Generative Design in Automotive
Generative Design in Automotive refers to the innovative process where algorithms and AI work collaboratively to create optimized vehicle designs. This approach allows engineers and designers to explore a multitude of design alternatives that meet specific performance criteria while considering factors like weight, materials, and manufacturing methods. As the automotive sector embraces digital transformation, this technology has become crucial for stakeholders aiming to enhance product offerings and streamline design processes.
The integration of AI within generative design is reshaping how automotive companies approach innovation and competition. By leveraging data-driven insights, organizations can accelerate development cycles, improve efficiency, and enhance decision-making capabilities. This evolving landscape presents significant growth opportunities, although it also poses challenges such as adoption hurdles, the complexity of integration into existing workflows, and shifting expectations from customers and regulators alike.
Transform Your Automotive Design with AI-Powered Generative Solutions
Automotive companies should strategically invest in partnerships with AI technology firms to harness the power of Generative Design, enhancing product development and manufacturing processes. Implementing these AI-driven solutions is expected to yield significant improvements in design efficiency, cost reduction, and competitive advantage in the market.
How is Generative Design Revolutionizing Automotive Innovation?
Implementation Framework
Start by integrating advanced AI algorithms into the design process, allowing for rapid prototyping and optimization while reducing material waste and enhancing performance, ultimately driving competitive advantages in the automotive sector.
Technology Partners
Adopt AI-driven simulation tools that evaluate design variations in real-time, facilitating data-driven decision-making and enhancing product performance, which helps in mitigating risks associated with new designs early in the process.
Industry Standards
Engage data scientists to analyze design data, uncovering insights that guide generative design choices, thus ensuring designs are not only innovative but also aligned with consumer preferences and market trends.
Internal R&D
Establish a feedback loop by incorporating user and stakeholder feedback into design iterations, enhancing the generative design process while ensuring alignment with customer expectations and driving continuous improvement.
Cloud Platform
Implement performance metrics to evaluate the success of generative design initiatives, focusing on efficiency gains, cost reductions, and market responsiveness, ensuring continuous alignment with strategic business goals throughout the design lifecycle.
Industry Reports
Best Practices for Automotive Manufacturers
-
Impact : Enhances design efficiency and speed
Example : Example: A leading automotive manufacturer utilized AI to generate over 1,000 design iterations for a new vehicle model in weeks, significantly reducing the design phase from months to mere weeks.
-
Impact : Reduces material waste significantly
Example : Example: By using generative design algorithms, an auto plant minimized material usage by 30%, leading to substantial cost savings in raw materials while maintaining structural integrity.
-
Impact : Allows for innovative design iterations
Example : Example: A sports car manufacturer used AI to iterate on aerodynamic designs, resulting in a 15% increase in fuel efficiency for their latest model, appealing to eco-conscious consumers.
-
Impact : Improves product performance metrics
Example : Example: Implementing AI-driven simulations allowed engineers to test 50 design prototypes virtually before physical production, enhancing performance metrics while reducing testing costs.
-
Impact : High initial investment for technology
Example : Example: An automotive company faced a budget crisis after estimating that AI software and hardware costs exceeded initial projections, delaying their generative design implementation by six months.
-
Impact : Uncertain regulatory compliance issues
Example : Example: New AI regulations in Europe raised compliance concerns for an automotive firm, leading to a temporary halt in their AI initiatives until legal assessments were completed.
-
Impact : Potential loss of creative control
Example : Example: Designers at a car manufacturer expressed frustration over AI-generated designs, feeling that they constrained creativity, leading to internal resistance against adopting the technology.
-
Impact : Integration with legacy systems challenges
Example : Example: A legacy manufacturing plant struggled to integrate new AI systems with outdated machinery, causing a slowdown in the production process and frustration among engineering teams.
-
Impact : Increases data visibility across teams
Example : Example: After implementing a centralized AI dashboard, a major automotive firm improved cross-departmental communication, leading to a 20% faster response to design-related issues during production.
-
Impact : Facilitates real-time performance monitoring
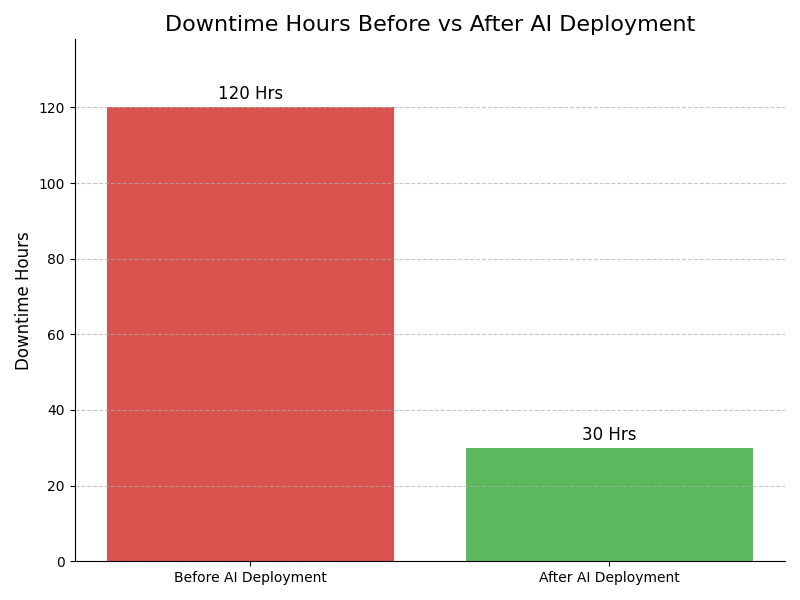
Example : Example: Real-time performance analytics allowed a factory to monitor equipment health, reducing machine downtime by 25% through timely maintenance alerts that kept production on schedule.
-
Impact : Enhances predictive maintenance capabilities
Example : Example: Predictive maintenance tools helped an automotive assembly line identify potential failures before they occurred, cutting unexpected downtime by 40% and ensuring smoother operations.
-
Impact : Improves collaboration on design changes
Example : Example: Designers collaborated more effectively using data insights to assess the impact of design changes, leading to a 30% reduction in revisions during the development phase.
-
Impact : Data security vulnerabilities with AI implementation
Example : Example: An automotive manufacturer faced a data breach, compromising sensitive design information due to inadequate security measures in their AI systems, leading to financial losses and reputational damage.
-
Impact : High costs of data management systems
Example : Example: A company underestimated the expenses for data storage and management, resulting in budget overruns that delayed AI project timelines and reduced available resources for innovation.
-
Impact : Over-reliance on automated insights
Example : Example: Relying heavily on AI predictions led to misjudgments when unexpected market shifts occurred, causing the company to miss critical design opportunities and lag behind competitors.
-
Impact : Difficulty in data interpretation
Example : Example: Engineers struggled to interpret complex AI-generated data, leading to confusion and delays in decision-making processes that negatively impacted project timelines.
-
Impact : Fosters collaborative innovation culture
Example : Example: A cross-functional team at a major automaker worked together on generative design, leading to a breakthrough in electric vehicle architecture that cut production time by 15%.
-
Impact : Combines diverse expertise for solutions
Example : Example: By bringing together design, engineering, and marketing professionals, an automotive company developed an innovative vehicle concept that appealed to a wider audience, boosting pre-sales by 25%.
-
Impact : Enhances adaptability in design processes
Example : Example: Daily stand-up meetings among cross-disciplinary teams helped quickly identify issues in the design process, enabling rapid adjustments and keeping projects on track.
-
Impact : Accelerates problem-solving capabilities
Example : Example: Collaboration between engineers and designers improved the adaptability of design processes, allowing the team to respond swiftly to evolving consumer preferences without major delays.
-
Impact : Potential communication breakdowns among teams
Example : Example: A lack of clear communication between the design and engineering teams led to misunderstandings about project requirements, causing delays and increased costs in vehicle development.
-
Impact : Conflicting priorities can arise
Example : Example: Differing priorities between marketing and engineering departments resulted in a conflict over design features, leading to a standstill in the project timeline and missed market opportunities.
-
Impact : Resistance to change from employees
Example : Example: Employees resisted adopting new AI tools due to fear of job displacement, leading to decreased morale and a slower pace in implementing generative design initiatives.
-
Impact : Time-consuming consensus-building processes
Example : Example: Lengthy discussions for consensus among diverse team members caused project timelines to extend, delaying the launch of a highly anticipated electric vehicle model.
-
Impact : Improves design consistency and quality
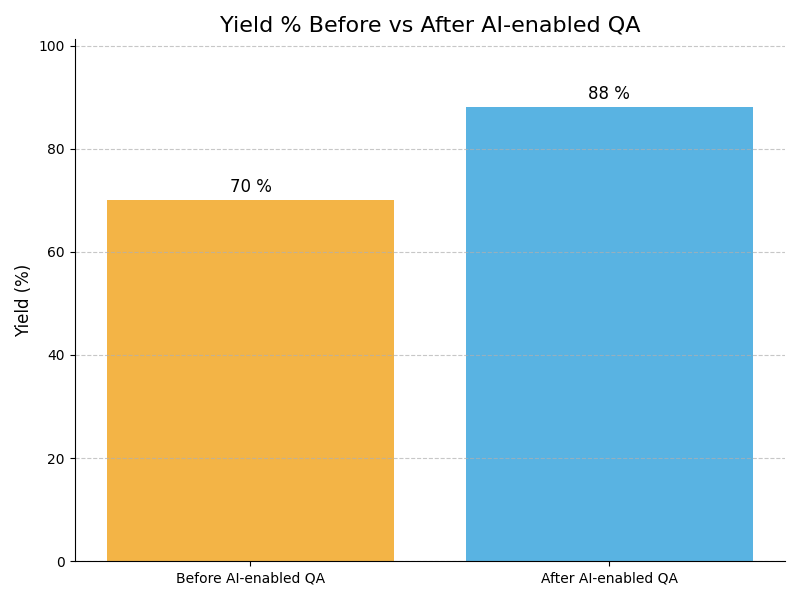
Example : Example: An automotive company standardized its AI design processes, resulting in a 50% reduction in design errors and improving overall product quality, leading to higher customer satisfaction ratings.
-
Impact : Reduces rework due to errors
Example : Example: By implementing a consistent framework for generative design, a manufacturer significantly decreased rework efforts, allowing the team to focus on innovation rather than corrections.
-
Impact : Facilitates easier onboarding of new staff
Example : Example: A well-defined onboarding process for new hires in the design team enabled them to quickly adapt to generative design tools, enhancing productivity and reducing training time.
-
Impact : Enhances scalability of design efforts
Example : Example: Standardizing design approaches allowed the company to scale its design efforts seamlessly across multiple projects, increasing efficiency and reducing time-to-market for new models.
-
Impact : May limit creative design flexibility
Example : Example: Standardizing generative design processes led to concerns among designers about losing creative freedom, resulting in tension and reluctance to adopt the new systems.
-
Impact : Difficulty in maintaining standards
Example : Example: A company struggled to maintain consistent standards in generative design, leading to variations in quality that confused customers and impacted brand reputation.
-
Impact : Increased training requirements for staff
Example : Example: The introduction of standardized processes required extensive training sessions, straining resources and delaying project timelines as employees adapted to new methods.
-
Impact : Potential for over-standardization issues
Example : Example: Over-standardization of design processes caused the company to miss out on unique, innovative approaches that could differentiate their vehicles in a competitive market.
-
Impact : Enhances validation of design concepts
Example : Example: Using AI-driven simulations, an automotive firm validated design concepts virtually, reducing the need for costly physical prototypes and expediting the development timeline by 30%.
-
Impact : Reduces physical prototyping costs
Example : Example: A car manufacturer leveraged simulation technology to test various crash scenarios, allowing them to refine safety features and ensure compliance with regulations without incurring high costs.
-
Impact : Improves understanding of performance factors
Example : Example: By simulating different driving environments, engineers gained insights into vehicle performance under various conditions, leading to improvements that enhanced customer satisfaction ratings.
-
Impact : Speeds up the design iteration cycle
Example : Example: Rapid iteration cycles were achieved through simulation testing, allowing engineers to quickly evaluate design changes and implement improvements without significant time delays.
-
Impact : High costs associated with simulation software
Example : Example: A major automotive manufacturer faced budget overruns after investing heavily in advanced simulation software, which delayed critical design projects due to financial constraints.
-
Impact : Requires specialized skills to operate
Example : Example: Engineers struggled to operate complex simulation software effectively, leading to misinterpretations of results and costly design errors that impacted product quality.
-
Impact : Potential inaccuracies in simulation results
Example : Example: Inaccuracies in input data during simulations led to significant discrepancies in real-world performance, causing the company to reevaluate their design approach and extend timelines.
-
Impact : Dependence on accurate input data
Example : Example: The reliance on precise data inputs for simulations caused delays when unexpected variations in material properties were encountered, complicating the validation process and extending project timelines.
Generative design powered by AI is not just a tool; it's a revolution that redefines how we innovate in automotive engineering.
– NVIDIA Editorial TeamCompliance Case Studies




Embrace the power of AI-driven Generative Design to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and stay ahead in the competitive automotive landscape. Don't miss this opportunity!
Leadership Challenges & Opportunities
Data Integration Challenges
Utilize Generative Design in Automotive to create a unified data management system that consolidates design, engineering, and manufacturing data. Implement advanced algorithms for real-time data synchronization, ensuring all departments have access to accurate information, thereby enhancing collaboration and reducing errors in the design process.
Cultural Resistance to Change
Foster a culture of innovation by integrating Generative Design in Automotive through hands-on workshops and pilot projects that showcase its advantages. Create cross-functional teams to champion the technology, allowing employees to experience benefits firsthand, which encourages acceptance and aligns organizational goals with advanced design methodologies.
High Initial Investment
Mitigate financial barriers by adopting Generative Design in Automotive via subscription-based models that allow phased investments. Start with targeted projects that promise quick returns to build momentum and demonstrate value, leading to further investment in broader applications and capabilities across the organization.
Skill Development Shortage
Address the skills gap by implementing targeted training programs focused on Generative Design in Automotive tools. Collaborate with educational institutions to create specialized curricula, and leverage online platforms for scalable training, ensuring the workforce is equipped with the necessary skills to utilize advanced design technologies effectively.
Assess how well your AI initiatives align with your business goals
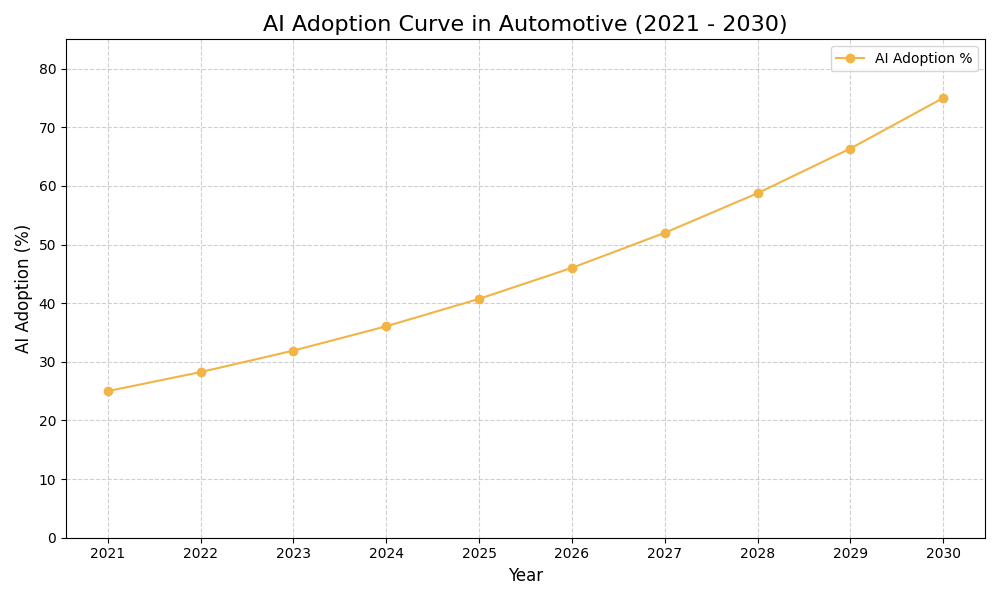
AI Use Case vs ROI Timeline
| AI Use Case | Description | Typical ROI Timeline | Expected ROI Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Optimized Component Design | Generative design algorithms create lightweight, strong components based on performance criteria. For example, automakers like Ford use AI to design intricate parts, reducing weight and improving fuel efficiency. | 6-12 months | Medium-High |
| Automated Design Iteration | AI accelerates the design process by generating multiple iterations in real-time. For example, BMW employs AI to explore variations in car designs, allowing faster prototyping and reduced development costs. | 12-18 months | High |
| Cost-Effective Material Selection | AI evaluates materials for cost and performance in generative design. For example, Tesla uses AI to select sustainable materials without compromising quality, leading to significant cost savings. | 6-12 months | Medium-High |
| Enhanced Aerodynamic Analysis | Generative design uses AI to optimize shapes for aerodynamics. For example, Audi implements AI-driven simulations to refine vehicle shapes, improving performance and reducing drag. | 12-18 months | High |
Glossary
Work with Atomic Loops to architect your AI implementation roadmap — from PoC to enterprise scale.
Contact NowFrequently Asked Questions
- Generative Design optimizes vehicle design by leveraging AI to create innovative solutions.
- It significantly reduces design time, enabling faster product development cycles.
- The technology enhances material efficiency, minimizing waste during production processes.
- Companies can achieve improved performance metrics through data-driven design decisions.
- Generative Design elevates competitive positioning by fostering innovation and agility.
- Begin by assessing your current design processes and identifying areas for improvement.
- Engage with AI specialists to tailor solutions that meet your specific requirements.
- Pilot projects can facilitate testing before full-scale implementation is pursued.
- Ensure team members are trained to effectively utilize new technologies and methodologies.
- A phased approach allows for gradual integration and adjustment based on feedback.
- Resistance to change from traditional design practices can hinder adoption efforts.
- Integration with legacy systems may present technical challenges and delays.
- Employees may require extensive training to adapt to new tools and processes.
- Data quality issues can impact the effectiveness of AI-driven design solutions.
- Strategic planning and clear communication can mitigate many of these challenges.
- Organizations often see reduced time-to-market for new vehicle models and features.
- Cost savings are realized through optimized resource allocation and material usage.
- Enhanced product performance metrics lead to improved customer satisfaction ratings.
- Firms can track innovation speed, measuring the frequency of new design implementations.
- Overall, businesses experience a stronger return on investment through enhanced efficiencies.
- Evaluate the organization’s readiness for digital transformation and innovation.
- Timing should align with the launch of new models or product lines.
- Market competition may necessitate faster adoption to maintain a competitive edge.
- Regular assessments of design processes can reveal urgent needs for improvement.
- Align adoption with strategic planning cycles for maximum organizational impact.
- AI can streamline data processing, making integration with existing systems smoother.
- Advanced analytics provide insights that facilitate strategic decision-making.
- Automated testing and simulations reduce the risk associated with new designs.
- AI-driven tools can enhance collaboration among cross-functional teams effectively.
- Continuous feedback loops enabled by AI foster ongoing improvement and adaptation.
- Identify leading companies in the automotive sector that successfully use Generative Design.
- Benchmark against industry standards to measure innovation and design efficiency.
- Regularly review advancements in AI technologies applicable to automotive design.
- Establish key performance indicators to track progress and outcomes over time.
- Collaborate with industry groups to stay informed about best practices and benchmarks.