Computer Vision for Surface Inspection
In the Automotive sector, "Computer Vision for Surface Inspection" refers to the use of advanced image analysis technologies to assess the quality and integrity of vehicle surfaces. This innovative approach enables manufacturers to detect defects and ensure high standards of production, thereby enhancing overall vehicle safety and performance. As the industry increasingly embraces digital transformation, this technology aligns with broader AI-led initiatives aimed at improving operational efficiency and product excellence.
The integration of AI within Computer Vision practices is significantly reshaping the Automotive landscape. Stakeholders are witnessing a shift in competitive dynamics, as organizations leverage these technologies to accelerate innovation and streamline processes. This AI-driven approach not only enhances decision-making but also fosters deeper collaboration among players in the ecosystem. However, while the potential for growth is substantial, challenges such as integration complexities and evolving expectations must be addressed to fully realize the benefits of this transformative technology.
Leverage AI for Enhanced Surface Inspection in Automotive Manufacturing
Automotive companies should strategically invest in partnerships focused on AI-driven Computer Vision technologies to enhance surface inspection processes. By implementing these advanced systems, they can expect significant improvements in quality control, reduction in production costs, and an overall boost in competitive advantage.
Transforming Quality Control: The Role of Computer Vision in Automotive Surface Inspection
Implementation Framework
Evaluate current surface inspection technologies and systems to identify gaps and opportunities for integrating AI-driven computer vision solutions, enhancing efficiency and accuracy in automotive production processes and ensuring high-quality standards.
Technology Partners
Deploy advanced machine learning algorithms to automate defect detection in surface inspection, improving accuracy and speed, thus enabling timely quality control decisions that enhance product reliability and customer satisfaction.
Industry Standards
Utilize historical inspection data to train machine learning models, enhancing their ability to identify defects accurately. This process improves the system's reliability and reduces false positives during automotive quality assessments.
Internal R&D
Establish real-time monitoring systems that leverage AI-driven computer vision for continuous surface inspection, enabling immediate detection of defects and facilitating proactive quality management throughout the automotive production line.
Cloud Platform
Create optimized feedback loops that allow AI systems to learn from inspection results, continuously improving detection algorithms and adapting to new challenges in surface inspection, ensuring ongoing operational excellence.
Technology Partners
Best Practices for Automotive Manufacturers
-
Impact : Increases defect detection rates significantly
Example : Example: A leading automotive manufacturer integrates advanced machine learning models, increasing defect detection rates by 25%. The system identifies minor surface flaws, which human inspectors often overlook, leading to significant quality improvements.
-
Impact : Optimizes inspection process workflows
Example : Example: By optimizing inspection workflows, a car assembly plant reduces cycle time by 15%. The AI model streamlines the inspection process, allowing for faster turnaround without compromising quality.
-
Impact : Reduces false positives in assessments
Example : Example: A manufacturer experiences a 30% reduction in false positives after implementing a refined AI model. This leads to fewer unnecessary reworks, saving time and resources in the production line.
-
Impact : Enhances real-time decision-making capabilities
Example : Example: A smart factory utilizes real-time decision-making capabilities of AI to dynamically adjust inspection criteria based on current production speed, ensuring high-quality output during peak times.
-
Impact : Complex model training requirements
Example : Example: A car manufacturer struggles with complex model training requirements, leading to delays in deployment. The intricate data needs result in extended timelines that push back the project schedule significantly.
-
Impact : High reliance on labeled training data
Example : Example: A new AI inspection system fails due to insufficient labeled training data. The lack of comprehensive datasets causes the model to underperform, resulting in missed defects on production lines.
-
Impact : Potential for model drift over time
Example : Example: Over time, an AI model experiences drift, leading to outdated performance metrics. The system flags fewer defects than before, resulting in a decline in product quality, unnoticed until customer complaints arise.
-
Impact : Integration costs with current systems
Example : Example: A major automotive plant faces high integration costs when connecting AI systems to legacy machinery. This unexpected financial burden forces the organization to reassess its technological investments.
-
Impact : Increases operational transparency and control
Example : Example: Implementing real-time monitoring in an automotive plant allows managers to oversee production processes continuously. This transparency leads to quicker adjustments and enhanced control over quality assurance measures.
-
Impact : Facilitates immediate issue detection
Example : Example: Real-time monitoring systems detect defects instantly, allowing for immediate corrective action. A car manufacturer stops the line promptly when a paint defect is detected, minimizing scrap rates.
-
Impact : Enhances responsiveness to production anomalies
Example : Example: An automotive assembly line experiences a 40% improvement in responsiveness to production anomalies due to real-time monitoring. Teams can address issues promptly, preventing cascading failures.
-
Impact : Improves collaboration across teams
Example : Example: With real-time data sharing, collaboration between quality control and production teams improves. A plant ensures everyone is aligned, significantly boosting overall efficiency and product quality.
-
Impact : Over-reliance on automated systems
Example : Example: A manufacturer becomes over-reliant on automated monitoring systems, leading to complacency among operators. This dependency results in missed manual inspections and a rise in defects escaping quality checks.
-
Impact : High costs of continuous monitoring
Example : Example: The costs of continuous monitoring systems escalate for a large automotive plant. Unexpected expenses force management to reconsider the sustainability of their AI investments, impacting budget allocations.
-
Impact : Potential for system overload
Example : Example: A system overload occurs during peak production, causing delays in defect detection. The AI struggles to process high volumes of data, leading to an increased risk of undetected flaws in vehicles.
-
Impact : Data accuracy issues affecting decisions
Example : Example: Data accuracy issues arise when sensors are miscalibrated, affecting decision-making processes. A faulty sensor leads to incorrect assessments, resulting in defective vehicles reaching customers.
-
Impact : Enhances team adaptability to technology
Example : Example: A car manufacturer conducts regular training sessions, enhancing team adaptability to new AI technologies. Employees become more proficient, leading to smoother AI integration into the inspection process.
-
Impact : Reduces resistance to AI implementation
Example : Example: Resistance to AI implementation decreases significantly after consistent training programs. Employees feel more confident in using AI tools, resulting in improved quality control efforts throughout the production line.
-
Impact : Improves overall operational efficiency
Example : Example: Regular workforce training results in a 20% increase in overall operational efficiency. Employees are better equipped to handle AI systems, leading to fewer errors and higher productivity levels.
-
Impact : Increases employee engagement and morale
Example : Example: Training enhances employee engagement and morale. Workers feel valued and more connected to the technology, fostering a culture of innovation and continuous improvement in the automotive sector.
-
Impact : Training may not cover all scenarios
Example : Example: Training programs fail to cover specific inspection scenarios, leaving employees unprepared. This gap leads to increased defect rates, as workers struggle with unforeseen challenges during inspections.
-
Impact : Short-term productivity loss during training
Example : Example: A temporary short-term productivity loss occurs as employees undergo training. The downtime affects production schedules, creating delays in vehicle deliveries and impacting customer satisfaction.
-
Impact : Inconsistent training quality across teams
Example : Example: Inconsistent training quality across different teams leads to disparities in AI usage. Some teams excel while others struggle, causing friction and inefficiencies in the overall production process.
-
Impact : Employee turnover impacting knowledge retention
Example : Example: High employee turnover results in knowledge retention issues. New hires are not adequately trained, leading to a lack of familiarity with AI systems, ultimately affecting quality inspection outcomes.
-
Impact : Ensures high-quality training datasets
Example : Example: A manufacturer develops robust data management strategies to ensure high-quality training datasets. This leads to improved AI performance in defect detection, enhancing overall product quality.
-
Impact : Facilitates easier model updates and maintenance
Example : Example: By standardizing data management practices, an automotive company facilitates easier model updates. This proactive approach ensures that AI models adapt to new production standards quickly and efficiently.
-
Impact : Reduces data redundancy and inefficiencies
Example : Example: Implementing effective data management reduces redundancy and inefficiencies in data collection processes. This streamlines operations and leads to significant cost savings in the long run.
-
Impact : Enhances compliance with industry regulations
Example : Example: A robust data management framework enhances compliance with industry regulations. The automotive plant ensures all data handling meets legal requirements, minimizing the risk of penalties or compliance issues.
-
Impact : Complexity in managing large datasets
Example : Example: Complexity in managing large datasets becomes a significant hurdle for an automotive manufacturer. Their outdated systems struggle to handle big data, causing delays in AI deployment and impacting quality assurance.
-
Impact : Potential data loss during migrations
Example : Example: A data migration process leads to potential data loss, affecting training datasets for AI models. This oversight results in inaccuracies in defect detection, ultimately harming product quality.
-
Impact : Resistance to new data practices
Example : Example: Employees show resistance to new data management practices, preferring old methods. This pushback delays the implementation of AI solutions, hindering overall operational efficiency in the automotive plant.
-
Impact : High costs of data management solutions
Example : Example: The high costs associated with advanced data management solutions strain the budget of a mid-sized automotive firm. This financial burden forces the organization to delay AI integration initiatives.
-
Impact : Brings specialized knowledge to projects
Example : Example: A car manufacturer collaborates with AI experts, bringing specialized knowledge to their surface inspection projects. This partnership speeds up the implementation process and ensures higher-quality AI outputs.
-
Impact : Accelerates AI implementation timelines
Example : Example: By leveraging expert insights, an automotive firm accelerates its AI implementation timeline. The collaboration allows for quicker identification of optimal solutions for surface inspections.
-
Impact : Enhances innovation through diverse perspectives
Example : Example: Collaborating with AI experts enhances innovation within the automotive sector. Diverse perspectives lead to creative approaches in defect detection, pushing the boundaries of traditional inspection methods.
-
Impact : Improves troubleshooting and support capabilities
Example : Example: The partnership improves troubleshooting capabilities. When issues arise, AI experts provide immediate support, ensuring minimal disruption to production lines and maintaining high quality standards.
-
Impact : Dependency on external expertise
Example : Example: A manufacturer becomes overly dependent on external AI experts, leading to a lack of in-house capabilities. This reliance becomes problematic when expert availability decreases, impacting project continuity.
-
Impact : Potential misalignment with internal goals
Example : Example: Potential misalignment with internal goals occurs when AI experts propose solutions that do not align with the company’s vision. This disconnect leads to wasted resources and potential project failures.
-
Impact : Higher costs for expert consultations
Example : Example: The costs associated with expert consultations escalate, straining the company's budget. The unexpected financial burden forces management to reassess future collaborations and project scopes.
-
Impact : Knowledge transfer challenges after project completion
Example : Example: After project completion, knowledge transfer challenges arise as experts leave. The internal team struggles to maintain and update the AI systems without adequate training or documentation from the consultants.
AI-driven computer vision is revolutionizing surface inspection in automotive, ensuring precision and quality at unprecedented speeds.
– Internal R&DCompliance Case Studies



Elevate your automotive quality control with AI-driven computer vision. Seize the opportunity to enhance efficiency, reduce errors, and outperform the competition today!
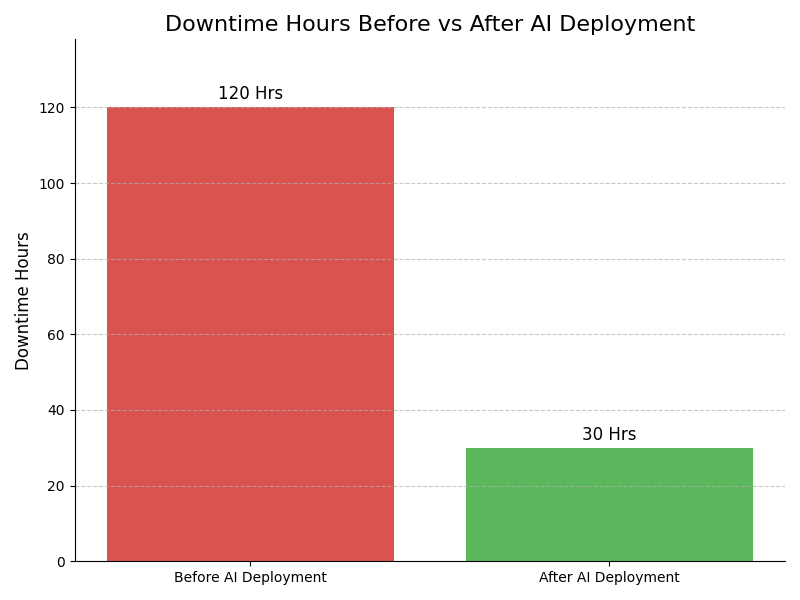

Leadership Challenges & Opportunities
Data Quality Challenges
Utilize Computer Vision for Surface Inspection to automate data collection and analysis, ensuring high accuracy and consistency. Implement advanced algorithms to filter out noise and enhance image quality. This approach minimizes human error, providing reliable data for quality assurance and decision-making.
Integration with Legacy Systems
Adopt a phased approach for integrating Computer Vision for Surface Inspection into existing Automotive systems. Use API-based solutions to bridge legacy technologies with modern capabilities, enabling seamless data flow and operational continuity. This strategy reduces disruption while enhancing overall inspection efficiency.
Resistance to Change
Foster a culture embracing innovation by demonstrating the benefits of Computer Vision for Surface Inspection through pilot projects. Engage stakeholders early, providing training and resources to ease transitions. Highlight successful case studies to build confidence and encourage widespread adoption across the organization.
High Implementation Costs
Leverage cost-effective, cloud-based Computer Vision for Surface Inspection solutions that minimize upfront investment. Start with targeted applications that yield immediate ROI, allowing for reinvestment into broader implementations. Utilize financial modeling to demonstrate long-term savings and value, making a compelling case for adoption.
Assess how well your AI initiatives align with your business goals
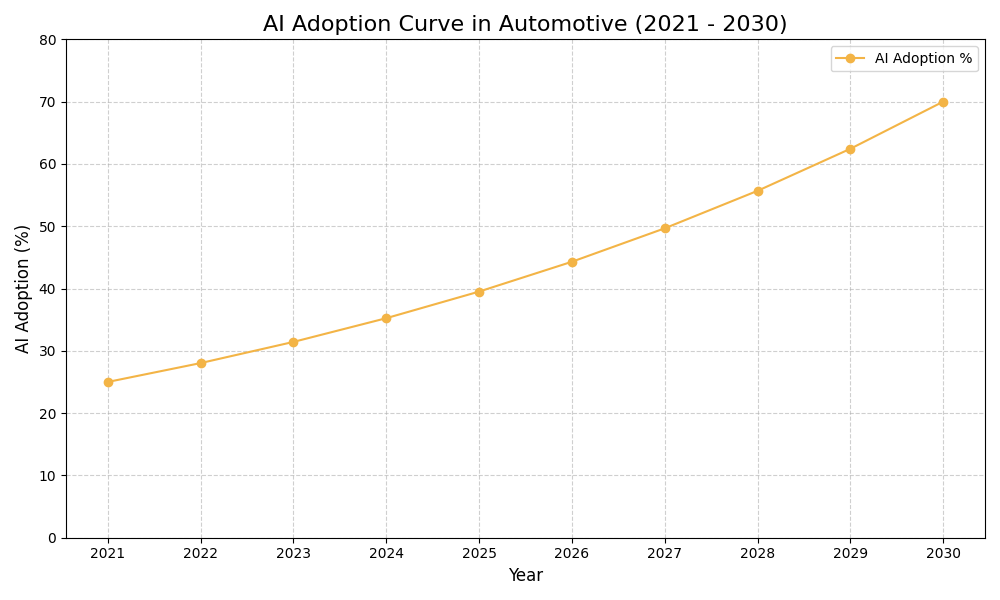
AI Use Case vs ROI Timeline
| AI Use Case | Description | Typical ROI Timeline | Expected ROI Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automated Defect Detection | Utilizing AI-driven cameras to identify surface defects on automotive parts in real-time. For example, a manufacturer uses this technology to ensure quality control on paint finishes, reducing human error and inspection time. | 6-12 months | High |
| Predictive Maintenance Alerts | Implementing computer vision to monitor equipment conditions and predict maintenance needs. For example, an automotive assembly line uses AI to analyze machinery wear, preventing unexpected breakdowns and production halts. | 12-18 months | Medium-High |
| Surface Quality Analysis | Employing AI tools to assess surface quality during production. For example, an automotive parts supplier uses AI to analyze the texture of molded components, ensuring they meet specifications before delivery. | 6-12 months | Medium-High |
| In-line Process Verification | Using computer vision to verify that production processes are followed correctly. For example, an automotive manufacturer applies AI to confirm that assembly steps are executed properly, reducing rework costs. | 6-12 months | High |
Glossary
Work with Atomic Loops to architect your AI implementation roadmap — from PoC to enterprise scale.
Contact NowFrequently Asked Questions
- Computer Vision for Surface Inspection automates visual checks using AI technology.
- This technology identifies defects, ensuring quality control in automotive manufacturing.
- It streamlines processes, reducing human error and improving efficiency.
- Organizations benefit from faster inspection cycles and consistent product quality.
- The approach enhances overall customer satisfaction by delivering superior products.
- Begin by assessing your current inspection processes and identifying areas for improvement.
- Select appropriate AI tools and platforms that fit your operational needs.
- Engage stakeholders for alignment and resource allocation throughout the process.
- Develop a pilot project to test the technology before full-scale implementation.
- Iterate based on findings to refine your approach and maximize effectiveness.
- AI enhances accuracy in defect detection, reducing costly recalls and rework.
- It enables real-time data analysis, providing actionable insights for decision-making.
- Businesses can achieve significant cost savings through process automation and efficiency.
- Improved quality control leads to higher customer satisfaction and brand loyalty.
- Organizations gain a competitive edge by innovating faster and reducing time to market.
- Common challenges include data quality issues that can affect AI performance.
- Integration with legacy systems may pose technical difficulties during deployment.
- Staff training is necessary to ensure smooth operation of new technologies.
- Managing change within the organization can create resistance among team members.
- Establishing a clear strategy for risk mitigation can address these obstacles effectively.
- The optimal time is during a planned technology upgrade or process overhaul.
- Consider implementing it when facing increased production demands or quality issues.
- Assess market conditions and competitive pressures to determine urgency.
- Align implementation with organizational goals and strategic initiatives for best results.
- Continuous evaluation of operational performance should guide timing decisions as well.
- Applications include detecting surface defects on painted and unpainted components.
- AI can monitor assembly line processes to ensure compliance with quality standards.
- It enhances safety inspections by identifying potential hazards in real-time.
- Automakers use it for evaluating parts and ensuring they meet regulatory requirements.
- This technology supports continuous improvement initiatives by providing actionable data insights.
- Establish clear metrics before implementation to track performance improvement.
- Monitor reductions in defect rates and associated cost savings over time.
- Evaluate increases in throughput and efficiency as direct benefits of AI adoption.
- Gather feedback from stakeholders to assess satisfaction and quality enhancements.
- Regularly review financial and operational data to ensure alignment with ROI expectations.
- Stay updated on industry standards and compliance requirements related to quality.
- Ensure that your technology complies with safety regulations governing manufacturing.
- Data privacy regulations must be adhered to when processing visual data.
- Understand how AI technologies align with existing legal frameworks in your region.
- Regular audits can help ensure ongoing compliance and mitigate potential risks.

