Machine Learning for Root Cause Analysis
In the Automotive sector, "Machine Learning for Root Cause Analysis" refers to the application of AI algorithms to identify and understand the underlying factors that contribute to failures or inefficiencies in systems and processes. This approach allows stakeholders to gain deeper insights into operational challenges, facilitating proactive measures that enhance vehicle performance and reliability. As the industry increasingly embraces digital transformation, the integration of machine learning into root cause analysis becomes essential for companies striving to adapt to evolving consumer demands and technological advancements.
The Automotive ecosystem is witnessing a profound shift driven by AI-enabled practices that redefine competitive landscapes and innovation frameworks. By leveraging machine learning, organizations can optimize decision-making processes, improve operational efficiency, and foster more collaborative stakeholder interactions. However, while the potential for growth is significant, challenges such as adoption hurdles, integration complexities, and shifting expectations must also be addressed to fully realize the benefits of this transformative technology. The journey toward effective implementation of machine learning for root cause analysis will require a balanced approach, combining optimism for future advancements with a pragmatic understanding of the obstacles ahead.
Unlock AI-Driven Insights for Automotive Excellence
Automotive companies should strategically invest in partnerships with AI-focused firms to develop robust Machine Learning solutions for Root Cause Analysis. Implementing these technologies is expected to enhance operational efficiencies, reduce downtime, and create significant competitive advantages in the marketplace.
Revolutionizing Automotive Insights: The Role of Machine Learning in Root Cause Analysis
Implementation Framework
Begin by identifying specific objectives for root cause analysis, such as reducing defect rates or improving safety. Clear goals guide AI integration and enhance operational efficiency within automotive production processes.
Internal R&D
Collect comprehensive datasets from various sources, including sensors and production logs, to train AI models. High-quality data is essential for accurate root cause analysis and predictive maintenance in automotive operations.
Industry Standards
Develop and test machine learning models tailored for root cause analysis. These models should analyze historical data and predict potential issues, enhancing proactive measures and minimizing downtime in automotive manufacturing.
Technology Partners
Integrate AI models into existing systems and conduct rigorous testing to ensure reliability and accuracy. Successful implementation allows for real-time analysis and immediate corrective actions, improving overall quality control in automotive manufacturing.
Cloud Platform
Establish a feedback loop to monitor AI system outputs and continuously optimize models based on new data. This ongoing refinement process ensures that root cause analysis remains effective and relevant in a dynamic automotive environment.
Internal R&D
Best Practices for Automotive Manufacturers
-
Impact : Reduces unplanned machine downtime significantly
Example : Example: A major automotive plant implements predictive maintenance using machine learning algorithms. This reduces unexpected breakdowns by 30%, allowing production schedules to be met consistently without costly delays.
-
Impact : Extends equipment lifespan through predictive care
Example : Example: By analyzing sensor data, a car manufacturer predicts engine wear and schedules timely maintenance. This proactive approach extends machinery lifespan by 20%, reducing replacement costs significantly.
-
Impact : Optimizes maintenance schedules and resources
Example : Example: An automotive assembly line integrates machine learning for maintenance. This allows them to optimize resource use, leading to a 25% reduction in maintenance costs and improved production efficiency.
-
Impact : Decreases overall operational costs
Example : Example: An AI system forecasts equipment failures, enabling the automotive company to schedule maintenance during off-peak hours, significantly lowering labor costs and improving overall productivity.
-
Impact : High initial investment for implementation
Example : Example: A leading automotive manufacturer hesitates to implement predictive maintenance due to initial costs related to sensor upgrades, software licenses, and training, which exceed budget expectations and cause project delays.
-
Impact : Dependence on reliable data sources
Example : Example: An automotive company relies on outdated data sources, leading to inaccurate predictions and ineffective maintenance schedules, ultimately resulting in increased downtime and higher costs.
-
Impact : Integration challenges with legacy systems
Example : Example: A car factory struggles to integrate new predictive maintenance software with its legacy systems, causing delays and requiring additional resources for manual data handling, hindering potential productivity gains.
-
Impact : Potential skill gaps in workforce
Example : Example: The workforce lacks training in machine learning applications, leading to a gap in skills needed to analyze predictive maintenance data effectively, creating reliance on external consultants and increasing operational costs.
-
Impact : Enhances defect detection accuracy significantly
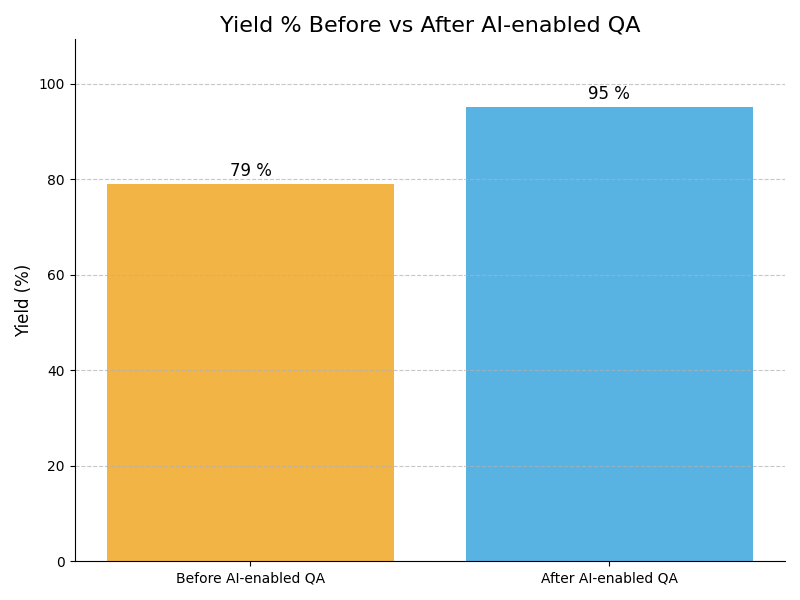
Example : Example: A high-end automotive manufacturer employs AI-driven quality control, catching 95% of defects during production. This accuracy significantly lowers recall rates, enhancing brand reputation and customer trust.
-
Impact : Reduces product recalls and warranty claims
Example : Example: An automotive supplier integrates AI to monitor production quality in real-time. This proactive approach reduces warranty claims by 40%, saving millions in potential liabilities and enhancing customer loyalty.
-
Impact : Streamlines quality assurance processes
Example : Example: A car manufacturing plant implements AI in the quality assurance process, allowing for real-time data analytics. This streamlining reduces inspection times by 50%, boosting overall productivity and quality standards.
-
Impact : Improves customer satisfaction ratings
Example : Example: An automotive company applies AI to analyze customer feedback on quality issues, leading to targeted improvements that increase customer satisfaction ratings by 30%, fostering brand loyalty.
-
Impact : High implementation costs for technology
Example : Example: An automotive company faces pushback from stakeholders due to high initial costs of AI-driven quality control systems, causing delays in implementation and resulting in prolonged inefficiencies in defect detection.
-
Impact : Data inaccuracies leading to false positives
Example : Example: An AI quality control system misidentifies a common manufacturing error as a defect, leading to increased production waste and scrutiny from management due to data inaccuracies.
-
Impact : Potential resistance from employees
Example : Example: Employees resist adopting AI quality control systems due to fears of job loss, creating a cultural barrier that hinders the successful implementation and utilization of the technology.
-
Impact : Complexity in system integration
Example : Example: A manufacturer experiences delays in integrating AI systems with existing production lines, causing workflow interruptions and leading to increased operational costs during the transition period.
-
Impact : Improves responsiveness to production issues
Example : Example: An automotive assembly line adopts real-time monitoring systems, allowing supervisors to address production issues immediately, resulting in a 20% increase in operational efficiency and reduced downtime.
-
Impact : Facilitates data-driven decision-making
Example : Example: A car manufacturer leverages real-time data analytics to make informed decisions quickly, improving production rates by 15% and ensuring optimal resource allocation throughout the facility.
-
Impact : Enhances operational transparency and accountability
Example : Example: By utilizing real-time monitoring, an automotive plant enhances transparency in operations, allowing management to track KPIs effectively and make data-driven adjustments that increase productivity significantly.
-
Impact : Boosts overall productivity and output
Example : Example: The implementation of real-time monitoring systems enables an automotive factory to detect bottlenecks instantly, leading to timely interventions and a 30% boost in overall output within a month.
-
Impact : Initial setup requires significant resources
Example : Example: A major automotive manufacturer struggles with the initial setup of its real-time monitoring system, facing unexpected costs related to hardware installation and network infrastructure, delaying project timelines.
-
Impact : Potential cybersecurity vulnerabilities
Example : Example: A car manufacturing plant experiences a cybersecurity breach, targeting its real-time monitoring systems and leading to production halts and data loss, highlighting vulnerabilities in their technology.
-
Impact : High dependency on technology reliability
Example : Example: An automotive factory becomes overly reliant on its real-time monitoring technology, facing challenges when the system fails unexpectedly, resulting in significant production delays and financial losses.
-
Impact : Need for continuous system updates
Example : Example: Continuous updates and maintenance of the monitoring system require dedicated IT resources, straining the already limited budget and leading to potential service interruptions during upgrade periods.
-
Impact : Enhances skill sets for advanced technologies
Example : Example: An automotive company invests in continuous training programs for its workforce, enhancing skills in machine learning, which leads to a 25% increase in innovation initiatives and improved operational efficiency.
-
Impact : Promotes a culture of innovation
Example : Example: By promoting a culture of continuous learning, an automotive manufacturer boosts employee engagement, resulting in lower turnover rates and a more committed workforce dedicated to quality and productivity.
-
Impact : Improves employee engagement and retention
Example : Example: Regular training sessions on AI technologies lead to successful implementation and adoption within the automotive plant, improving overall productivity rates by 30% and fostering a collaborative environment.
-
Impact : Ensures successful technology adoption
Example : Example: A comprehensive training program ensures employees are well-versed in new AI tools, leading to smoother transitions during technology upgrades and maintaining high production standards without disruption.
-
Impact : Training costs may strain budgets
Example : Example: A mid-sized automotive manufacturer faces budget constraints that limit training opportunities for employees, resulting in skill gaps that slow down the adoption of new technologies and processes.
-
Impact : Resistance to change from employees
Example : Example: Employees express resistance to adopting new technologies after training sessions, leading to frustration and underutilization of the advanced systems implemented in the automotive plant.
-
Impact : Inconsistent training quality across teams
Example : Example: Variability in training quality across different teams creates inefficiencies, causing some teams to excel while others lag behind, ultimately impacting overall productivity in the automotive facility.
-
Impact : Time away from production during training
Example : Example: Employees spend significant time away from production during training sessions, creating short-term productivity issues that affect output and revenue, highlighting the need for balanced scheduling.
-
Impact : Enhances data interpretation for insights
Example : Example: An automotive company integrates advanced analytics tools, allowing teams to derive actionable insights from production data, leading to a 20% improvement in operational efficiency and reduced waste.
-
Impact : Supports proactive decision-making strategies
Example : Example: By employing advanced analytics, a car manufacturer supports proactive decision-making, enabling teams to respond to market shifts quickly, resulting in a 15% increase in competitiveness.
-
Impact : Improves operational efficiency across processes
Example : Example: Advanced analytics tools enable an automotive plant to streamline processes, enhancing overall efficiency, leading to a 25% reduction in cycle times and significant cost savings.
-
Impact : Facilitates cross-departmental collaboration
Example : Example: The implementation of advanced analytics fosters cross-departmental collaboration, ensuring alignment in strategies, which ultimately enhances overall productivity and innovation within the automotive organization.
-
Impact : High initial costs for analytics tools
Example : Example: A leading auto manufacturer hesitates to implement advanced analytics due to high initial costs associated with acquiring software licenses and training staff, delaying potential operational improvements.
-
Impact : Data security and compliance issues
Example : Example: An automotive company faces data security concerns during the implementation of analytics tools, leading to compliance issues that require additional resources to address and mitigate risks.
-
Impact : Dependence on specialized skill sets
Example : Example: The reliance on specialized skill sets for analytics creates challenges when key personnel leave the organization, resulting in a knowledge gap that hampers effective decision-making and operational efficiency.
-
Impact : Integration challenges with existing workflows
Example : Example: Integrating advanced analytics tools with existing workflows proves complex, causing disruptions in daily operations and leading to a temporary decline in productivity as teams adapt.
AI-driven root cause analysis transforms the automotive industry by enabling precise defect identification and prevention, fundamentally changing how we approach quality management.
– Internal R&DCompliance Case Studies



Embrace AI-driven solutions to identify issues faster and boost efficiency. Stay ahead of competitors and unlock transformative insights in your automotive operations today!

Leadership Challenges & Opportunities
Data Quality Issues
Utilize Machine Learning for Root Cause Analysis to enhance data validation and cleaning processes. Implement automated data quality checks and anomaly detection algorithms to ensure accuracy. This approach improves decision-making and reduces operational risks by providing reliable insights into underlying issues.
Change Resistance
Facilitate a cultural shift by integrating Machine Learning for Root Cause Analysis through stakeholder engagement and change management strategies. Provide interactive demonstrations and pilot projects to showcase benefits, fostering acceptance. Empower teams with data-driven insights that encourage proactive problem-solving and innovation.
Resource Allocation Challenges
Leverage Machine Learning for Root Cause Analysis to optimize resource distribution based on predictive analytics. Implement algorithms that forecast demand and identify bottlenecks, ensuring efficient utilization of assets. This strategy enhances operational efficiency and reduces costs while improving overall productivity in the Automotive sector.
Skill Shortages in AI
Address the talent gap by partnering with educational institutions to create targeted training programs in Machine Learning for Root Cause Analysis. Implement mentorship initiatives and online learning platforms that provide accessible resources. This approach cultivates a skilled workforce capable of leveraging advanced analytics for operational improvements.
Assess how well your AI initiatives align with your business goals

AI Use Case vs ROI Timeline
| AI Use Case | Description | Typical ROI Timeline | Expected ROI Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Predictive Maintenance Scheduling | AI analyzes historical machine data to predict failures and schedule maintenance. For example, automotive manufacturers use this to preemptively replace parts, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. | 6-12 months | Medium-High |
| Quality Control Optimization | Machine learning algorithms identify defects in real-time during production. For example, automotive assembly lines leverage AI to analyze images of parts, enhancing quality assurance and minimizing waste. | 6-12 months | High |
| Anomaly Detection in Production | AI systems monitor production processes for anomalies. For example, automotive plants use ML to detect unusual patterns in assembly lines, allowing for immediate corrective actions and reducing scrap rates. | 12-18 months | Medium |
| Supply Chain Optimization | ML models analyze supply chain data to identify root causes of delays. For example, automotive companies use AI to forecast disruptions, improving delivery timelines and reducing excess inventory. | 12-18 months | Medium-High |
Glossary
Work with Atomic Loops to architect your AI implementation roadmap — from PoC to enterprise scale.
Contact NowFrequently Asked Questions
- Machine Learning for Root Cause Analysis helps identify issues in automotive processes efficiently.
- It automates data analysis, allowing for faster detection of underlying problems.
- The technology leverages historical data to predict future failures and enhance reliability.
- Automakers benefit from improved quality control and reduced defect rates.
- Ultimately, it supports better decision-making and increased operational efficiency.
- Start by assessing your current data infrastructure and quality for effective analysis.
- Identify key stakeholders and form a dedicated team to guide the implementation process.
- Select a pilot project that demonstrates clear value and aligns with business goals.
- Invest in training to ensure your team understands Machine Learning fundamentals.
- Consider collaborating with AI specialists to optimize the implementation approach.
- Companies experience increased efficiency through faster identification of root causes.
- Operational costs decrease as issues are resolved quicker, leading to fewer recalls.
- Customer satisfaction improves due to enhanced product quality and reliability.
- Data-driven insights lead to informed strategic decisions and optimizations.
- Overall, businesses gain a competitive edge in the automotive market through innovation.
- Data quality and availability are common hurdles that must be addressed initially.
- Resistance to change from staff can impede successful adoption of new technologies.
- Integration with legacy systems may present technical difficulties requiring careful planning.
- Ensuring compliance with industry regulations is crucial during implementation phases.
- A clear change management strategy can help mitigate these challenges effectively.
- Organizations should consider implementation when they have sufficient data for analysis.
- Timing is ideal during periods of operational inefficiency or quality issues.
- Evaluate readiness by assessing technological infrastructure and team capabilities.
- Strategic planning ensures alignment with broader organizational goals and innovations.
- Monitor industry trends to remain competitive and proactive in adopting new technologies.
- Begin with a clear understanding of business objectives to guide your efforts.
- Invest in high-quality data collection and maintain data integrity throughout processes.
- Engage cross-functional teams to foster collaboration and knowledge sharing.
- Iterate and refine models continually based on feedback and performance metrics.
- Ensure ongoing training and support for staff to maximize technology adoption.
- Compliance with safety standards and industry regulations is paramount during implementation.
- Data privacy laws must be adhered to when collecting and processing customer data.
- Documentation and transparency in algorithms help ensure regulatory compliance.
- Regular audits can identify potential compliance issues before they escalate.
- Staying informed on regulatory changes is crucial for ongoing compliance and strategy.

