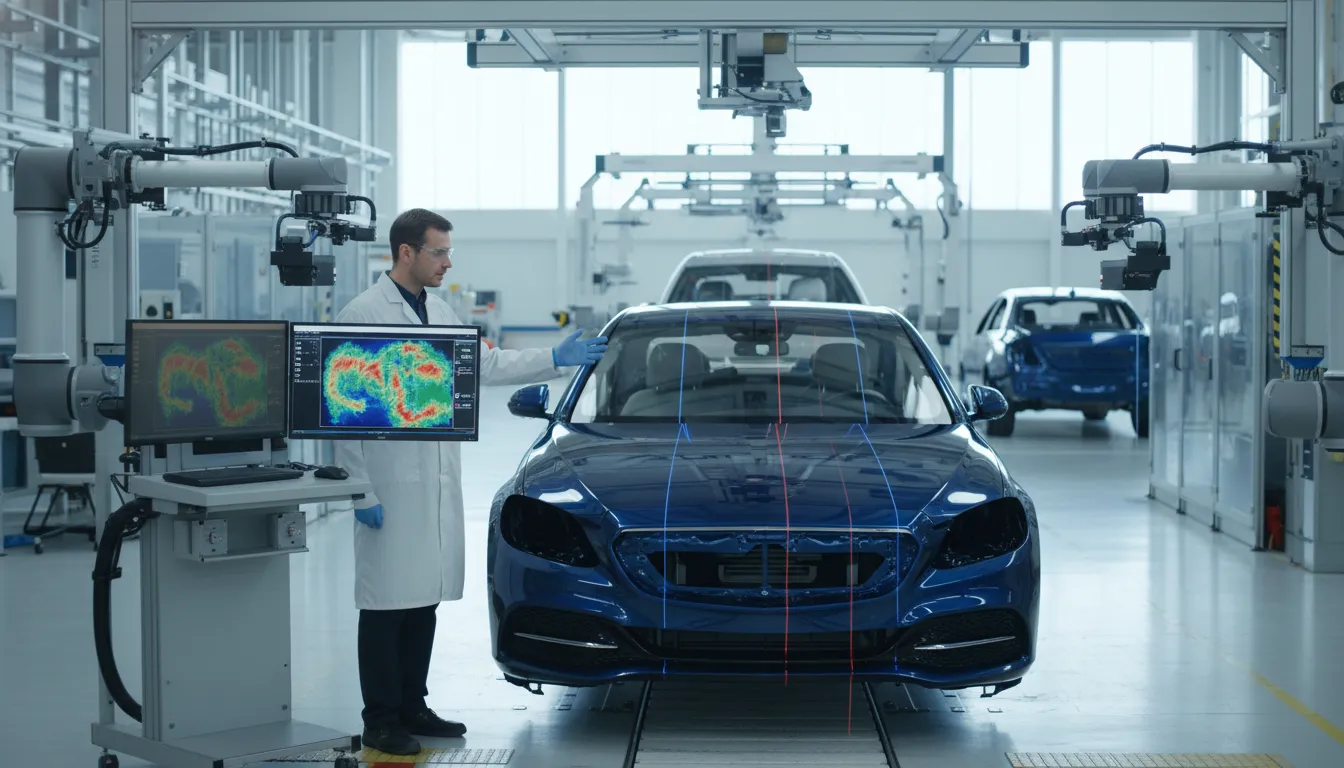
Computer Vision in Paint Defect Inspection
Computer Vision in Paint Defect Inspection is an innovative approach that leverages advanced imaging technologies to identify imperfections in vehicle finishes. This method is crucial for ensuring quality control within the automotive sector, as it allows manufacturers to detect flaws that may compromise product integrity and customer satisfaction. By integrating this technology into production lines, stakeholders can enhance operational efficiency and maintain competitive advantage. The relevance of this approach is underscored by the ongoing AI-led transformation, which is reshaping traditional practices and aligning with modern strategic priorities.
The significance of the Automotive ecosystem in relation to Computer Vision in Paint Defect Inspection is profound. AI-driven methodologies are not only streamlining inspection processes but also redefining competitive dynamics and innovation cycles. As manufacturers adopt these technologies, they can enhance decision-making, improve overall efficiency, and strategically position themselves for future advancements. However, challenges such as integration complexity, adoption barriers, and evolving stakeholder expectations must be addressed to fully realize the potential of this transformative technology. Despite these hurdles, the opportunities for growth remain substantial, promising a more resilient and responsive automotive landscape.
Maximize ROI with AI-Driven Paint Defect Inspection Strategies
Automotive manufacturers should strategically invest in partnerships focused on AI technologies for Computer Vision in Paint Defect Inspection, fostering collaboration with leading tech firms to innovate inspection processes. By implementing these AI solutions, companies can enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, and gain a significant competitive advantage in quality assurance and customer satisfaction.
Transforming Quality Control: The Role of AI in Paint Defect Inspection
Implementation Framework
Integrating specific AI algorithms enhances the detection of paint defects by analyzing images in real-time, allowing for immediate corrective actions to improve overall quality and operational efficiency in automotive manufacturing.
Industry Standards
Enhancing data collection by using varied and extensive datasets improves model training accuracy for paint defect detection, facilitating a more robust AI system that performs reliably across different automotive environments and conditions.
Cloud Platform
Deploying real-time monitoring systems integrates AI-driven inspections directly into production lines, enabling immediate defect identification and rectification, thus minimizing waste and ensuring high quality throughout the automotive manufacturing process.
Technology Partners
Optimizing feedback loops involves utilizing AI insights to refine inspection processes continuously, ensuring that adjustments are made based on data-driven decisions, which leads to sustainable improvements in paint quality inspection.
Internal R&D
Best Practices for Automotive Manufacturers
-
Impact : Enhances defect detection accuracy significantly
Example : Example: In an automotive assembly line, a vision-based AI system flags microscopic paint defects in real time as car bodies pass under cameras, catching flaws human inspectors previously missed during night shifts.
-
Impact : Reduces production downtime and costs
Example : Example: A semiconductor factory uses AI to detect early soldering anomalies. The system stops the line immediately, preventing a full batch failure that would have caused hours of rework and shutdown.
-
Impact : Improves quality control standards
Example : Example: A food packaging plant uses AI image recognition to verify seal integrity on every packet, ensuring non-compliant packages are rejected instantly before shipping.
-
Impact : Boosts overall operational efficiency
Example : Example: AI dynamically adjusts inspection thresholds based on production speed, allowing the factory to increase output during peak demand without sacrificing quality.
-
Impact : High initial investment for implementation
Example : Example: A mid-sized electronics manufacturer delays AI rollout after realizing camera hardware, GPUs, and system integration push upfront costs beyond budget approvals.
-
Impact : Potential data privacy concerns
Example : Example: AI quality systems capturing worker activity unintentionally store employee facial data, triggering compliance issues with internal privacy policies.
-
Impact : Integration challenges with existing systems
Example : Example: AI software cannot communicate with a 15-year-old PLC controller, forcing engineers to manually export data and slowing decision-making.
-
Impact : Dependence on continuous data quality
Example : Example: Dust accumulation on camera lenses causes the AI to misclassify normal products as defective, leading to unnecessary scrap until recalibration.
-
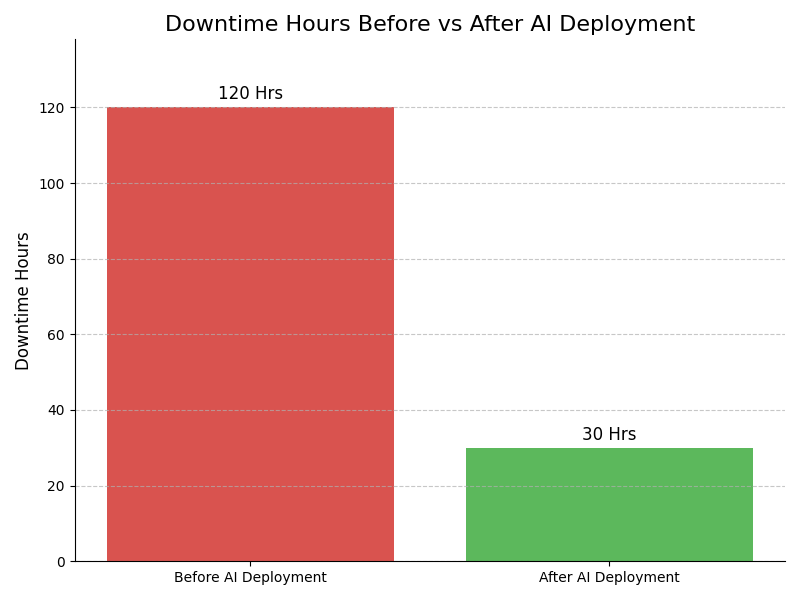
Impact : Improves immediate defect identification
Example : Example: A car manufacturing plant employs real-time monitoring to instantly flag paint inconsistencies, allowing operators to adjust the spray system immediately, resulting in a 20% reduction in repainting costs.
-
Impact : Facilitates quicker corrective actions
Example : Example: During a production run, real-time AI monitors paint application, providing instant feedback that allows operators to correct issues on the fly, preventing defects from accumulating.
-
Impact : Enhances overall production flow
Example : Example: An automotive supplier uses real-time data to optimize its paint booth environment, achieving a 15% improvement in defect rates by swiftly adjusting temperature and humidity levels.
-
Impact : Supports continuous quality assurance
Example : Example: A vehicle assembly plant leverages real-time data analytics to predict paint defect trends, allowing preemptive adjustments that help maintain consistent quality across production shifts.
-
Impact : Requires robust IT infrastructure
Example : Example: A leading automotive manufacturer faced challenges in scaling their real-time monitoring system due to inadequate IT infrastructure, causing delays in defect detection and increased costs.
-
Impact : May lead to information overload
Example : Example: An automotive paint shop struggled with information overload from real-time monitoring, leading to confusion among operators as they missed critical alerts for significant defects.
-
Impact : Dependence on reliable internet connectivity
Example : Example: A factory’s reliance on cloud-based real-time monitoring resulted in production halts when internet connectivity issues arose, impacting overall operational efficiency.
-
Impact : Potential for system downtime impacts
Example : Example: A vehicle assembly line experienced system downtime due to software glitches in the real-time monitoring system, resulting in significant financial losses and delays in production schedules.
-
Impact : Enhances staff competency in AI tools
Example : Example: An automotive manufacturer implemented a regular training program, resulting in a 30% increase in staff proficiency with AI inspection tools, leading to improved defect identification rates.
-
Impact : Improves defect recognition skills
Example : Example: A paint plant organized workshops that improved workers' understanding of AI systems, enhancing their ability to recognize and respond to defects promptly during production.
-
Impact : Boosts confidence in technology adoption
Example : Example: Regular training sessions enabled staff to utilize AI-driven insights effectively, resulting in a 25% faster corrective action process when defects were detected.
-
Impact : Fosters a culture of continuous improvement
Example : Example: By fostering a culture of continuous improvement through training, an automotive factory saw a marked increase in employee engagement and a decrease in defect rates over time.
-
Impact : Training costs can be significant
Example : Example: A major automotive firm faced significant training costs while implementing AI systems, impacting their operational budget and delaying deployment timelines.
-
Impact : Resistance to adopting new technologies
Example : Example: Some employees resisted adopting AI technology, leading to a divide between tech-savvy workers and those who preferred traditional inspection methods, affecting overall efficiency.
-
Impact : Inconsistent knowledge retention
Example : Example: Inconsistent knowledge retention among staff after training sessions led to varying levels of proficiency in using AI tools, causing discrepancies in defect detection accuracy.
-
Impact : Dependence on skilled trainers
Example : Example: A factory's reliance on a few skilled trainers resulted in knowledge gaps when trainers left the organization, creating challenges in continuous staff development and AI utilization.
-
Impact : Anticipates potential defects proactively
Example : Example: An automotive manufacturer integrated predictive analytics into their paint inspection process, allowing them to anticipate defects before they occurred, reducing rework by 40%.
-
Impact : Optimizes maintenance schedules effectively
Example : Example: By implementing predictive maintenance analytics, an automotive paint facility optimized its equipment schedules, reducing unexpected breakdowns and increasing overall productivity by 15%.
-
Impact : Improves resource allocation decisions
Example : Example: An automotive plant leveraged predictive analytics to allocate resources more effectively, resulting in a 20% decrease in production delays caused by paint defects.
-
Impact : Enhances overall manufacturing resilience
Example : Example: A vehicle assembly line used predictive analytics to improve resilience against supply chain disruptions, ensuring consistent paint quality by managing inventory levels proactively.
-
Impact : Requires advanced data analytics skills
Example : Example: An automotive manufacturer struggled with implementing predictive analytics due to a lack of in-house data analytics expertise, delaying the project and increasing costs.
-
Impact : Potential for inaccurate predictions
Example : Example: A paint shop faced challenges when predictions from their analytics tool proved inaccurate, leading to misallocated resources and unanticipated production issues.
-
Impact : Dependence on historical data quality
Example : Example: Inconsistent data quality from historical records hindered the accuracy of predictive models, causing an automotive plant to miss critical defects during production.
-
Impact : Integration complexities with legacy systems
Example : Example: Integration of predictive analytics with legacy systems encountered complexities that slowed down the process, resulting in missed opportunities for optimizing defect detection.
-
Impact : Enhances continuous improvement initiatives
Example : Example: An automotive company established feedback loops between production teams and AI developers, leading to significant improvements in the AI system based on frontline insights, enhancing defect detection.
-
Impact : Informs AI system updates effectively
Example : Example: A paint shop's feedback loop allowed workers to report issues with AI systems, resulting in updates that improved accuracy, leading to a 50% reduction in false positives.
-
Impact : Strengthens team collaboration
Example : Example: Regular feedback sessions among teams fostered collaboration, resulting in innovative solutions that addressed production challenges, thereby improving overall product quality.
-
Impact : Boosts overall product quality
Example : Example: By implementing structured feedback loops, an automotive assembly line achieved a more responsive quality control process, allowing rapid adjustments to the paint application process.
-
Impact : Potential for feedback overload
Example : Example: The establishment of feedback loops in an automotive factory led to overwhelming amounts of data, making it difficult for teams to identify critical insights necessary for improvement.
-
Impact : Requires commitment from all levels
Example : Example: A paint facility struggled to gain commitment from all levels of staff for feedback initiatives, resulting in inconsistencies and a lack of actionable insights.
-
Impact : Time-consuming to implement effectively
Example : Example: Time-consuming processes for gathering feedback slowed down the implementation of improvements, leading to frustration among employees who sought quicker resolutions.
-
Impact : Dependence on clear communication channels
Example : Example: Ineffective communication channels hindered the feedback loop process in an automotive plant, causing misunderstandings and missed opportunities for addressing paint defects.
-
Impact : Improves consistency across inspections
Example : Example: An automotive paint shop standardized inspection protocols, resulting in a 30% decrease in inspection time and a significant reduction in variability of detected defects.
-
Impact : Facilitates easier training processes
Example : Example: By implementing standardized protocols, a vehicle manufacturer streamlined training processes, enabling new employees to reach competency levels faster and with more confidence.
-
Impact : Enhances compliance with quality standards
Example : Example: Standardized inspection protocols ensured compliance with industry quality standards, leading to improved customer satisfaction and fewer warranty claims related to paint defects.
-
Impact : Reduces variability in defect rates
Example : Example: A factory noted a 25% reduction in defect rates after establishing standardized inspection procedures, allowing for more reliable quality assurance across production shifts.
-
Impact : May limit flexibility in inspection
Example : Example: Standardization in an automotive paint facility limited inspectors' flexibility to adapt to unique defects, causing frustration and affecting employee morale.
-
Impact : Initial resistance from inspectors
Example : Example: Some inspectors resisted adopting standardized protocols, leading to inconsistencies in quality checks until management intervened to highlight the benefits.
-
Impact : Potential for outdated protocols
Example : Example: An automotive manufacturer faced challenges when outdated inspection protocols led to missed defects, resulting in increased rework and customer dissatisfaction.
-
Impact : Requires regular updates to remain relevant
Example : Example: The need for regular updates to standardized protocols became a burden on management, often leading to delays in addressing emerging paint inspection challenges.
AI-driven computer vision is revolutionizing paint defect inspection, ensuring precision and quality in automotive manufacturing.
– Murali Krishna Reddy MandalapuCompliance Case Studies




Seize the future of automotive excellence by implementing AI-driven computer vision for paint defect inspection. Elevate quality and outpace competitors today!

Leadership Challenges & Opportunities
Data Quality Challenges
Implement Computer Vision in Paint Defect Inspection to automate data capture and analysis, ensuring high-quality, consistent data. Use advanced image processing algorithms to enhance defect detection accuracy. This enhances decision-making by providing reliable insights into paint quality, thereby reducing waste and improving overall efficiency.
Integration with Legacy Systems
Adopt Computer Vision in Paint Defect Inspection through modular architecture that allows seamless integration with existing Automotive systems. Utilize API endpoints for data exchange and implement middleware solutions to bridge gaps. This strategy minimizes disruption and allows for a gradual transition to modern inspection processes, enhancing operational efficiency.
Resistance to Technological Change
Promote Computer Vision in Paint Defect Inspection by fostering a culture of innovation and continuous improvement. Engage employees through workshops and hands-on training to demonstrate the technology's benefits. This approach helps alleviate resistance, ensuring smoother adoption and enabling teams to leverage data-driven insights effectively.
High Initial Investment
Mitigate financial barriers to Computer Vision in Paint Defect Inspection by pursuing phased implementation strategies. Start with pilot projects that deliver quick ROI and utilize cloud-based solutions to reduce upfront costs. This approach allows organizations to validate benefits before committing to full-scale deployment, ensuring financial sustainability.
Assess how well your AI initiatives align with your business goals
AI Use Case vs ROI Timeline
| AI Use Case | Description | Typical ROI Timeline | Expected ROI Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automated Defect Detection | AI systems can analyze images from production lines to identify paint defects in real-time. For example, a major automotive manufacturer implemented this technology to reduce manual inspections, leading to a significant decrease in defect rates. | 6-12 months | High |
| Predictive Maintenance for Paint Systems | By using AI to monitor paint application systems, companies can predict when maintenance is needed before defects arise. For example, an automotive plant used predictive models to schedule maintenance, reducing downtime and paint defects. | 12-18 months | Medium-High |
| Quality Control Reporting Automation | AI can automate reporting processes for paint quality inspections, providing real-time insights. For example, a vehicle manufacturer used AI to generate instant quality reports, improving decision-making and reducing inspection times. | 6-9 months | Medium-High |
| Root Cause Analysis of Paint Defects | Utilizing AI to analyze defect patterns helps identify root causes. For example, an automotive supplier employed AI tools, leading to actionable insights that reduced recurring defects in paint processes. | 12-15 months | Medium-High |
Glossary
Work with Atomic Loops to architect your AI implementation roadmap — from PoC to enterprise scale.
Contact NowFrequently Asked Questions
- Computer Vision facilitates the automated detection of paint defects in vehicles.
- It enhances quality control processes by ensuring consistent paint application standards.
- The technology reduces manual inspection errors, increasing overall efficiency.
- With real-time data, companies can make informed production decisions rapidly.
- Ultimately, it contributes to higher customer satisfaction through improved product quality.
- Begin with a thorough assessment of existing inspection processes and equipment.
- Select appropriate AI-driven algorithms tailored for paint defect detection tasks.
- Integrate the solution with current manufacturing systems for seamless operation.
- Train staff on new technology to ensure smooth adoption and usage.
- Regularly evaluate and optimize the system based on performance metrics and feedback.
- AI technology increases inspection speed, allowing for faster production cycles.
- Companies can significantly reduce costs related to manual inspection processes.
- Improved accuracy leads to fewer defects, enhancing overall product quality.
- AI-driven insights enable proactive adjustments to manufacturing processes.
- The competitive edge gained aids in market positioning and customer loyalty.
- Integration with legacy systems can present significant technical hurdles.
- Data quality issues may impede the effectiveness of AI algorithms.
- Staff resistance to new technology can slow down implementation efforts.
- Ongoing maintenance and updates are essential for optimal system performance.
- Ensuring compliance with industry standards requires careful planning and execution.
- Organizations should assess their current inspection processes for efficiency gaps.
- Adopting this technology is optimal during major manufacturing upgrades or expansions.
- Evaluate market competition; lagging behind may necessitate quicker adoption.
- Consider customer feedback indicating quality concerns as a trigger for change.
- Financial readiness and resource availability are crucial factors in planning adoption.
- Automotive manufacturers use it for detecting surface imperfections in painted parts.
- It assists in verifying color consistency and finish quality throughout production.
- Specific applications include inspections for scratches, bubbles, and uneven textures.
- The technology is also used in quality assurance stages before vehicle assembly.
- Compliance with safety and aesthetic standards is enhanced through consistent evaluations.
- Investing in AI technology can lead to significant long-term cost savings.
- It enhances operational efficiency by automating tedious inspection processes.
- Companies can achieve higher quality standards, improving brand reputation.
- Data-driven insights provide a competitive advantage in the market.
- The long-term ROI justifies the initial investment, ensuring sustainable growth.

