Digital Twin Implementation Automotive
Digital Twin Implementation in the automotive sector refers to the creation of a virtual model that accurately reflects a physical vehicle or system. This innovative concept serves as a critical tool for stakeholders, enabling real-time monitoring and predictive analysis, which enhances decision-making processes. As the automotive landscape evolves, the integration of digital twins aligns seamlessly with AI-driven initiatives, fostering operational efficiency and strategic agility that are imperative for maintaining competitiveness.
The significance of Digital Twin Implementation is profound, as it empowers automotive entities to harness AI for enhancing innovation cycles and competitive advantage. By facilitating data-driven insights, AI transforms how stakeholders collaborate, adapt, and respond to consumer demands. However, while the prospects for growth and efficiency are substantial, challenges such as integration complexities and shifting expectations necessitate a careful approach to adoption, ensuring that the transition is both effective and aligned with long-term strategic goals.
Accelerate AI-Driven Digital Twin Implementation in Automotive
Automotive companies should strategically invest in partnerships focused on AI technologies to enhance Digital Twin implementations, fostering innovation and efficiency. By leveraging AI, organizations can expect substantial improvements in operational workflows and a significant competitive edge in the marketplace.
How Digital Twin Technology is Transforming the Automotive Sector?
Implementation Framework
Conduct a thorough assessment of current automotive infrastructure to identify gaps and opportunities for integrating AI-driven Digital Twin technologies, enhancing operational efficiency and predictive maintenance capabilities significantly. This foundational step is critical for successful implementation.
Industry Standards
Develop advanced AI models that simulate automotive processes within Digital Twin frameworks, enabling real-time data analysis and predictive insights, ultimately leading to improved decision-making and operational agility in manufacturing and supply chain management.
Technology Partners
Implement robust data integration strategies that connect various automotive systems and platforms, ensuring seamless data flow for the AI-driven Digital Twin, which enhances real-time analytics and collaborative decision-making across departments and stakeholders.
Cloud Platform
Monitor key performance metrics continuously to evaluate the effectiveness of AI-driven Digital Twin implementations, allowing for timely adjustments and enhancements to improve operational performance and responsiveness to market changes.
Internal R&D
Optimize automotive processes continuously by leveraging insights derived from AI-driven Digital Twin data, enhancing predictive maintenance and operational efficiency, which directly contributes to reduced costs and improved supply chain resilience.
Industry Standards
Best Practices for Automotive Manufacturers
-
Impact : Increases predictive maintenance accuracy
Example : Example: A major automotive manufacturer employs predictive analytics to foresee engine part failures, reducing unexpected downtimes from 20% to 5%, significantly enhancing overall equipment effectiveness.
-
Impact : Reduces unexpected equipment failures
Example : Example: An automotive supplier utilizes AI-driven predictive maintenance, which alerts technicians before tool malfunctions, ensuring a smooth production flow and reducing tool replacement costs by 30%.
-
Impact : Enhances production planning efficiency
Example : Example: By analyzing historical data, a car assembly plant optimizes production schedules, resulting in a 15% increase in throughput without additional labor costs.
-
Impact : Lowers overall operational costs
Example : Example: AI algorithms analyze sensor data to predict wear and tear on machinery, allowing timely interventions and cutting maintenance costs by 25% over a year.
-
Impact : Complexity in data integration processes
Example : Example: A global automaker struggles with integrating data from multiple sources, leading to skewed insights that hinder timely decision-making and affecting production schedules.
-
Impact : Potential resistance from workforce
Example : Example: Employees at a vehicle assembly line resist AI tools, fearing job displacement, which slows down the implementation process and limits the technology's effectiveness.
-
Impact : Over-reliance on AI predictions
Example : Example: A manufacturer relies too heavily on AI predictions for quality control, overlooking manual inspections, which leads to a spike in defective products reaching customers.
-
Impact : High maintenance costs for AI systems
Example : Example: Continuous updates and maintenance of AI systems require skilled personnel. A company underestimates this need, resulting in spiraling operational costs and budget overruns.
-
Impact : Enhances operational visibility and control
Example : Example: An automotive plant installs real-time monitoring systems that alert managers to production lags, allowing for swift corrective actions that keep the assembly line running smoothly.
-
Impact : Facilitates immediate issue resolution
Example : Example: A vehicle manufacturer uses real-time data to adjust supply chain logistics, ensuring parts arrive just in time, reducing inventory holding costs significantly.
-
Impact : Improves supply chain coordination
Example : Example: By monitoring customer feedback in real time, an automotive brand quickly resolves service issues, increasing customer satisfaction scores by 15% over six months.
-
Impact : Boosts customer satisfaction levels
Example : Example: AI-powered monitoring systems at a manufacturing facility detect anomalies in production quality, enabling teams to address issues before they escalate, thus maintaining high standards.
-
Impact : Dependence on technology reliability
Example : Example: A car manufacturer experiences system failures during a peak production period, leading to significant delays and missed delivery deadlines, exposing reliance on technology.
-
Impact : Potential for system overload
Example : Example: During a high-demand season, real-time monitoring systems become overwhelmed with data, causing delays in processing alerts and impacting production efficiency.
-
Impact : Data security vulnerabilities
Example : Example: A new monitoring system exposes sensitive production data to cyber threats, leading to a data breach that incurs hefty fines and damages the brand's reputation.
-
Impact : Challenges with legacy system integration
Example : Example: Integrating real-time monitoring into a legacy system proves difficult, resulting in increased downtime and requiring additional IT resources for troubleshooting.
-
Impact : Boosts employee confidence and skills
Example : Example: An automotive company implements ongoing training for employees on AI tools, leading to a 30% reduction in operational errors and an increase in employee satisfaction scores.
-
Impact : Ensures effective AI tool utilization
Example : Example: Continuous learning programs empower technicians to utilize AI analytics effectively, resulting in a noticeable boost in production efficiency and reduced scrap rates.
-
Impact : Reduces operational errors and waste
Example : Example: Regular workshops on AI technologies cultivate an innovative mindset among employees, inspiring new ideas that improve production processes and enhance product quality.
-
Impact : Encourages innovation and adaptability
Example : Example: A training initiative on AI tools helps employees adapt quickly to changes, reducing resistance and increasing the speed of technology adoption on the factory floor.
-
Impact : Training costs may escalate
Example : Example: A major automotive firm overspends on extensive training programs without measurable outcomes, leading to budget overruns and uncertain ROI for the training investment.
-
Impact : Difficulty in measuring training effectiveness
Example : Example: A company struggles to quantify the effectiveness of its training initiatives, resulting in continuous investment without clear improvement in employee performance or productivity.
-
Impact : Resistance to change from employees
Example : Example: Employees at a manufacturing facility resist adopting new AI tools due to lack of understanding, creating friction and slowing down the implementation process.
-
Impact : Time constraints on training sessions
Example : Example: Time constraints lead to rushed training sessions at an automotive plant, leaving employees underprepared to utilize AI tools effectively in their roles.
-
Impact : Improves design and testing processes
Example : Example: An automotive design team uses simulation models to test vehicle performance under various conditions, reducing physical prototyping needs and shortening the overall development cycle.
-
Impact : Reduces time-to-market for new models
Example : Example: A car manufacturer uses AI-driven simulations to refine production processes before full-scale implementation, leading to a 20% reduction in time-to-market for their latest model.
-
Impact : Enhances resource allocation strategies
Example : Example: Resource allocation becomes more efficient with simulation models that predict machine performance, allowing the automotive factory to schedule maintenance during low-demand periods.
-
Impact : Facilitates risk management and mitigation
Example : Example: By simulating various risk scenarios, an automotive company develops contingency plans, which significantly mitigates the impact of supply chain disruptions during crises.
-
Impact : High costs associated with simulations
Example : Example: An automotive firm invests heavily in simulation technology but faces budget issues due to unexpected costs, causing delays in project timelines and resource allocation.
-
Impact : Complex interpretation of simulation data
Example : Example: Engineers struggle to interpret complex simulation data, leading to misaligned expectations and decisions that hinder project progress and effectiveness.
-
Impact : Potential inaccuracies in models
Example : Example: A simulation model inaccurately predicts vehicle performance, resulting in costly recalls and damage to the brand's reputation in the market due to faulty assumptions.
-
Impact : Dependency on skilled personnel
Example : Example: The need for specialized skills to operate simulation software creates a talent gap, delaying projects as the automotive firm struggles to find qualified personnel.
-
Impact : Enhances collaboration among teams
Example : Example: A leading automotive manufacturer adopts agile methodologies, resulting in improved cross-department collaboration, ultimately speeding up the development of new electric vehicle models.
-
Impact : Speeds up innovation cycles
Example : Example: Agile practices enable quick iterations in design, allowing a car company to respond rapidly to market feedback and introduce enhancements within weeks rather than months.
-
Impact : Improves responsiveness to market changes
Example : Example: By implementing agile frameworks, an automotive firm reduces risk in new product launches, as teams can adapt based on real-time customer insights and testing outcomes.
-
Impact : Reduces project risks significantly
Example : Example: An agile development approach allows an automotive supplier to pivot quickly in response to supply chain disruptions, minimizing delays and maintaining production schedules effectively.
-
Impact : Inconsistency in team dynamics
Example : Example: An automotive firm's transition to agile meets resistance from traditional teams, leading to inconsistencies in project execution and delayed timelines, undermining the initiative's effectiveness.
-
Impact : Potential for scope creep
Example : Example: A project team faces scope creep as stakeholders continuously introduce new requirements, complicating timelines and creating confusion over project deliverables.
-
Impact : Requires cultural shift in organization
Example : Example: Employees struggle to embrace agile practices, resulting in a cultural clash that hampers collaboration and slows down innovation cycles within the organization.
-
Impact : Difficulty in scaling agile practices
Example : Example: Scaling agile practices across multiple departments proves challenging for an automotive company, leading to fragmented efforts and reduced overall effectiveness of the approach.
Digital twins, powered by AI, are not just tools; they are the future of automotive innovation, enabling unprecedented efficiency and insight.
– Murali Krishna Reddy MandalapuCompliance Case Studies




Embrace AI-driven Digital Twin solutions to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and stay ahead in the competitive automotive landscape. Transform your operations today!
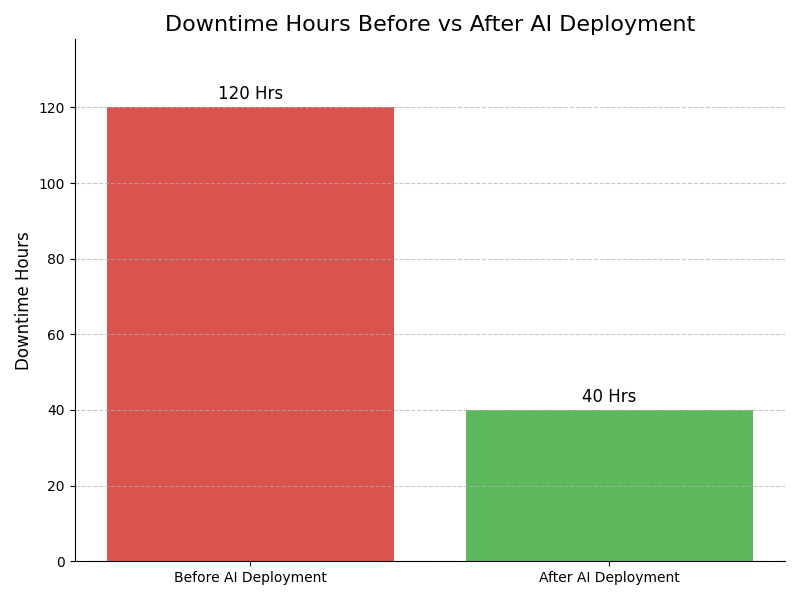
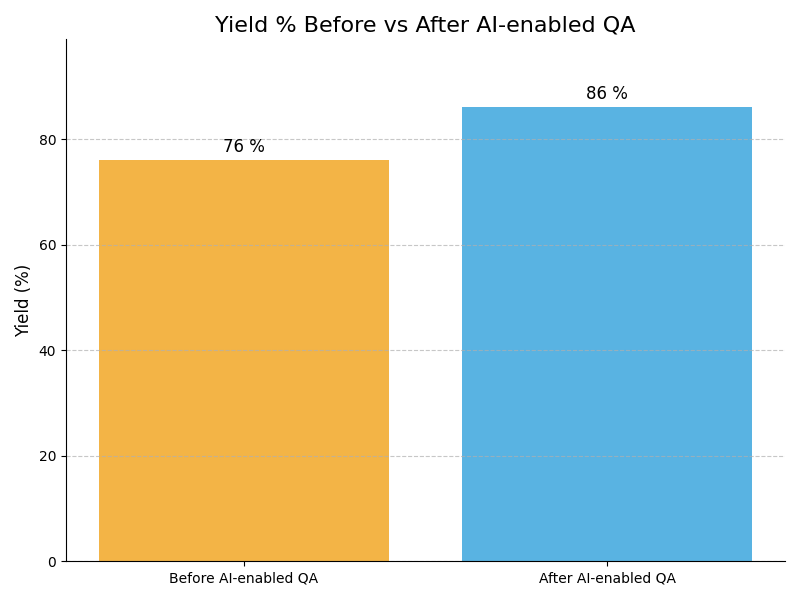
Leadership Challenges & Opportunities
Data Integration Challenges
Utilize Digital Twin Implementation Automotive to create a unified data ecosystem that integrates disparate sources, enabling real-time data flow. This ensures accurate simulations and enhances decision-making. Employ data standardization techniques and middleware solutions to facilitate seamless interoperability across platforms.
Cultural Resistance to Change
Foster a culture of innovation by utilizing Digital Twin Implementation Automotive as a collaborative tool for cross-functional teams. Implement workshops and training sessions that demonstrate its value, encouraging engagement and buy-in. This approach helps to shift mindsets and promotes a more agile, data-driven culture.
High Implementation Costs
Adopt a phased approach to Digital Twin Implementation Automotive, starting with cost-effective pilot projects that demonstrate value. Use cloud-based solutions to lower upfront costs, and leverage existing resources. This strategy allows for incremental investment based on proven ROI, ensuring budget alignment with business goals.
Skill Shortages in Workforce
Address workforce skill gaps by integrating Digital Twin Implementation Automotive with tailored training programs that focus on simulation and analytics. Partner with educational institutions for internships and workshops, and utilize user-friendly interfaces to ease the learning curve, thus enhancing team capabilities and productivity.
Assess how well your AI initiatives align with your business goals
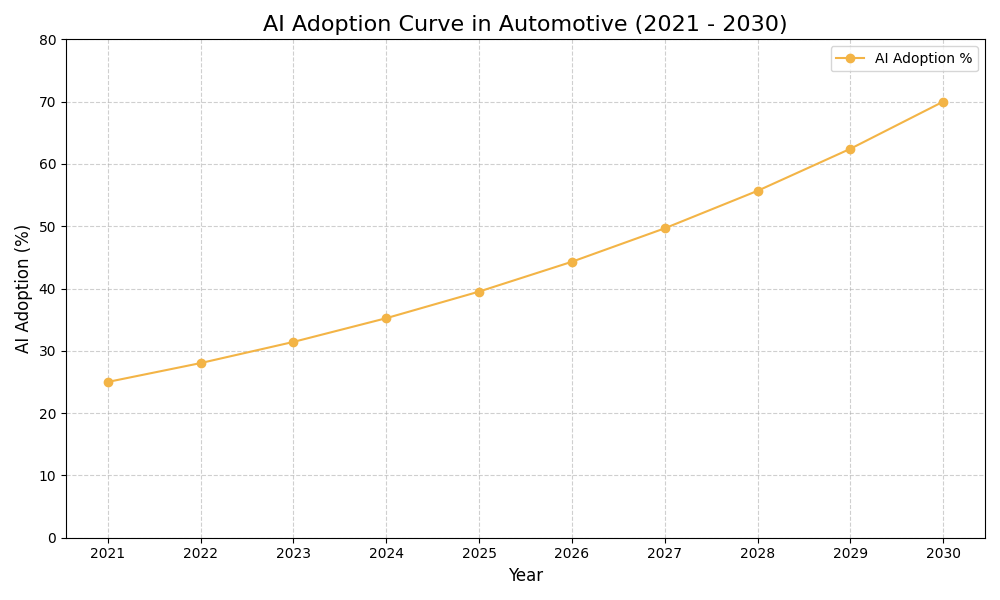
AI Use Case vs ROI Timeline
| AI Use Case | Description | Typical ROI Timeline | Expected ROI Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Predictive Maintenance Optimization | By leveraging digital twins, manufacturers can predict equipment failures before they occur. For example, a car manufacturer uses AI algorithms to analyze real-time data from machinery, reducing downtime and maintenance costs significantly. | 6-12 months | High |
| Enhanced Vehicle Design Simulation | Digital twins allow for real-time simulation of vehicle designs to optimize performance. For example, an automotive company uses AI to simulate crash tests, leading to safer designs and reduced prototyping costs. | 12-18 months | Medium-High |
| Supply Chain Efficiency Improvement | AI-driven digital twins can optimize supply chain logistics by simulating various scenarios. For example, an automaker uses a digital twin to streamline parts delivery, improving production timelines and reducing inventory costs. | 6-12 months | Medium-High |
| Personalized Customer Experience | Digital twins help automotive companies tailor products to individual preferences. For example, a car manufacturer uses customer data to create personalized vehicle configurations, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty. | 12-18 months | Medium-High |
Glossary
Work with Atomic Loops to architect your AI implementation roadmap — from PoC to enterprise scale.
Contact NowFrequently Asked Questions
- Digital Twin Implementation Automotive creates virtual replicas of physical vehicles for analysis.
- It enhances predictive maintenance, allowing for proactive issue resolution before failures occur.
- This technology facilitates real-time monitoring, improving operational efficiency and safety.
- AI-driven insights help in optimizing design and production processes effectively.
- Companies gain a strategic edge through data-driven decision making and innovation.
- Start by assessing your current systems and identifying integration points for digital twins.
- Engage stakeholders to define objectives and expected outcomes for the implementation process.
- Develop a phased approach, beginning with pilot projects to test concepts and technologies.
- Utilize AI tools to analyze data from the digital twin for actionable insights.
- Ensure continuous training and support for teams during and after implementation.
- AI enhances predictive analytics, leading to improved vehicle performance and reliability.
- Cost savings arise from reduced downtime and optimized maintenance schedules.
- Real-time data allows for agile responses to market demands and customer preferences.
- Companies can innovate faster, resulting in a shorter time-to-market for new models.
- The technology enables better resource management, increasing overall operational efficiency.
- Integration with legacy systems can pose significant technical hurdles and require substantial resources.
- Data quality and availability are critical; inadequate data can hinder effective analysis.
- Change management is essential to ensure team buy-in and successful adoption of new processes.
- Regulatory compliance must be addressed to avoid legal complications in the automotive sector.
- Adopting best practices and learning from industry benchmarks can mitigate these challenges.
- Organizations should consider implementation when they have clear business objectives and goals.
- A readiness assessment of current digital capabilities can guide the timing for deployment.
- Market pressures and competitive dynamics often necessitate immediate adoption to stay relevant.
- Phased implementation allows flexibility, enabling adjustments based on initial feedback and results.
- Regular reviews of technological advancements can signal the right timing for upgrades.
- Digital twins can simulate vehicle performance under various conditions for optimal design adjustments.
- They assist in monitoring supply chain logistics, improving efficiency and reducing costs.
- The technology can enhance driver safety through real-time analytics of vehicle behavior.
- Regulatory compliance can be streamlined by simulating scenarios for better adherence to standards.
- Real-world testing can be minimized, saving time and resources in development cycles.
- Investing in these technologies enables organizations to stay competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
- They provide actionable insights that improve decision-making and operational efficiency.
- AI integration enhances predictive maintenance, reducing unexpected downtimes and costs.
- Companies can leverage digital twins to innovate products more effectively and quickly.
- Long-term, this investment drives better customer satisfaction and loyalty through improved offerings.

