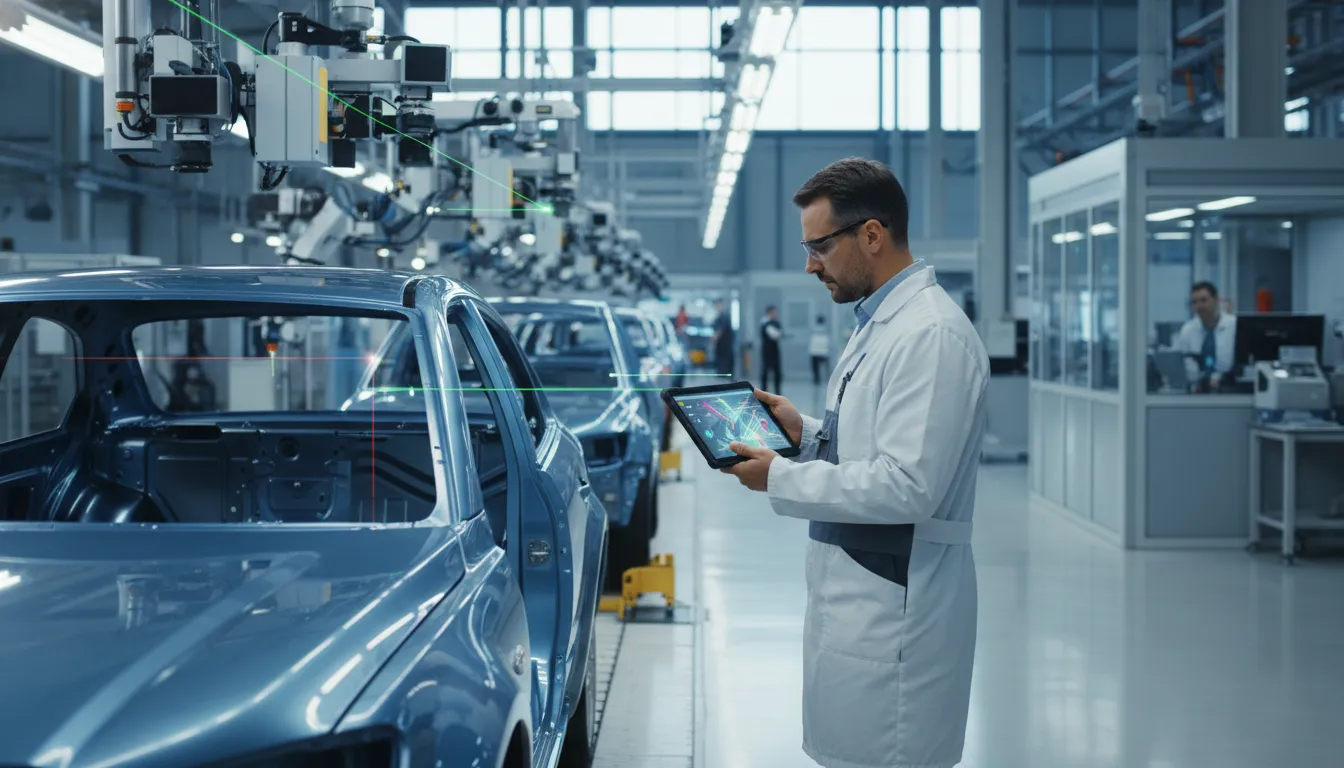
Computer Vision for Defect Detection
In the Automotive sector, "Computer Vision for Defect Detection" refers to the use of advanced imaging technologies and algorithms to identify faults during manufacturing and quality assurance processes. This innovative approach enhances the precision of inspections and significantly reduces the risk of defects in vehicles, which is critical as consumer expectations for quality and reliability continue to rise. By integrating computer vision systems, stakeholders can streamline operations and ensure that safety standards are met, aligning with the broader trend of leveraging AI to boost operational efficiency and strategic capabilities.
The significance of this technology within the Automotive ecosystem cannot be overstated. AI-driven computer vision practices are redefining competitive landscapes, fostering innovation cycles that prioritize quicker and more accurate defect detection. This transformation enhances efficiency, optimizes decision-making, and shapes long-term strategic goals for manufacturers. Despite the promising outlook, challenges such as integration complexity, varying levels of AI maturity, and changing stakeholder expectations remain. Embracing these advancements presents substantial growth opportunities, urging companies to navigate the evolving landscape while addressing potential barriers to implementation.
Transform Your Quality Control with AI-Driven Computer Vision Solutions
Automotive companies should strategically invest in partnerships focused on AI-enhanced Computer Vision for Defect Detection while prioritizing data integrity and security. By implementing these technologies, businesses can expect significant improvements in defect identification, operational efficiency, and overall product quality, driving competitive advantages in the marketplace.
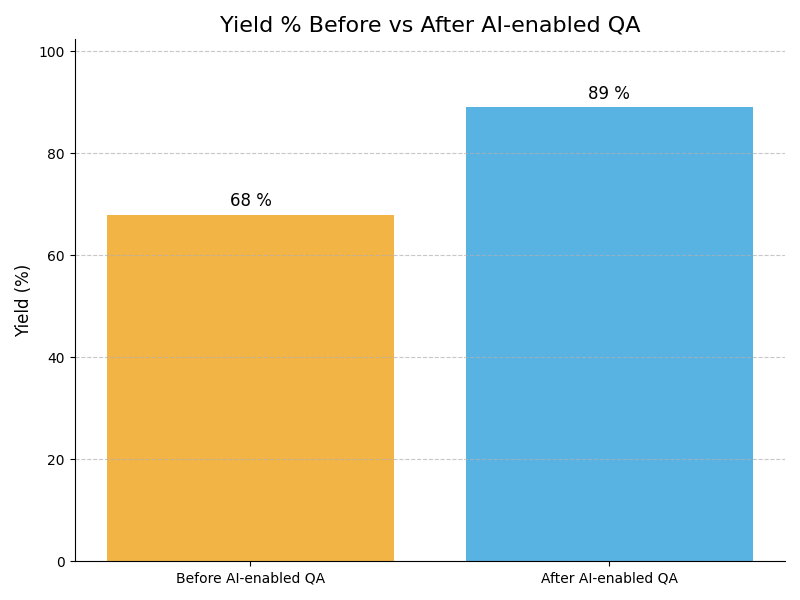
How is AI Transforming Defect Detection in the Automotive Industry?
Implementation Framework
Evaluate operational workflows to identify key areas where computer vision can enhance defect detection, ensuring alignment with business objectives and enabling more efficient quality control processes across production lines.
Industry Standards
Research and select advanced AI technologies tailored for computer vision applications, ensuring compatibility with existing systems to enhance defect detection capabilities and streamline operational processes across the automotive supply chain.
Technology Partners
Implement training protocols to develop AI models that recognize defects in automotive components, utilizing high-quality image datasets to enhance accuracy and reduce false positives in detection processes across production lines.
Internal R&D
Seamlessly integrate AI-driven computer vision systems into existing automotive production workflows to enhance real-time defect detection capabilities, ensuring minimal disruption and fostering a culture of continuous improvement and quality assurance.
Cloud Platform
Conduct regular assessments of AI-enhanced defect detection systems to evaluate their performance, making necessary adjustments to algorithms and processes based on data-driven insights to continuously improve quality control standards.
Industry Standards
Best Practices for Automotive Manufacturers
-
Impact : Enhances defect detection accuracy significantly
Example : Example: In an automotive assembly line, a vision-based AI system flags microscopic paint defects in real time as car bodies pass under cameras, catching flaws human inspectors previously missed during night shifts.
-
Impact : Reduces production downtime and costs
Example : Example: A semiconductor factory uses AI to detect early soldering anomalies. The system stops the line immediately, preventing a full batch failure that would have caused hours of rework and shutdown.
-
Impact : Improves quality control standards
Example : Example: A food packaging plant uses AI image recognition to verify seal integrity on every packet, ensuring non-compliant packages are rejected instantly before shipping.
-
Impact : Boosts overall operational efficiency
Example : Example: AI dynamically adjusts inspection thresholds based on production speed, allowing the factory to increase output during peak demand without sacrificing quality.
-
Impact : High initial investment for implementation
Example : Example: A mid-sized electronics manufacturer delays AI rollout after realizing camera hardware, GPUs, and system integration push upfront costs beyond budget approvals.
-
Impact : Potential data privacy concerns
Example : Example: AI quality systems capturing worker activity unintentionally store employee facial data, triggering compliance issues with internal privacy policies.
-
Impact : Integration challenges with existing systems
Example : Example: AI software cannot communicate with a 15-year-old PLC controller, forcing engineers to manually export data and slowing decision-making.
-
Impact : Dependence on continuous data quality
Example : Example: Dust accumulation on camera lenses causes the AI to misclassify normal products as defective, leading to unnecessary scrap until recalibration.
-
Impact : Increases detection speed for defects
Example : Example: A major automotive manufacturer implements real-time monitoring, allowing instant detection of assembly line defects, resulting in a 30% reduction in faulty units produced each month.
-
Impact : Minimizes human error during inspections
Example : Example: A vehicle production plant reduces inspection errors significantly by using real-time vision systems, leading to a 25% decrease in rework costs within six months.
-
Impact : Enables immediate corrective actions
Example : Example: An electric vehicle factory uses continuous monitoring to spot defects instantly, enabling engineers to adjust machinery settings on-the-fly, improving overall production quality.
-
Impact : Improves resource allocation during production
Example : Example: By employing real-time data analytics, a car manufacturer optimizes labor deployment, ensuring maintenance teams are allocated to areas needing immediate attention, enhancing efficiency.
-
Impact : Requires reliable network infrastructure
Example : Example: A luxury car manufacturer faces production delays due to inadequate network infrastructure, which causes real-time monitoring systems to lag, preventing timely defect detection.
-
Impact : Potential for system overload during peak
Example : Example: During a seasonal production ramp-up, an automotive plant’s real-time monitoring system experiences overload, resulting in delayed alerts and increased defect rates.
-
Impact : Risk of false positives in detection
Example : Example: A manufacturing line suffers from false positives when the AI misidentifies non-defective units as faulty, leading to unnecessary scrapping and increased costs.
-
Impact : Dependency on constant software updates
Example : Example: Frequent software updates needed for real-time systems lead to downtime, disrupting production schedules and impacting overall efficiency.
-
Impact : Enhances employee skills in AI tools
Example : Example: A global automotive firm invests in regular AI training workshops, leading to a 40% increase in employee confidence and competence when using new defect detection systems.
-
Impact : Fosters an adaptive work culture
Example : Example: By providing ongoing training, a car manufacturer fosters a culture of innovation, resulting in employees proactively suggesting improvements that lead to a 15% productivity boost.
-
Impact : Reduces resistance to new technologies
Example : Example: A medium-sized auto parts supplier notices a sharp decline in technology resistance as regular training sessions make employees more comfortable with AI tools and systems.
-
Impact : Increases overall team productivity
Example : Example: Training sessions equip workers with skills to effectively address AI system alerts, increasing production efficiency by 20% due to quicker response times.
-
Impact : Training resources may be underfunded
Example : Example: A new automotive startup struggles to allocate sufficient budget for training resources, leading to a workforce unable to properly utilize AI defect detection tools and inefficiencies in production.
-
Impact : Employee turnover may disrupt training
Example : Example: High turnover rates in a plant mean that training sessions need to be repeated frequently, costing time and delaying full implementation of AI systems.
-
Impact : Resistance from less tech-savvy workers
Example : Example: Employees resistant to adopting AI technologies express frustration during training, which hampers team dynamics and slows down the integration process.
-
Impact : Long learning curves for complex systems
Example : Example: Workers face long learning curves with advanced AI systems, resulting in initial drops in productivity as they struggle to adapt to new workflows.
-
Impact : Drives innovation in defect detection
Example : Example: An automotive manufacturer establishes a continuous improvement program that leads to innovative AI solutions, increasing defect detection rates by 25% within a year.
-
Impact : Promotes a culture of excellence
Example : Example: By fostering a culture of excellence, a car company enhances team performance, resulting in a 30% reduction in defective parts produced during assembly.
-
Impact : Enhances competitiveness in the market
Example : Example: An auto manufacturer’s commitment to continuous improvement helps it respond to market demands swiftly, allowing for quicker adaptations in production processes and reducing lead times.
-
Impact : Facilitates rapid adaptation to changes
Example : Example: Regular evaluations of defect detection systems lead to ongoing improvements, keeping the company competitive in a fast-evolving automotive market.
-
Impact : Requires ongoing financial investment
Example : Example: An automotive firm finds that ongoing investments in continuous improvement initiatives strain budgets, leading to reluctance in pursuing further AI advancements in defect detection.
-
Impact : Potential employee burnout from constant change
Example : Example: Employees express fatigue from continuous changes in processes, resulting in decreased morale and productivity as they struggle to keep up with new methods and technologies.
-
Impact : Difficult to measure improvement success
Example : Example: A manufacturer struggles to quantify the success of its continuous improvement efforts, making it difficult to justify further investments in AI systems for defect detection.
-
Impact : Resistance to new methodologies
Example : Example: Resistance to adopting new methodologies hampers the effectiveness of continuous improvement initiatives, leading to stagnation in defect detection advancements.
-
Impact : Improves decision-making processes
Example : Example: A leading automotive company leverages data analytics to make informed decisions regarding defect detection, resulting in a 20% improvement in production efficiency over six months.
-
Impact : Identifies patterns in defects
Example : Example: By analyzing defect patterns, an automotive manufacturer identifies recurrent issues in its supply chain, leading to targeted corrective actions and a 15% decrease in defects.
-
Impact : Optimizes resource allocation
Example : Example: Data analytics insights enable a car manufacturer to optimize resource allocation, improving production scheduling and reducing idle times by 30%.
-
Impact : Enhances predictive maintenance strategies
Example : Example: Predictive maintenance strategies based on data analytics result in fewer machine downtimes, allowing an automotive plant to maintain high-quality standards consistently.
-
Impact : Relies heavily on data accuracy
Example : Example: An automotive manufacturer finds that inaccurate data input leads to flawed analytics, resulting in misguided decisions that increase defect rates in production.
-
Impact : Requires skilled analysts for insights
Example : Example: A company struggles to hire skilled analysts for interpreting data insights, leading to missed opportunities for improvement in defect detection processes.
-
Impact : May lead to information overload
Example : Example: Employees become overwhelmed by excessive data analytics, causing confusion and delays in decision-making regarding defect detection strategies.
-
Impact : High costs for data storage solutions
Example : Example: The costs associated with advanced data storage solutions strain budgets, limiting the ability of automotive firms to fully leverage data analytics for defect detection.
AI-driven computer vision is revolutionizing defect detection in automotive manufacturing, ensuring precision and quality at unprecedented speeds.
– Bernard MarrCompliance Case Studies
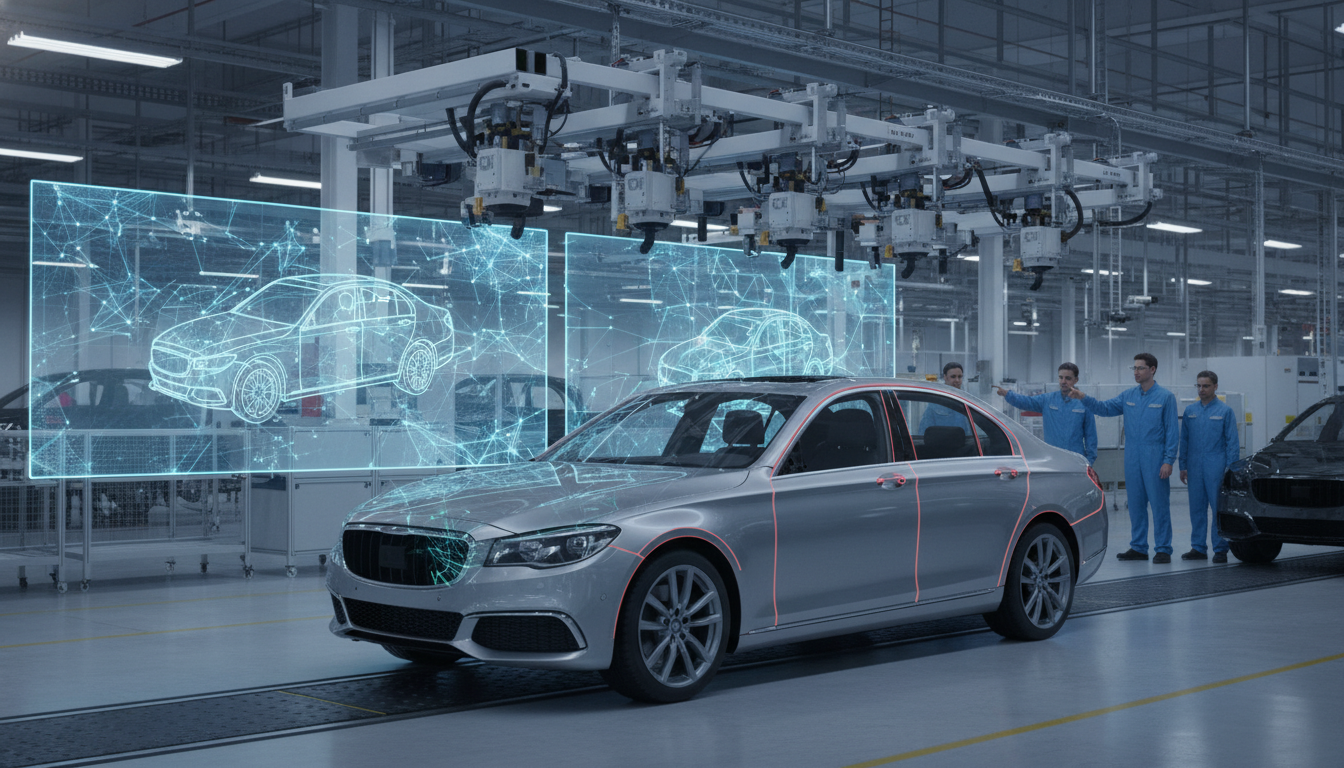
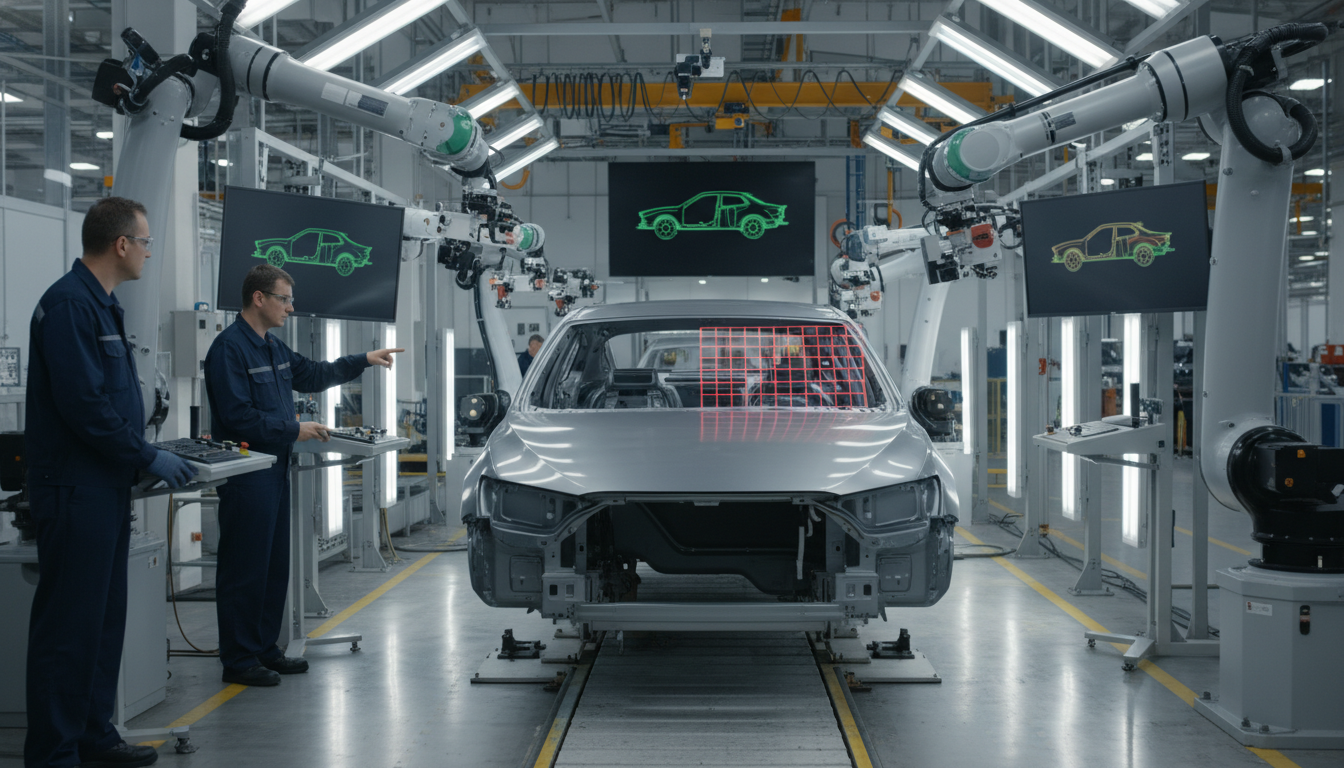
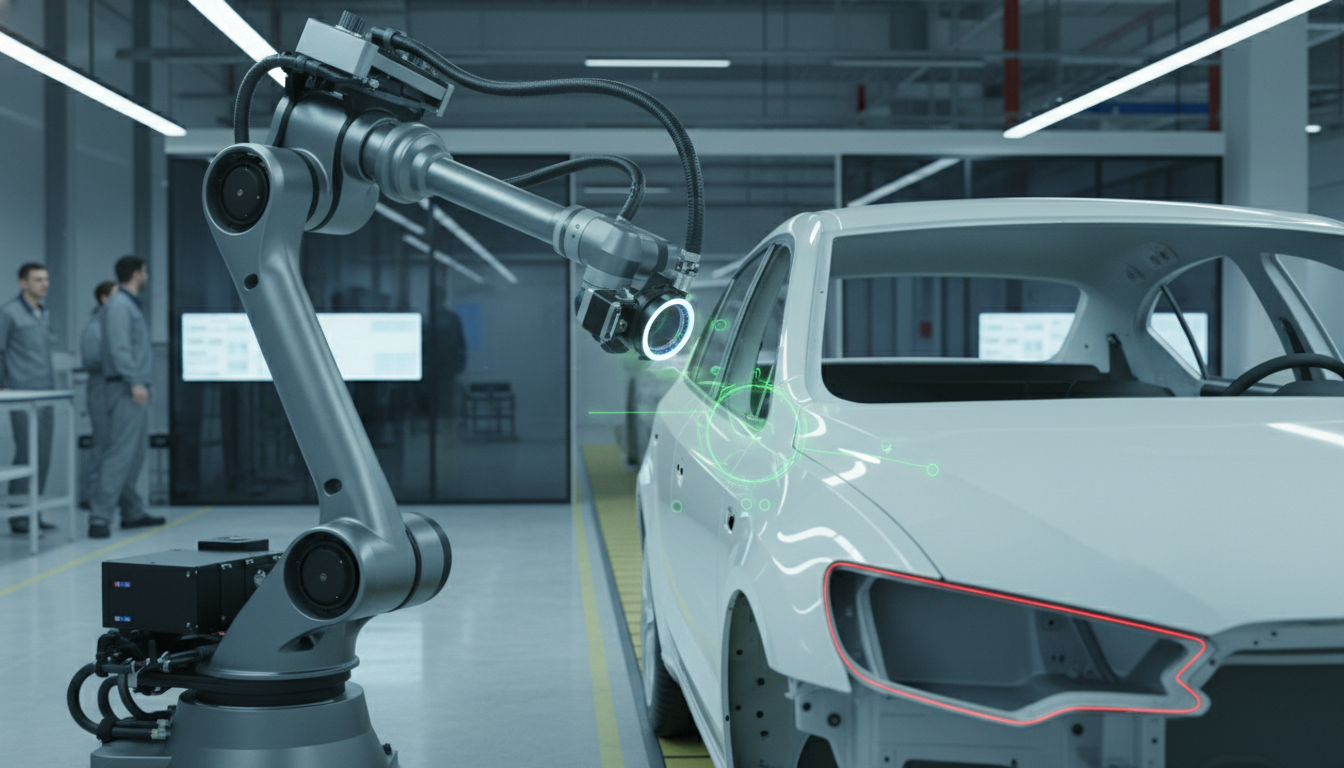




Embrace AI-driven Computer Vision to enhance quality control and outpace competitors. Transform your automotive processes for superior results and efficiency.

Leadership Challenges & Opportunities
Data Quality Challenges
Utilize Computer Vision for Defect Detection to enhance data integrity through real-time image processing and automated anomaly detection. Implement robust data validation protocols and feedback loops that continuously refine model accuracy. This ensures reliable insights for decision-making, reducing rework and improving overall product quality.
Integration with Legacy Systems
Adopt Computer Vision for Defect Detection using APIs to facilitate seamless integration with existing automotive systems. Implement middleware solutions to bridge data silos, enabling smooth data flow and interoperability. This strategy enhances operational efficiency without the need for complete system overhauls.
Resistance to Change
Foster a culture of innovation by involving stakeholders in the Computer Vision for Defect Detection implementation process. Conduct workshops and demonstrations to showcase benefits, leveraging success stories to build buy-in. This approach cultivates acceptance and enthusiasm, easing the transition to advanced technologies.
Talent Acquisition and Retention
Address talent shortages by integrating Computer Vision for Defect Detection with user-friendly tools and training programs. Collaborate with educational institutions for skill development and offer internships to attract new talent. This proactive strategy builds a skilled workforce adept in cutting-edge technologies.
Assess how well your AI initiatives align with your business goals

AI Use Case vs ROI Timeline
| AI Use Case | Description | Typical ROI Timeline | Expected ROI Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automated Visual Inspection Systems | AI-driven cameras inspect automotive parts for defects in real-time. For example, an assembly line uses computer vision to detect flaws in paint quality, reducing rework time significantly and enhancing overall quality control. | 6-12 months | High |
| Predictive Maintenance through Imaging | Utilizing computer vision to monitor machinery for wear and tear. For example, sensors on manufacturing equipment detect visual anomalies, allowing for timely maintenance before failures occur, thereby minimizing downtime and repair costs. | 12-18 months | Medium-High |
| Quality Assurance in Assembly Lines | Implementing AI systems that analyze assembly line products for defects. For example, a car manufacturer uses computer vision to check for loose components, ensuring each vehicle meets safety standards before leaving the line. | 6-9 months | High |
| Defect Tracking and Reporting | AI tools track defect trends over time using image data. For example, a company collects defect images from production runs, identifying patterns that guide design improvements and process adjustments. | 9-12 months | Medium-High |
Glossary
Work with Atomic Loops to architect your AI implementation roadmap — from PoC to enterprise scale.
Contact NowFrequently Asked Questions
- Computer Vision for Defect Detection employs AI to identify flaws during production.
- It automates visual inspections, enhancing accuracy and speed in quality assurance.
- The technology significantly reduces human error and operational costs.
- It enables real-time monitoring and data collection for continuous improvement.
- Organizations can leverage insights for better decision-making and quality control.
- Start by assessing your current production processes and technological capabilities.
- Engage stakeholders to define clear objectives and success metrics for implementation.
- Select appropriate AI tools and frameworks that integrate seamlessly with existing systems.
- Pilot projects can demonstrate feasibility before full-scale deployment.
- Train staff on new technologies to ensure smooth transitions and user adoption.
- AI-driven defect detection reduces costs associated with manual inspections and errors.
- It enhances product quality and reliability, leading to improved customer satisfaction.
- The technology provides a competitive edge through faster production cycles.
- Automated systems enable more efficient resource allocation and labor utilization.
- Investing in AI allows for scalability and adaptability in evolving market demands.
- Integration with legacy systems can be a significant hurdle during implementation.
- Data quality and accuracy are critical for successful AI model training.
- Staff resistance to new technology can slow down adoption rates.
- Budget constraints may limit the scope of initial implementations.
- Establishing clear metrics is essential for evaluating success and making adjustments.
- Organizations should consider adoption during new product launches or process overhauls.
- Early implementation can help in addressing quality issues from the start.
- Assess market demands, as competition may drive the need for faster production.
- Timing should align with technological readiness and available resources.
- Regular evaluations of existing processes can highlight opportunities for timely adoption.
- Applications include detecting paint defects, surface irregularities, and assembly errors.
- Computer Vision systems can monitor component wear and tear during production.
- The technology assists in verifying compliance with safety and regulatory standards.
- Real-time analysis can help in optimizing supply chain quality control.
- Industry benchmarks guide implementation strategies to meet quality expectations.
- Start with a clear understanding of specific defect types to target.
- Involve cross-functional teams to ensure comprehensive feedback and insights.
- Invest in high-quality training data to improve AI model accuracy.
- Regularly update systems and retrain models to adapt to new challenges.
- Monitor outcomes continuously to refine processes and enhance performance.
- Initial investment includes software, hardware, and integration costs with existing systems.
- Consider ongoing maintenance costs and updates for AI models and systems.
- Evaluate potential savings from reduced labor costs and improved efficiency.
- Long-term ROI can stem from enhanced product quality and customer loyalty.
- Budgeting for pilot projects can mitigate risks before full-scale investments.

