Autonomous Vehicle Component Manufacturing
Autonomous Vehicle Component Manufacturing refers to the specialized production of parts and systems essential for self-driving vehicles within the Automotive sector. This encompasses a wide range of components, including sensors, software, and control systems, which are critical for enabling automation. As the demand for safer, more efficient transportation solutions grows, this sector becomes increasingly relevant for stakeholders seeking to innovate and remain competitive. The integration of advanced technologies, particularly artificial intelligence, is driving a paradigm shift in manufacturing processes and operational strategies, aligning with broader trends of digital transformation.
The significance of Autonomous Vehicle Component Manufacturing lies in its capacity to reshape the entire Automotive ecosystem. AI-driven practices are redefining how companies approach innovation cycles and stakeholder interactions, fostering a dynamic environment for collaboration and growth. The influence of AI extends to enhancing operational efficiency, improving decision-making capabilities, and setting long-term strategic directions. However, while there are substantial growth opportunities, challenges such as adoption barriers, integration complexities, and evolving expectations must be navigated carefully to realize the full potential of this transformative journey.
Accelerate AI Integration in Autonomous Vehicle Component Manufacturing
Companies in the automotive industry should strategically invest in partnerships with AI technology leaders to enhance their Autonomous Vehicle Component Manufacturing capabilities. Implementing AI-driven solutions can lead to significant improvements in production efficiency, cost reduction, and a stronger competitive edge in the market.
How AI is Transforming Autonomous Vehicle Component Manufacturing
Implementation Framework
Integrating AI systems enables predictive analytics for component performance and supply chain optimization, enhancing efficiency and reducing downtime, thereby improving overall manufacturing capabilities and competitiveness in the automotive industry.
Technology Partners
Deploying machine learning algorithms for quality control enhances defect detection and reduces errors in component manufacturing, significantly lowering costs and improving product reliability in autonomous vehicle systems.
Internal R&D
Establishing a robust data infrastructure facilitates real-time data collection and analysis, enabling effective monitoring of manufacturing processes and enhancing AI-driven decision-making within autonomous vehicle component production.
Industry Standards
Implementing robotics automation in manufacturing processes streamlines production and increases precision, drastically improving throughput and reducing human error, which is essential for the efficiency of autonomous vehicle components.
Cloud Platform
Enhancing cybersecurity measures protects sensitive data and AI systems against cyber threats, ensuring safe and reliable operations in autonomous vehicle manufacturing, which is increasingly vulnerable to digital attacks.
Cybersecurity Experts
Best Practices for Automotive Manufacturers
-
Impact : Reduces unexpected equipment failures
Example : Example: A leading automotive parts manufacturer employs predictive maintenance using AI to monitor machinery health. This approach reduced unexpected breakdowns by 30%, saving significant downtime costs and enhancing productivity.
-
Impact : Optimizes maintenance scheduling effectively
Example : Example: An electric vehicle battery factory uses AI to predict machine maintenance needs, resulting in a 20% reduction in scheduled downtime and allowing for more efficient production scheduling.
-
Impact : Lowers overall operational costs
Example : Example: A tire manufacturing plant employs AI-driven insights to identify wear patterns in machinery, extending their operational lifespan by 15% and reducing replacement costs.
-
Impact : Extends equipment lifecycle significantly
Example : Example: By implementing predictive maintenance, a component manufacturer decreased annual maintenance costs by 25%, allowing funds to be reallocated to innovation projects.
-
Impact : High initial investment for technology
Example : Example: An automotive supplier faced budget overruns when attempting to implement predictive maintenance, as initial costs for sensors and software exceeded forecasts, delaying the project.
-
Impact : Data integration challenges with legacy systems
Example : Example: A manufacturer struggled with integrating AI into their existing systems, as outdated machinery could not support new technologies, causing significant project delays.
-
Impact : Dependence on accurate data inputs
Example : Example: A plant experienced issues when inaccurate sensor data led to premature machine shutdowns, resulting in production halts and confusion among staff.
-
Impact : Resistance from workforce during transition
Example : Example: Employee resistance to new AI tools slowed down implementation, requiring additional training and change management efforts, which delayed productivity gains.
-
Impact : Enhances decision-making speed significantly
Example : Example: An automotive component manufacturer leverages real-time data analytics to monitor production flows, enabling managers to make informed decisions that cut response time by 40% during peak hours.
-
Impact : Improves operational transparency across departments
Example : Example: A car assembly plant uses real-time dashboards that integrate data from multiple departments, improving cross-functional communication and transparency, leading to faster issue resolution.
-
Impact : Facilitates proactive issue resolution
Example : Example: Continuous monitoring of production metrics at a brake system factory allows engineers to identify and resolve quality issues proactively, reducing rework by 25%.
-
Impact : Drives continuous improvement initiatives
Example : Example: By implementing real-time analytics, a vehicle parts producer drives continuous improvement initiatives, resulting in a 15% increase in process efficiency over six months.
-
Impact : Overwhelming data management challenges
Example : Example: An automotive electronics manufacturer faced significant data overload due to too many metrics being monitored, complicating analysis and delaying decision-making processes.
-
Impact : Potential for inaccurate data interpretation
Example : Example: A car manufacturer misinterpreted real-time data due to lack of training, leading to unnecessary production adjustments and inefficiencies that cost thousands in lost revenue.
-
Impact : Integration issues with existing infrastructure
Example : Example: When integrating new analytics software, a plant discovered compatibility issues with legacy systems, causing delays and requiring costly upgrades to infrastructure.
-
Impact : Need for ongoing data security measures
Example : Example: After a data breach, an automotive supplier realized they needed robust security measures to protect sensitive production data, leading to unplanned expenses and resource allocation.
-
Impact : Improves employee engagement and satisfaction
Example : Example: A major automotive manufacturer revamped its training programs to include AI technology, resulting in a 15% increase in employee satisfaction and a noticeable drop in operational errors.
-
Impact : Boosts productivity through skill upgrades
Example : Example: By providing regular training on new AI tools, a vehicle component supplier saw a 20% increase in productivity as workers became adept at using advanced systems.
-
Impact : Reduces errors in manufacturing processes
Example : Example: A tire manufacturing facility rolled out an AI training initiative that reduced assembly errors by 30%, significantly improving overall product quality and consistency.
-
Impact : Facilitates smoother technology transitions
Example : Example: Training sessions focused on AI integration helped staff adapt to new technologies seamlessly, minimizing disruptions during the transition phase and improving operational efficiency.
-
Impact : Training costs can escalate quickly
Example : Example: An automotive parts supplier underestimated training costs for AI tools, leading to budget overruns that negatively impacted other operational investments.
-
Impact : Potential for knowledge gaps among staff
Example : Example: A component manufacturer faced knowledge gaps among employees after introducing AI, as not all staff were adequately trained, resulting in inconsistent output quality.
-
Impact : Resistance to new training methodologies
Example : Example: Resistance from the workforce to adopt new training methodologies delayed the adoption of AI tools, causing setbacks in production goals.
-
Impact : Time-consuming training processes impact productivity
Example : Example: An automotive assembly line experienced productivity dips during extensive training periods, leading to missed deadlines and increased labor costs.
-
Impact : Increases responsiveness to market changes
Example : Example: An autonomous vehicle parts manufacturer adopted agile practices, allowing them to respond to market fluctuations swiftly and reducing lead times by 25%.
-
Impact : Enhances collaboration among teams
Example : Example: Implementing agile methodologies in a vehicle production facility fostered collaboration among cross-functional teams, resulting in faster problem resolution and improved project timelines.
-
Impact : Improves resource allocation efficiency
Example : Example: By optimizing resource allocation through agile techniques, a car components manufacturer achieved a 20% reduction in waste and improved profitability.
-
Impact : Drives innovation through flexibility
Example : Example: Agile practices facilitated a culture of innovation, allowing a parts manufacturer to develop and launch new products 30% faster than traditional methods.
-
Impact : Requires cultural shift within organization
Example : Example: An automotive supplier struggled with cultural resistance during the transition to agile practices, leading to confusion and delays in project timelines.
-
Impact : Initial disruption to established processes
Example : Example: Initial implementation of agile methodologies disrupted established workflows in a vehicle assembly line, causing temporary production slowdowns and increased costs.
-
Impact : Potential for fragmented team efforts
Example : Example: Fragmented efforts among teams adapting to agile project management led to miscommunication and project overlap, hindering productivity and efficiency.
-
Impact : Difficulty in measuring agile success
Example : Example: A manufacturer found it challenging to measure success in agile initiatives, resulting in uncertainty about the effectiveness of the new practices and initiatives.
-
Impact : Enhances defect detection accuracy significantly
Example : Example: In an automotive assembly line, a vision-based AI system flags microscopic paint defects in real time as car bodies pass under cameras, catching flaws human inspectors previously missed during night shifts.
-
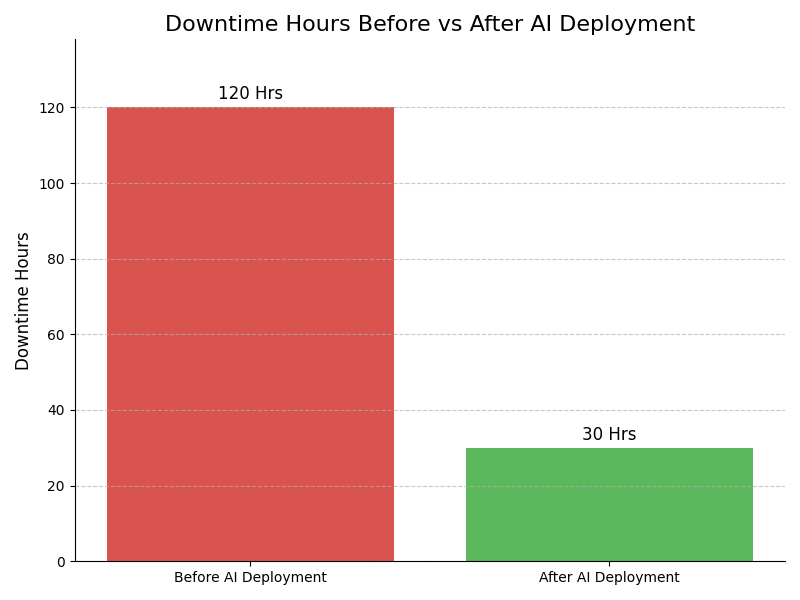
Impact : Reduces production downtime and costs
Example : Example: A semiconductor factory uses AI to detect early soldering anomalies. The system stops the line immediately, preventing a full batch failure that would have caused hours of rework and shutdown.
-
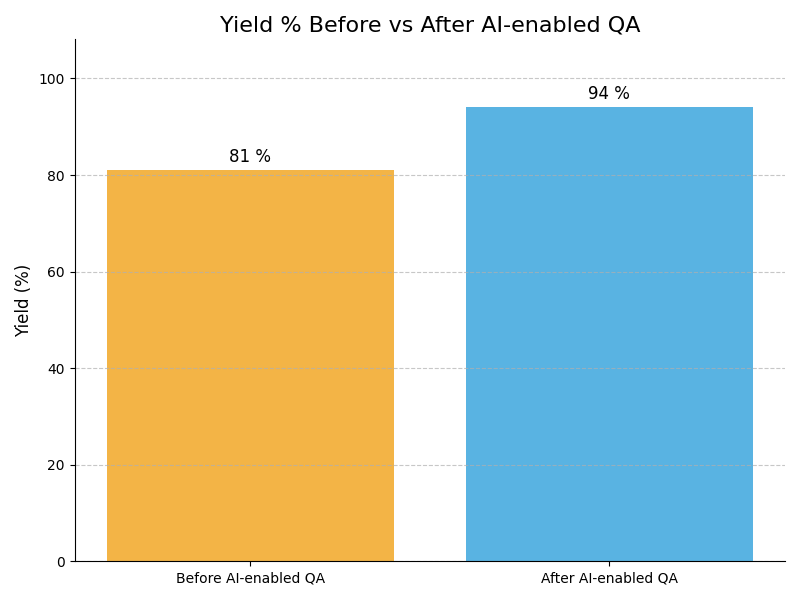
Impact : Improves quality control standards
Example : Example: A food packaging plant uses AI image recognition to verify seal integrity on every packet, ensuring non-compliant packages are rejected instantly before shipping.
-
Impact : Boosts overall operational efficiency
Example : Example: AI dynamically adjusts inspection thresholds based on production speed, allowing the factory to increase output during peak demand without sacrificing quality.
-
Impact : High initial investment for implementation
Example : Example: A mid-sized electronics manufacturer delays AI rollout after realizing camera hardware, GPUs, and system integration push upfront costs beyond budget approvals.
-
Impact : Potential data privacy concerns
Example : Example: AI quality systems capturing worker activity unintentionally store employee facial data, triggering compliance issues with internal privacy policies.
-
Impact : Integration challenges with existing systems
Example : Example: AI software cannot communicate with a 15-year-old PLC controller, forcing engineers to manually export data and slowing decision-making.
-
Impact : Dependence on continuous data quality
Example : Example: Dust accumulation on camera lenses causes the AI to misclassify normal products as defective, leading to unnecessary scrap until recalibration.
AI is revolutionizing automotive manufacturing, enabling unprecedented efficiency and innovation in the production of autonomous vehicle components.
– Randy SchmelzerCompliance Case Studies



Seize the opportunity to lead in Autonomous Vehicle Component Manufacturing with AI-driven solutions. Transform your processes and gain a competitive edge today!
Leadership Challenges & Opportunities
Supply Chain Disruptions
Utilize Autonomous Vehicle Component Manufacturing to enhance supply chain transparency through real-time data analytics and IoT integration. Implement predictive analytics to forecast disruptions and establish contingency plans. This approach minimizes delays, ensures timely deliveries, and optimizes inventory management for smoother operations.
Component Standardization Challenges
Adopt modular designs in Autonomous Vehicle Component Manufacturing to facilitate component standardization across different vehicle models. Collaborate with industry stakeholders to establish uniform specifications, reducing compatibility issues and streamlining production processes, which ultimately enhances scalability and reduces costs.
Integration of AI Technologies
Implement Autonomous Vehicle Component Manufacturing with advanced AI algorithms for seamless integration into existing systems. Focus on a phased approach that includes pilot testing for data management and processing. This strategy not only enhances operational efficiency but also provides valuable insights for continuous improvement.
Talent Acquisition Hurdles
Address talent acquisition challenges by establishing partnerships with educational institutions for Autonomous Vehicle Component Manufacturing training programs. Utilize targeted internships and mentorships to attract skilled workers. This proactive approach builds a pipeline of qualified talent and fosters a culture of innovation within the organization.
Assess how well your AI initiatives align with your business goals

AI Use Case vs ROI Timeline
| AI Use Case | Description | Typical ROI Timeline | Expected ROI Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Predictive Maintenance Scheduling | AI algorithms analyze sensor data to predict equipment failures before they happen. For example, a manufacturer uses predictive maintenance to schedule repairs on robotic arms, reducing unexpected downtimes and optimizing workflow efficiency. | 6-12 months | High |
| Quality Control Automation | Machine learning models assess component quality using image recognition. For example, an autonomous vehicle parts manufacturer implements AI to inspect welds, leading to a significant reduction in defective parts reaching assembly lines. | 12-18 months | Medium-High |
| Supply Chain Optimization | AI-driven analytics enhance supply chain efficiency by predicting demand fluctuations. For example, a parts supplier utilizes AI to adjust inventory levels dynamically, minimizing overstock and understock situations. | 6-12 months | Medium |
| Enhanced Design Simulation | AI simulates various design scenarios to improve component performance. For example, engineers use AI to test different materials for durability in vehicle components, leading to better resource allocation and innovation. | 12-18 months | Medium-High |
Glossary
Work with Atomic Loops to architect your AI implementation roadmap — from PoC to enterprise scale.
Contact NowFrequently Asked Questions
- Autonomous Vehicle Component Manufacturing focuses on automating production for efficiency and quality.
- It leverages AI to optimize supply chains and enhance predictive maintenance capabilities.
- This innovation reduces reliance on manual labor, thereby minimizing human error.
- The approach fosters rapid prototyping and faster go-to-market strategies.
- Ultimately, it positions companies to meet evolving consumer demands effectively.
- Start with a clear strategy that identifies specific areas for AI integration.
- Conduct a thorough assessment of existing systems and potential resource needs.
- Engage with AI vendors to explore tailored solutions that fit your needs.
- Pilot programs can validate AI solutions before full-scale implementation.
- Ongoing training for employees ensures smooth integration and operational continuity.
- AI enhances operational efficiency by automating repetitive tasks and processes.
- It provides real-time analytics for informed decision-making and strategy adjustments.
- Companies can achieve significant cost savings through optimized resource allocation.
- AI contributes to higher quality control standards, reducing defects in production.
- Competitive advantages arise from faster innovation cycles and improved customer satisfaction.
- Resistance to change among staff can hinder successful implementation of AI technologies.
- Integration issues may arise with existing legacy systems and processes.
- Data security and privacy concerns must be addressed to ensure compliance.
- Investment in training and development is crucial for maximizing AI benefits.
- Establishing clear risk mitigation strategies will help navigate potential pitfalls.
- Companies should assess their readiness based on current technological capabilities.
- Market demand and competition can influence the urgency of adoption.
- Long-term strategic goals should align with the timing of implementation efforts.
- Evaluating existing processes can reveal opportunities for immediate improvement.
- Regularly reviewing industry trends helps identify optimal adoption windows.
- Businesses must stay informed about evolving regulations in the automotive sector.
- Compliance with safety standards is crucial for both manufacturing and end products.
- Data handling practices must align with relevant privacy laws and guidelines.
- Collaboration with regulatory bodies can facilitate smoother transitions to new technologies.
- Regular audits and assessments ensure adherence to industry benchmarks and standards.
- Manufacturers can use AI-driven robotics for assembling complex vehicle components efficiently.
- Predictive maintenance ensures optimal performance and reliability of manufacturing equipment.
- Supply chain optimization minimizes delays and enhances inventory management practices.
- Quality assurance processes can be automated to improve consistency and reduce errors.
- Customization and personalization of vehicles can be achieved through advanced manufacturing techniques.