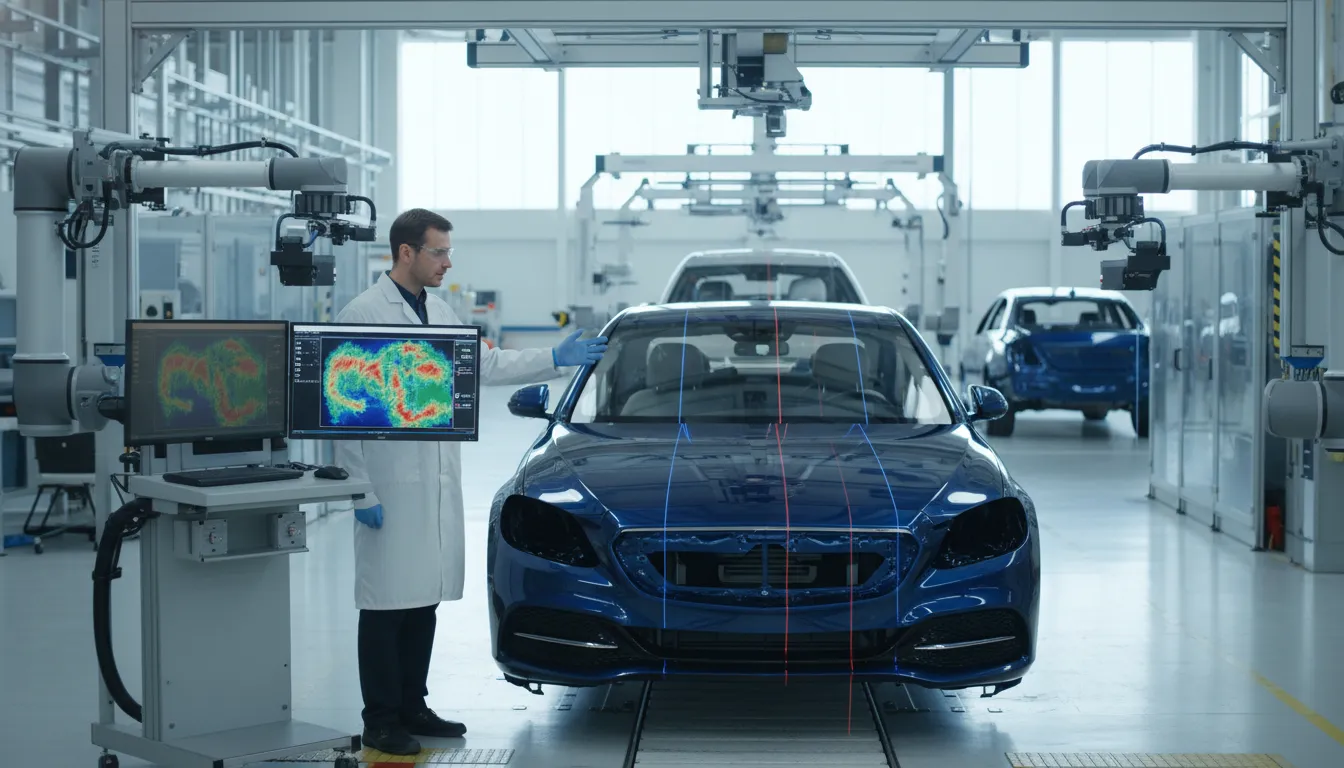
Computer Vision for Assembly Line Monitoring
Computer Vision for Assembly Line Monitoring represents a pivotal advancement in the Automotive sector, leveraging AI technologies to enhance operational efficiency and quality assurance. This innovative approach encompasses the use of sophisticated algorithms and real-time data analysis to monitor assembly processes, ensuring that vehicles meet stringent quality standards. As the industry evolves, this technology becomes increasingly relevant, aligning with the push towards automation and smart manufacturing, thereby meeting the strategic priorities of stakeholders focused on operational excellence.
The integration of AI-driven practices into Computer Vision is fundamentally reshaping the competitive landscape of the Automotive ecosystem. This transformation fosters a culture of innovation, enhancing collaboration among stakeholders and streamlining decision-making processes. The adoption of such technologies not only drives efficiency but also sets a long-term strategic direction for firms, presenting myriad growth opportunities. However, organizations must navigate challenges related to integration complexity and shifting expectations, ensuring that they are prepared to harness the full potential of these advancements while addressing potential barriers to adoption.
Transform Your Assembly Line with AI-Powered Computer Vision
Automotive companies should strategically invest in Computer Vision technologies and foster partnerships with AI innovators to optimize assembly line monitoring. Implementing these AI-driven solutions can yield significant improvements in quality control, operational efficiency, and overall competitiveness in the automotive sector.
Transforming Automotive Assembly: The Role of Computer Vision
Implementation Framework
Identify specific use cases where computer vision can enhance monitoring, such as defect detection or process optimization, which boosts quality control and efficiency, crucial for automotive production.
Industry Standards
Engage with established AI technology vendors who specialize in computer vision solutions, ensuring access to cutting-edge tools and expertise, which enhances operational capabilities and reduces project risks significantly.
Technology Partners
Implement AI-driven computer vision systems across assembly lines, focusing on real-time data processing and analytics to minimize defects and streamline operations, ultimately improving product quality and reducing waste.
Internal R&D
Provide comprehensive training for employees on using AI-powered monitoring tools, emphasizing the importance of adapting to technology changes, which fosters a culture of innovation and maximizes operational effectiveness.
Industry Standards
Regularly assess the performance of AI-driven computer vision systems, using metrics to evaluate their impact on production efficiency and quality, which helps identify areas for continuous improvement and operational resilience.
Cloud Platform
Best Practices for Automotive Manufacturers
-
Impact : Enhances image clarity for better analysis
Example : Example: In an automotive plant, advanced image enhancement algorithms clarify low-light images of components, enabling accurate detection of surface flaws that were previously overlooked during inspections.
-
Impact : Reduces processing time significantly
Example : Example: A manufacturer integrates faster processing techniques, cutting analysis time from 5 seconds to 2 seconds, allowing for real-time defect detection and minimizing production delays.
-
Impact : Increases detection of subtle defects
Example : Example: By refining image processing techniques, a car factory identifies paint imperfections during high-speed assembly, reducing the number of faulty units shipped to customers.
-
Impact : Improves overall system reliability
Example : Example: Enhanced image clarity leads to fewer false positives, resulting in a more reliable inspection process and reducing unnecessary rework on the assembly line.
-
Impact : Increased complexity of processing algorithms
Example : Example: A car manufacturer struggles with complex algorithms that require constant adjustments, leading to a steep learning curve for the engineering team and delays in project timelines.
-
Impact : Need for specialized training for staff
Example : Example: Employees find it challenging to operate advanced vision systems, resulting in production slowdowns and necessitating additional training sessions to enhance their skills.
-
Impact : Potential for overfitting in models
Example : Example: An AI model trained too narrowly on specific defect types fails to generalize, missing other significant defects that could compromise product quality during inspections.
-
Impact : Maintenance costs of advanced systems
Example : Example: A factory faces unexpected maintenance costs as advanced vision systems require specialized technicians, straining the budget and affecting operational efficiency.
-
Impact : Improves model accuracy over time
Example : Example: An automotive manufacturer implements a continuous learning system that regularly updates detection models, significantly improving accuracy for newly emerging defects identified during production.
-
Impact : Adapts to new defect types quickly
Example : Example: By adapting to new defect types swiftly, a car manufacturer reduces the risk of quality issues, enhancing their reputation and customer trust in the automotive market.
-
Impact : Enhances competitiveness in the market
Example : Example: Continuous learning systems allow a company to stay ahead of competitors, as they can efficiently manage new product lines with rapidly changing inspection criteria.
-
Impact : Reduces long-term operational costs
Example : Example: Long-term operational costs decrease as the system becomes more efficient at detecting defects, reducing labor costs associated with manual inspection and rework.
-
Impact : Risk of model drift over time
Example : Example: A major car manufacturer faces challenges with model drift, as changes in production processes lead to increased errors in defect detection, requiring constant model adjustments.
-
Impact : Dependence on extensive data sets
Example : Example: The need for extensive data sets to retrain models becomes a bottleneck, delaying updates and affecting production quality in an automotive assembly line.
-
Impact : High computational demand for updates
Example : Example: High computational demand for continuous updates strains existing infrastructure, leading to slowdowns in real-time monitoring and ultimately affecting production timelines.
-
Impact : Potential resistance from staff
Example : Example: Resistance from staff towards adopting new AI-driven systems creates friction, slowing down the implementation of continuous learning strategies and hindering operational improvements.
-
Impact : Facilitates accurate data collection
Example : Example: A leading automotive firm implements a robust data management system, ensuring accurate collection of visual data which is crucial for AI training and defect detection.
-
Impact : Improves data accessibility for teams
Example : Example: Improved data accessibility allows cross-functional teams to analyze production metrics efficiently, leading to faster identification of quality issues on the assembly line.
-
Impact : Enhances compliance with regulations
Example : Example: By adhering to stringent data management practices, an automotive manufacturer complies with industry regulations, avoiding potential legal penalties and ensuring customer trust.
-
Impact : Supports better decision-making processes
Example : Example: Reliable data management supports better decision-making processes, enabling managers to make informed choices regarding production changes and quality improvements.
-
Impact : Data silos may hinder communication
Example : Example: Data silos in a car manufacturing facility hinder communication between teams, leading to inconsistent quality checks and increased error rates on the assembly line.
-
Impact : Inadequate data security measures
Example : Example: A breach in inadequate data security measures exposes sensitive production data, resulting in compliance penalties and damaging the company's reputation.
-
Impact : High costs associated with data management
Example : Example: The automotive company faces high costs associated with implementing a comprehensive data management system, straining budgets and delaying other critical investments.
-
Impact : Risk of data loss during transfers
Example : Example: During data transfers, a significant loss of critical image data occurs, impacting the AI model's ability to detect defects accurately, causing production inefficiencies.
-
Impact : Enables scalable data storage solutions
Example : Example: By leveraging cloud computing, a car manufacturer scales its data storage effortlessly, allowing for the collection of high-resolution images from multiple inspection points without constraints.
-
Impact : Facilitates real-time data processing
Example : Example: Cloud-based solutions enable real-time data processing, allowing assembly line managers to receive instant feedback on defect detection, making immediate adjustments to production.
-
Impact : Improves collaboration across teams
Example : Example: Improved collaboration through cloud computing allows cross-departmental teams to access and analyze data simultaneously, leading to better alignment on quality improvement strategies.
-
Impact : Reduces costs associated with infrastructure
Example : Example: The automotive plant reduces infrastructure costs significantly by using cloud solutions, eliminating the need for physical servers and allowing for more flexible budgeting.
-
Impact : Dependence on internet connectivity
Example : Example: An automotive firm experiences production delays due to internet connectivity issues, rendering cloud-based defect detection systems unavailable during critical production hours.
-
Impact : Potential for cloud service outages
Example : Example: A sudden cloud service outage halts real-time monitoring in a car assembly line, leading to a backlog of undetected defects that compromise quality.
-
Impact : Data privacy concerns in the cloud
Example : Example: Data privacy concerns arise when sensitive production data is stored in the cloud, prompting audits and security enhancements to comply with regulations.
-
Impact : Integration challenges with legacy systems
Example : Example: Integration challenges occur as legacy systems struggle to communicate with newly adopted cloud solutions, causing disruptions in the data flow necessary for effective monitoring.
-
Impact : Identifies potential system vulnerabilities
Example : Example: Regular audits reveal vulnerabilities in the AI inspection system of a car manufacturer, prompting timely upgrades that prevent costly production failures due to undetected defects.
-
Impact : Ensures compliance with industry standards
Example : Example: Compliance with strict automotive industry standards is ensured through systematic audits, mitigating legal risks and bolstering the company’s market reputation as a quality leader.
-
Impact : Enhances overall system performance
Example : Example: System performance improves significantly after audits highlight bottlenecks in the AI processing chain, enabling targeted optimizations that enhance defect detection rates.
-
Impact : Improves stakeholder confidence
Example : Example: Stakeholder confidence increases as regular audits demonstrate the effectiveness of the AI monitoring systems, reassuring investors about the company’s commitment to quality and innovation.
-
Impact : Time-consuming audit processes
Example : Example: Time-consuming audit processes delay the implementation of new AI monitoring systems, causing frustration among team members eager to improve production efficiency.
-
Impact : High costs of external audits
Example : Example: High costs associated with hiring external auditors strain the budget of an automotive firm, leading to compromises on the frequency and depth of future audits.
-
Impact : Risk of overlooking critical issues
Example : Example: A critical issue is overlooked during an audit due to rushed timelines, leading to a significant defect in the final product that negatively impacts customer satisfaction.
-
Impact : Potential resistance from teams
Example : Example: Teams resist audit processes, viewing them as punitive rather than constructive, which creates a culture of apprehension and could impede improvement initiatives in the organization.
AI-driven computer vision is revolutionizing assembly lines, enabling unprecedented accuracy and efficiency in automotive manufacturing.
– Guardian tech staffCompliance Case Studies



Seize the opportunity to enhance your production capabilities with AI-driven Computer Vision solutions. Stay ahead in the automotive industry by transforming your assembly line monitoring today.
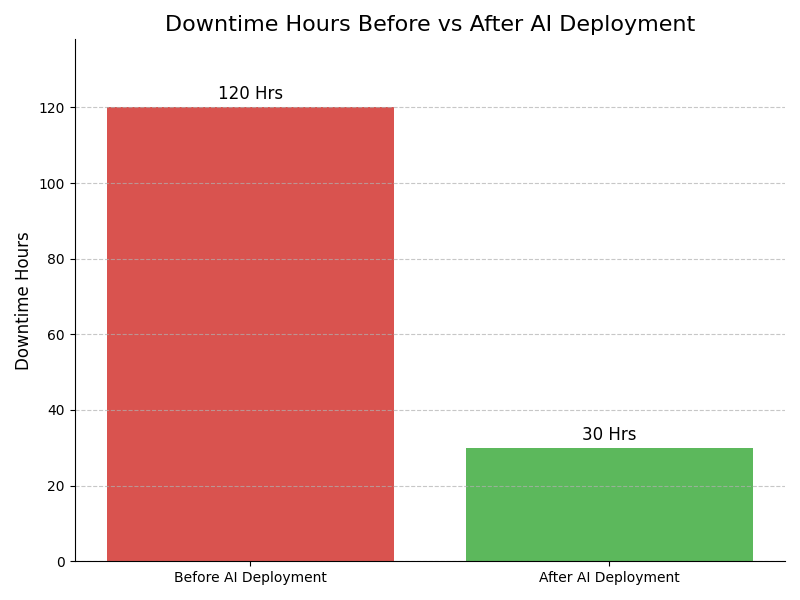

Leadership Challenges & Opportunities
Data Integration Challenges
Utilize Computer Vision for Assembly Line Monitoring to establish seamless data pipelines that integrate with existing Automotive systems. Implement edge computing to process data in real-time, reducing latency and enhancing decision-making. This ensures a unified view of operations and optimizes workflow efficiency.
Resistance to Change
Foster a culture of innovation by demonstrating the tangible benefits of Computer Vision for Assembly Line Monitoring. Engage employees through workshops and pilot programs that highlight success stories. Incorporate feedback loops to refine solutions, ensuring staff buy-in and smoother transitions to new technologies.
High Implementation Costs
Mitigate financial barriers by leveraging phased implementation of Computer Vision for Assembly Line Monitoring. Start with pilot projects targeting critical areas, using cloud-based solutions to lower initial investments. Showcase quick ROI to secure additional funding for broader application across the assembly line.
Regulatory Compliance Complexity
Employ Computer Vision for Assembly Line Monitoring to automate compliance tracking and reporting for Automotive regulations. Integrate real-time monitoring features that flag deviations and generate compliance documentation automatically, ensuring adherence to standards while reducing administrative burdens and associated costs.
Assess how well your AI initiatives align with your business goals
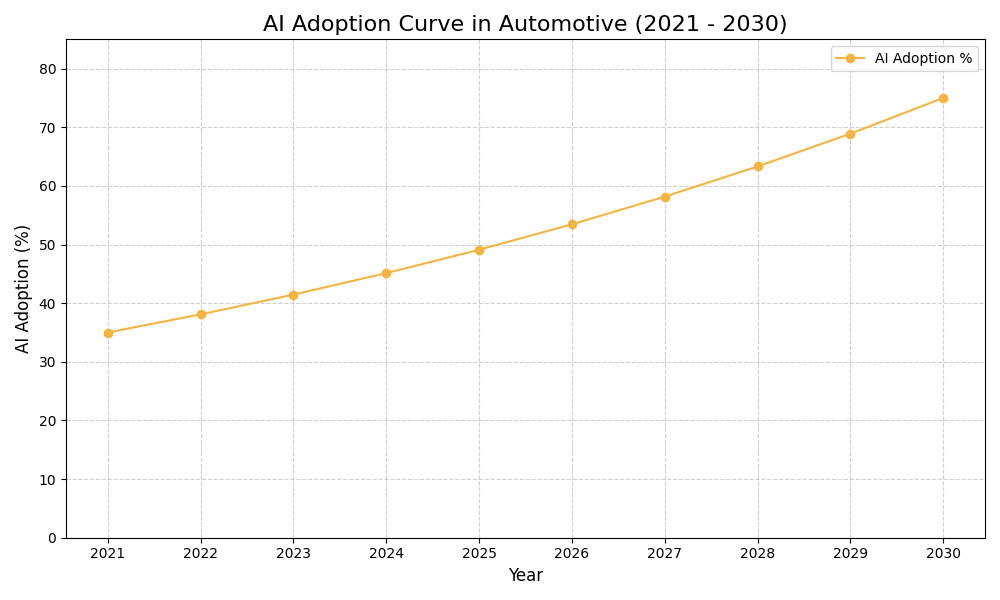
AI Use Case vs ROI Timeline
| AI Use Case | Description | Typical ROI Timeline | Expected ROI Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Defect Detection Automation | Implementing AI-driven computer vision to automatically identify defects in products during assembly. For example, cameras scan components for scratches or misalignments, reducing manual inspection time and errors. | 6-12 months | High |
| Real-Time Process Monitoring | Using computer vision to monitor assembly line processes in real-time. For example, AI analyzes video feeds to ensure machinery operates within optimal parameters, alerting operators to deviations immediately. | 6-12 months | Medium-High |
| Predictive Maintenance Alerts | Leveraging AI to analyze visual data from assembly line equipment to predict maintenance needs. For example, visual inspections can indicate wear on machinery, prompting timely maintenance before breakdowns occur. | 12-18 months | Medium-High |
| Worker Safety Compliance Monitoring | Employing AI for monitoring worker safety gear compliance on the assembly line. For example, cameras check if workers are wearing helmets and gloves, ensuring adherence to safety protocols. | 6-12 months | High |
Glossary
Work with Atomic Loops to architect your AI implementation roadmap — from PoC to enterprise scale.
Contact NowFrequently Asked Questions
- Computer Vision enhances production efficiency by automating visual inspections in manufacturing.
- It enables real-time monitoring of assembly line processes, reducing human error significantly.
- AI-driven algorithms analyze visual data to detect defects and quality issues promptly.
- The technology supports predictive maintenance by identifying equipment anomalies early.
- Overall, it improves product quality and operational reliability across automotive production lines.
- Begin by assessing current processes to identify areas for improvement with Computer Vision.
- Engage stakeholders to define objectives and establish a clear implementation roadmap.
- Pilot projects can help validate the technology before full-scale deployment.
- Integrate Computer Vision systems with existing manufacturing software for seamless operation.
- Train staff to adapt to new technologies, ensuring smooth transitions and adoption.
- AI enhances operational efficiency by reducing manual inspection times significantly.
- It leads to better quality control, minimizing defects and rework costs.
- Organizations experience improved decision-making through data-driven insights from AI analysis.
- Cost savings from reduced labor and increased production capacity are substantial.
- Ultimately, AI provides a competitive edge by accelerating innovation and responsiveness.
- Common challenges include resistance to change among staff and existing workflows.
- Data quality issues can hinder the effectiveness of Computer Vision solutions.
- Integration with legacy systems may require additional resources and time.
- Addressing cybersecurity concerns is crucial to protect sensitive manufacturing data.
- Developing clear strategies for training and support can mitigate implementation risks.
- The adoption is most effective during planned upgrades or digital transformation initiatives.
- Organizations should consider market pressures and competitive dynamics as motivators.
- Early adoption can lead to significant long-term cost savings and efficiency gains.
- Evaluate readiness by assessing current technology and workforce capabilities.
- Align adoption with strategic business goals for maximum impact and ROI.
- Compliance with safety regulations is paramount when implementing AI technologies.
- Data privacy laws affect how visual data is collected and processed.
- It's essential to stay updated on industry standards for quality assurance practices.
- Collaboration with regulatory bodies can ensure adherence to legal requirements.
- Establishing clear documentation and protocols supports compliance efforts effectively.
- Organizations typically see a decrease in defect rates, enhancing overall product quality.
- Time savings in inspection processes can lead to increased production throughput.
- Cost reductions in labor and materials contribute to better profit margins.
- Real-time analytics provide actionable insights for continuous improvement initiatives.
- Improved customer satisfaction metrics result from higher-quality products and faster delivery.
- Start with a clear strategy that aligns AI capabilities with business objectives.
- Conduct thorough training sessions to equip staff with necessary skills and knowledge.
- Regularly monitor and evaluate AI systems for performance and optimization opportunities.
- Collaborate with technology partners to leverage expertise in Computer Vision solutions.
- Foster a culture of innovation to encourage ongoing improvements and adaptation.

