics software with legacy systems proves challenging, causing delays in project timelines and additional costs for necessary upgrades.
-
Impact : Potential for incorrect predictions
Example : Example: A faulty predictive model incorrectly forecasts equipment maintenance needs, leading to unnecessary maintenance work and increased operational costs.
-
Impact : Increases operational visibility significantly
Example : Example: A car manufacturer implements real-time monitoring sensors in assembly lines, allowing instant visibility into machine performance, which boosts overall productivity by 15% during peak hours.
-
Impact : Enables swift decision-making processes
Example : Example: Real-time data from production equipment enables managers to make immediate adjustments, resulting in a 20% decrease in line stoppages due to unexpected failures.
-
Impact : Enhances safety and compliance standards
Example : Example: Monitoring systems help ensure safety compliance, as anomalies trigger alerts, reducing workplace incidents by 40% and improving employee morale.
-
Impact : Reduces maintenance response times
Example : Example: With real-time monitoring, maintenance teams respond to machine alerts swiftly, cutting downtime by 30% and maintaining consistent production schedules.
-
Impact : High costs of real-time technologies
Example : Example: An automotive factory halts its real-time monitoring project after discovering that the costs for advanced sensors and software exceed the initial budget by 50%.
-
Impact : Data overload from monitoring systems
Example : Example: A parts manufacturer faces data overload from multiple monitoring systems, leading to analysis paralysis among staff who cannot prioritize actionable insights.
-
Impact : Integration issues with legacy systems
Example : Example: Legacy systems at an automotive plant struggle to integrate with new real-time monitoring tools, causing significant project delays and increased costs.
-
Impact : Potential cybersecurity vulnerabilities
Example : Example: A cyber-attack on an automotive company's real-time monitoring system compromises sensitive production data, raising serious security concerns among management.
-
Impact : Boosts employee skill sets effectively
Example : Example: An automotive manufacturer conducts regular training on AI tools, resulting in a 25% increase in employee productivity as workers become adept at using advanced technologies.
-
Impact : Enhances adaptation to new technologies
Example : Example: Continuous education initiatives help factory staff adapt quickly to AI integration, reducing resistance and improving machine usage efficiency by 30%.
-
Impact : Improves overall operational efficiency
Example : Example: By training employees on AI-driven maintenance scheduling, a company reduces errors caused by human oversight, leading to a 15% increase in operational efficiency.
-
Impact : Reduces knowledge gaps in teams
Example : Example: Regular workshops help bridge knowledge gaps, allowing cross-training among teams, which enhances collaboration and reduces downtime by 20%.
-
Impact : Training costs can escalate quickly
Example : Example: An automotive company overspends on training programs, leading to budget constraints that affect other operational areas, ultimately diminishing overall productivity.
-
Impact : Potential employee turnover during training
Example : Example: High turnover rates during AI training sessions result in lost investment as new hires constantly replace departing employees, complicating knowledge retention.
-
Impact : Inconsistent training effectiveness
Example : Example: A lack of standardized training leads to inconsistent understanding of AI systems across teams, resulting in operational inefficiencies and errors in maintenance scheduling.
-
Impact : Resistance to ongoing education
Example : Example: Employees resist ongoing training initiatives, causing friction between management and staff and ultimately hindering the adoption of AI technologies.
-
Impact : Improves decision-making accuracy
Example : Example: An automotive plant uses machine learning algorithms to analyze maintenance data, leading to a 20% improvement in decision-making accuracy regarding equipment repairs.
-
Impact : Enhances equipment lifespan significantly
Example : Example: By leveraging insights from machine learning, a car assembly line extends equipment lifespan by 15%, reducing replacement costs significantly over the years.
-
Impact : Increases forecasting precision
Example : Example: Machine learning models refine maintenance forecasting, increasing precision by 30%, which allows for better resource allocation and planning in production schedules.
-
Impact : Drives innovation in maintenance practices
Example : Example: An automotive company implements machine learning to innovate maintenance processes, resulting in a 40% reduction in resource wastage and improved operational efficiency.
-
Impact : Complexity in understanding algorithms
Example : Example: Engineers at an automotive firm struggle to understand complex machine learning algorithms, leading to ineffective implementation and missed opportunities for efficiency gains.
-
Impact : Initial setup can be time-consuming
Example : Example: A company’s machine learning system requires extensive initial setup, causing project delays and frustrating management expectations for immediate results.
-
Impact : Dependence on historical data quality
Example : Example: Relying on poor-quality historical data, a machine learning model mispredicts maintenance needs, causing unexpected equipment failures and increased downtime.
-
Impact : Misinterpretation of machine learning outputs
Example : Example: Misinterpretation of machine learning outputs by staff leads to incorrect decisions, resulting in wasted resources and operational inefficiencies.
-
Impact : Enhances consistency in maintenance tasks
Example : Example: A standardized maintenance protocol across an automotive plant ensures every team member follows the same procedures, reducing defects and enhancing efficiency by 30%.
-
Impact : Reduces variations in equipment performance
Example : Example: Consistent protocols minimize variations in equipment performance, resulting in a 15% increase in reliability across production lines, which improves output.
-
Impact : Improves team collaboration across departments
Example : Example: Standardization leads to better collaboration between maintenance and production teams, reducing downtime by 25% and ensuring smoother operations.
-
Impact : Streamlines operational workflows effectively
Example : Example: Streamlined workflows from standardized procedures allow faster task completions, ultimately improving overall productivity and lowering operational costs.
-
Impact : Resistance from staff to standardization
Example : Example: Employees resist standardized protocols, arguing that their unique methods are more efficient, leading to inconsistency and increased equipment downtime.
-
Impact : Initial time investment for development
Example : Example: Developing standardized maintenance procedures requires significant time investment, delaying implementation and creating frustration among teams wanting immediate results.
-
Impact : May overlook unique equipment needs
Example : Example: A one-size-fits-all approach overlooks specific equipment needs, leading to increased failures and maintenance delays due to lack of tailored strategies.
-
Impact : Potential for rigid processes
Example : Example: Rigid adherence to standardized protocols can stifle innovation, causing missed opportunities for process improvements that could enhance efficiency.
-
Impact : Improves continuous process optimization
Example : Example: An automotive assembly line incorporates feedback loops where operators report issues, leading to a 20% decrease in recurring problems through targeted adjustments.
-
Impact : Enhances responsiveness to operational issues
Example : Example: Continuous feedback from maintenance teams allows for rapid responses to operational issues, improving machine uptime by 30% and enhancing overall workflow efficiency.
-
Impact : Fosters innovation through iterative feedback
Example : Example: Iterative feedback mechanisms foster innovation, with employees suggesting improvements that cut maintenance times by 15%, driving productivity gains.
-
Impact : Encourages employee engagement in processes
Example : Example: Incorporating employee feedback leads to higher engagement, as workers feel valued, resulting in a 10% increase in morale and collaboration among teams.
-
Impact : Over-reliance on feedback can mislead
Example : Example: An automotive company over-relies on operator feedback, leading to misguided changes that complicate maintenance processes and increase downtime.
-
Impact : Implementation may require cultural shifts
Example : Example: Implementing feedback loops requires a cultural shift, causing pushback from management and slowing down the adoption of new practices.
-
Impact : Feedback collection can be time-consuming
Example : Example: Collecting feedback from multiple teams takes time, delaying necessary adjustments and hindering operational responsiveness during peak production periods.
-
Impact : Potential for conflicting feedback among teams
Example : Example: Conflicting feedback from different departments can lead to confusion, resulting in inconsistent practices that undermine process improvements and create inefficiencies.
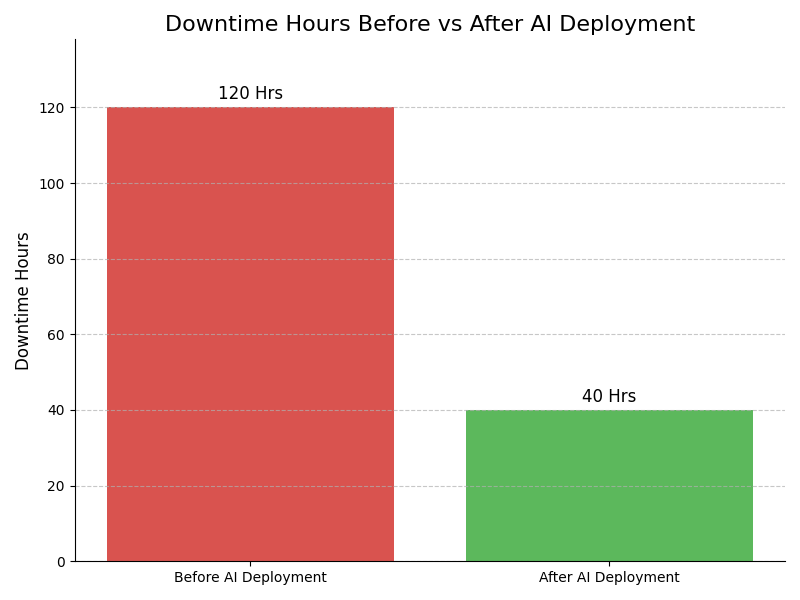
AI-powered maintenance scheduling is not just about efficiency; it's about redefining how we ensure vehicle reliability and safety in real-time.
– Anan BisharaCompliance Case Studies




Embrace AI-powered scheduling to optimize operations and minimize downtime. Stay ahead of the competition and transform your automotive business with cutting-edge technology.

Leadership Challenges & Opportunities
Data Integration Challenges
Utilize AI Powered Maintenance Scheduling to centralize data from disparate sources, ensuring seamless integration across platforms. Implement robust APIs and data lakes to facilitate real-time data flow, enhancing predictive analytics. This approach improves decision-making and optimizes maintenance timelines, reducing operational downtime.
Cultural Resistance to Change
Foster a culture of innovation by involving stakeholders early in the AI Powered Maintenance Scheduling implementation process. Conduct workshops and showcase pilot results to demonstrate tangible benefits, addressing concerns proactively. This commitment to transparency encourages buy-in and smooths the transition to AI-driven processes.
Cost of Implementation
Leverage AI Powered Maintenance Scheduling through phased implementation strategies that prioritize high-impact areas. Utilize cloud solutions to minimize upfront costs and adopt a subscription model that aligns expenses with usage. This approach maximizes ROI while spreading financial impact over time, making budgeting easier.
Talent Acquisition Issues
Address talent shortages by integrating AI Powered Maintenance Scheduling with user-friendly interfaces and automated processes that require less specialized knowledge. Establish partnerships with educational institutions to develop training programs, ensuring a steady pipeline of skilled workers adept in AI technologies and maintenance practices.
Assess how well your AI initiatives align with your business goals
AI Use Case vs ROI Timeline
| AI Use Case | Description | Typical ROI Timeline | Expected ROI Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Predictive Maintenance Alerts | AI analyzes vehicle data to predict maintenance needs before failures occur. For example, sensors in fleet vehicles send real-time data, allowing scheduling of maintenance during non-peak hours, reducing downtime. | 6-12 months | High |
| Optimized Repair Scheduling | AI algorithms optimize repair schedules based on parts availability and technician skill sets. For example, a dealership automates appointment bookings, leveraging AI to match service requests with technician schedules efficiently. | 6-12 months | Medium-High |
| Resource Allocation Management | AI enhances resource allocation by predicting parts and labor needs. For example, a manufacturing plant uses AI to analyze historical data, ensuring optimal staffing and inventory levels for maintenance tasks. | 12-18 months | Medium-High |
| Automated Inventory Management | AI maintains optimal inventory levels for spare parts, reducing costs. For example, an automotive service center employs AI to automatically reorder parts based on predictive analytics, minimizing stockouts. | 6-12 months | High},{ |
Glossary
Work with Atomic Loops to architect your AI implementation roadmap — from PoC to enterprise scale.
Contact NowFrequently Asked Questions
- AI Powered Maintenance Scheduling utilizes advanced algorithms to optimize vehicle maintenance processes.
- It enhances operational efficiency by predicting maintenance needs based on real-time data.
- The approach minimizes downtime and improves asset longevity through proactive scheduling.
- Data-driven insights help in making informed decisions about resource allocation.
- Companies gain a competitive edge by leveraging innovative technology for maintenance.
- Begin by assessing your current maintenance processes and identifying areas for improvement.
- Choose AI tools that integrate seamlessly with your existing systems and workflows.
- Develop a clear implementation plan, outlining timelines, resources, and key stakeholders.
- Engage your team in training to ensure everyone understands the new technology.
- Start with pilot projects to test and refine your approach before full deployment.
- AI can significantly reduce maintenance costs by optimizing resource allocation and scheduling.
- Organizations often see improved equipment uptime through proactive maintenance strategies.
- Enhanced data analytics capabilities lead to better decision-making and operational efficiency.
- Customer satisfaction typically improves due to decreased service disruptions and faster repairs.
- Competitive advantages arise from the ability to innovate and adapt quickly to market demands.
- Resistance to change from staff can hinder the adoption of new technologies.
- Data quality issues may arise, affecting the reliability of AI-driven insights.
- Integration with legacy systems can be complex and resource-intensive.
- Training staff to utilize AI tools effectively is crucial for successful implementation.
- Establishing clear governance and oversight can help mitigate implementation risks.
- The right time is when your organization faces increasing maintenance costs and downtime.
- Evaluate your readiness based on existing digital capabilities and infrastructure maturity.
- Consider adopting AI when seeking to enhance competitive positioning in the market.
- Emerging technologies can be integrated when aligned with strategic business goals.
- Seasonal fluctuations in demand can signal opportune times for implementation.
- AI applications include predictive maintenance for fleet management and logistics optimization.
- Automotive manufacturers can use AI to streamline assembly line maintenance schedules.
- Dealerships leverage AI to enhance service department efficiency and customer experience.
- AI can support compliance with regulatory standards in vehicle maintenance and safety.
- Benchmarking against industry standards helps identify areas for improvement and innovation.

