Machine Learning in Production Scheduling
Machine Learning in Production Scheduling refers to the integration of advanced algorithms and data analytics in optimizing production processes within the Automotive sector. As manufacturers face increasing pressure to enhance efficiency and reduce lead times, these intelligent systems enable real-time adjustments and predictive maintenance, aligning with the broader trends of AI-led transformation. This approach not only streamlines operations but also supports strategic decision-making, fostering a culture of continuous improvement among stakeholders.
The significance of the Automotive ecosystem in relation to Machine Learning in Production Scheduling cannot be overstated. AI-driven practices are revolutionizing how companies compete, innovate, and interact with stakeholders, leading to improved operational efficiencies and data-driven insights. The adoption of these technologies is setting new benchmarks for decision-making processes, while also presenting growth opportunities. However, organizations must navigate challenges such as integration complexities, varying levels of technological readiness, and shifting expectations in a rapidly evolving landscape.
Drive Competitiveness with AI-Enhanced Production Scheduling
Automotive companies should strategically invest in partnerships that leverage machine learning technologies for production scheduling, ensuring a focus on data-driven decision-making. Implementing these AI strategies is expected to enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, and significantly improve product delivery timelines, thus creating a sustainable competitive edge.
How is Machine Learning Revolutionizing Production Scheduling in Automotive?
Implementation Framework
Conduct a thorough assessment of existing data quality to ensure it meets AI-driven analytics standards. This step is crucial for reliable machine learning models that enhance production scheduling efficiency and accuracy.
Industry Standards
Integrate predictive analytics into production scheduling to anticipate demand fluctuations. This enables proactive adjustments, optimizing resource allocation while minimizing waste and enhancing overall operational efficiency in the automotive supply chain.
Technology Partners
Set up a real-time monitoring system to track production metrics and performance. This fosters immediate decision-making and quick adjustments, significantly improving operational efficiency and responsiveness to potential disruptions in automotive manufacturing.
Cloud Platform
Incorporate AI-driven automation in scheduling processes to enhance accuracy and efficiency. This reduces manual errors and allows for dynamic adjustments based on real-time data, significantly optimizing production workflows in the automotive industry.
Internal R&D
Establish a continuous training program for staff to ensure they are equipped with the necessary AI skills and knowledge. This investment in human capital is essential for maximizing the benefits of AI-driven production scheduling and maintaining competitiveness.
Industry Standards
Best Practices for Automotive Manufacturers
-
Impact : Enhances defect detection accuracy significantly
Example : Example: In an automotive assembly line, a vision-based AI system flags microscopic paint defects in real time as car bodies pass under cameras, catching flaws human inspectors previously missed during night shifts.
-
Impact : Reduces production downtime and costs
Example : Example: A semiconductor factory uses AI to detect early soldering anomalies. The system stops the line immediately, preventing a full batch failure that would have caused hours of rework and shutdown.
-
Impact : Improves quality control standards
Example : Example: A food packaging plant uses AI image recognition to verify seal integrity on every packet, ensuring non-compliant packages are rejected instantly before shipping.
-
Impact : Boosts overall operational efficiency
Example : Example: AI dynamically adjusts inspection thresholds based on production speed, allowing the factory to increase output during peak demand without sacrificing quality.
-
Impact : High initial investment for implementation
Example : Example: A mid-sized electronics manufacturer delays AI rollout after realizing camera hardware, GPUs, and system integration push upfront costs beyond budget approvals.
-
Impact : Potential data privacy concerns
Example : Example: AI quality systems capturing worker activity unintentionally store employee facial data, triggering compliance issues with internal privacy policies.
-
Impact : Integration challenges with existing systems
Example : Example: AI software cannot communicate with a 15-year-old PLC controller, forcing engineers to manually export data and slowing decision-making.
-
Impact : Dependence on continuous data quality
Example : Example: Dust accumulation on camera lenses causes the AI to misclassify normal products as defective, leading to unnecessary scrap until recalibration.
-
Impact : Enables quick response to production anomalies
Example : Example: A major automotive manufacturer uses real-time monitoring to detect machine vibrations, allowing engineers to address issues before they escalate into costly downtime.
-
Impact : Improves scheduling accuracy and efficiency
Example : Example: By implementing AI-driven scheduling, a factory reduces idle time for robots, increasing throughput by 15% and delivering vehicles ahead of schedule.
-
Impact : Facilitates proactive maintenance strategies
Example : Example: A predictive maintenance system alerts technicians to machinery wear, enabling repairs before breakdowns occur, effectively reducing maintenance costs by 20%.
-
Impact : Enhances supply chain visibility and coordination
Example : Example: Real-time tracking of parts inventory ensures that production schedules align with supply chain deliveries, minimizing delays and optimizing workflow.
-
Impact : Requires robust IT infrastructure
Example : Example: A leading automotive firm invested heavily in real-time monitoring but faced significant IT infrastructure failures during initial deployment, causing production disruptions and loss of trust.
-
Impact : Potential resistance from workforce
Example : Example: Workers resist adopting new AI technologies, fearing job loss. This leads to incomplete system utilization, hampering the benefits of real-time analytics and monitoring.
-
Impact : Over-reliance on technology
Example : Example: An automotive plant overly relies on AI for scheduling, leading to chaos when the system fails. Manual overrides are complicated and time-consuming, resulting in missed deadlines.
-
Impact : Complexity in real-time data integration
Example : Example: Integrating real-time data from disparate sources proves complex, leading to delays in actionable insights and causing confusion within the production team.
-
Impact : Increases employee engagement and retention
Example : Example: An automotive company offers regular AI training sessions, significantly increasing employee satisfaction scores and reducing turnover rates by 25% over two years.
-
Impact : Enhances skills for future technologies
Example : Example: By equipping workers with skills in machine learning, a factory saw a 30% decrease in production errors, directly impacting product quality and customer satisfaction.
-
Impact : Fosters a culture of innovation
Example : Example: Monthly workshops on AI trends encourage innovation, leading to new process improvements that enhance productivity and reduce waste by 15%.
-
Impact : Reduces errors in production processes
Example : Example: A well-trained workforce can quickly adapt to new technologies, facilitating smoother transitions during system upgrades and minimizing disruption to production schedules.
-
Impact : Training costs can be substantial
Example : Example: An automotive company invests heavily in training but finds that ongoing costs strain the budget, leading to cutbacks in other operational areas.
-
Impact : Resistance to change among employees
Example : Example: Employees show reluctance to adopt new AI tools, with many preferring traditional methods. This resistance prevents full integration of innovative practices in production.
-
Impact : Knowledge retention can be low
Example : Example: After several training sessions, many employees forget key concepts, resulting in a lack of proficiency that hampers productivity and quality standards.
-
Impact : Skill gaps may persist despite training
Example : Example: Despite training efforts, some workers still struggle with advanced AI applications, necessitating additional resources and time investments to bridge skill gaps.
-
Impact : Anticipates equipment failures effectively
Example : Example: A car manufacturer implements predictive analytics to anticipate equipment failures, resulting in a 40% reduction in unexpected downtime over six months, enhancing overall productivity.
-
Impact : Optimizes inventory management processes
Example : Example: By utilizing AI for inventory predictions, a factory reduced excess stock and associated holding costs by 20%, streamlining operations and improving cash flow.
-
Impact : Improves demand forecasting accuracy
Example : Example: Advanced algorithms improve demand forecasting, enabling a manufacturer to adjust production schedules, leading to a 30% increase in on-time deliveries to dealerships.
-
Impact : Enhances production planning efficiency
Example : Example: Predictive analytics in production planning allows for optimized resource allocation, reducing waste and increasing efficiency across the assembly line by 25%.
-
Impact : Data quality issues can arise
Example : Example: An automotive company faces challenges as inaccurate data inputs skew predictive analytics outcomes, leading to misguided production decisions and increased costs.
-
Impact : Initial integration can be complex
Example : Example: Integrating predictive analytics into existing systems proves complex, requiring significant time and resources, causing delays and frustration among the operational team.
-
Impact : Requires ongoing model adjustments
Example : Example: After initial success, a factory neglects to adjust its predictive models, resulting in outdated forecasts and unexpected inventory shortages during peak demand.
-
Impact : May lead to overconfidence in predictions
Example : Example: Overconfidence in predictive analytics leads a manufacturer to reduce safety stock levels, resulting in production halts when unexpected demand spikes occur.
-
Impact : Reduces manual intervention in production
Example : Example: A leading automotive plant automates assembly line tasks, reducing manual labor by 50%, which in turn speeds up production and lowers operational costs significantly.
-
Impact : Increases throughput and efficiency
Example : Example: Workflow automation enables a factory to increase its throughput by 30%, allowing them to meet rising market demands without compromising quality standards.
-
Impact : Enhances product consistency and quality
Example : Example: Automated quality checks ensure that each vehicle meets stringent safety standards consistently, reducing recalls and enhancing brand reputation in the market.
-
Impact : Streamlines communication across departments
Example : Example: Streamlined communication through automated systems allows for quicker decision-making between production and supply chain teams, improving overall operational efficiency.
-
Impact : Automation can lead to job losses
Example : Example: A fully automated automotive factory faces backlash from workers fearing job losses, leading to morale issues and potential strikes affecting production schedules.
-
Impact : System failures may disrupt production
Example : Example: A sudden system failure in an automated assembly line halts production for hours, resulting in significant financial losses and delays in vehicle deliveries.
-
Impact : Initial setup can be costly
Example : Example: The initial setup costs for automation systems strain the budget, leading to cutbacks in other important areas such as employee training and safety improvements.
-
Impact : Complexity in system management
Example : Example: Managing a complex automated system requires specialized skills, leading to challenges in finding qualified personnel and increasing operational risks.
-
Impact : Supports informed strategic planning
Example : Example: Using data analytics, a leading automotive manufacturer identifies market trends, allowing for strategic planning that leads to a 15% increase in market share over two years.
-
Impact : Enhances operational transparency
Example : Example: Enhanced operational transparency through data-driven insights allows managers to pinpoint inefficiencies, resulting in targeted improvements that save costs by 10%.
-
Impact : Facilitates real-time decision-making
Example : Example: Real-time data analysis enables quick decision-making during production shifts, allowing for immediate adjustments that enhance productivity and reduce delays.
-
Impact : Boosts competitive advantage in market
Example : Example: A data-driven approach empowers an automotive firm to anticipate market changes, giving them a competitive edge that results in a 20% increase in sales.
-
Impact : Data overload can occur
Example : Example: An automotive company struggles with data overload, leading to analysis paralysis where managers are unable to make timely decisions, impacting production schedules.
-
Impact : Requires skilled data analysts
Example : Example: The lack of skilled data analysts hampers the effectiveness of data-driven initiatives, resulting in poor insights that do not translate into actionable strategies.
-
Impact : Misinterpretation of data may happen
Example : Example: A misinterpretation of key data trends leads to misguided decisions, causing production inefficiencies that cost the company significant revenue.
-
Impact : Dependence on accurate data sources
Example : Example: A manufacturer’s reliance on inaccurate data sources results in flawed strategic decisions, ultimately impacting their market positioning and profitability.
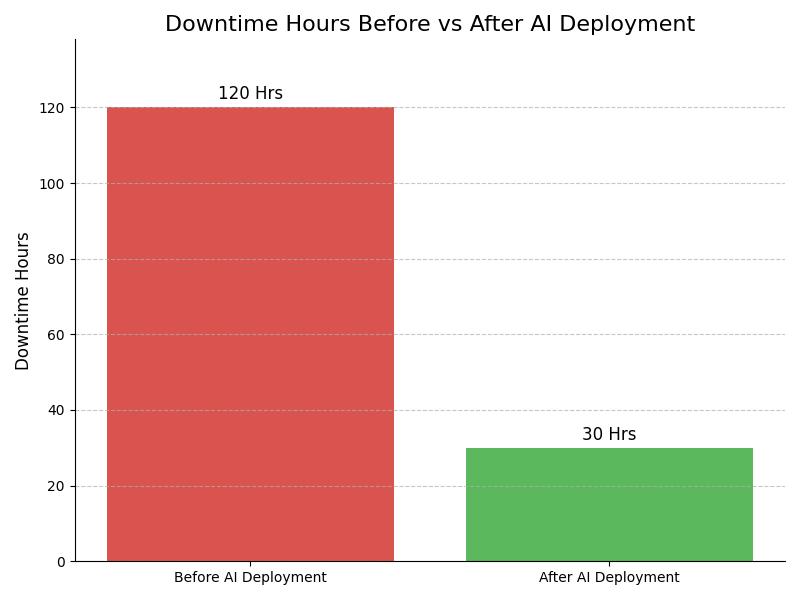
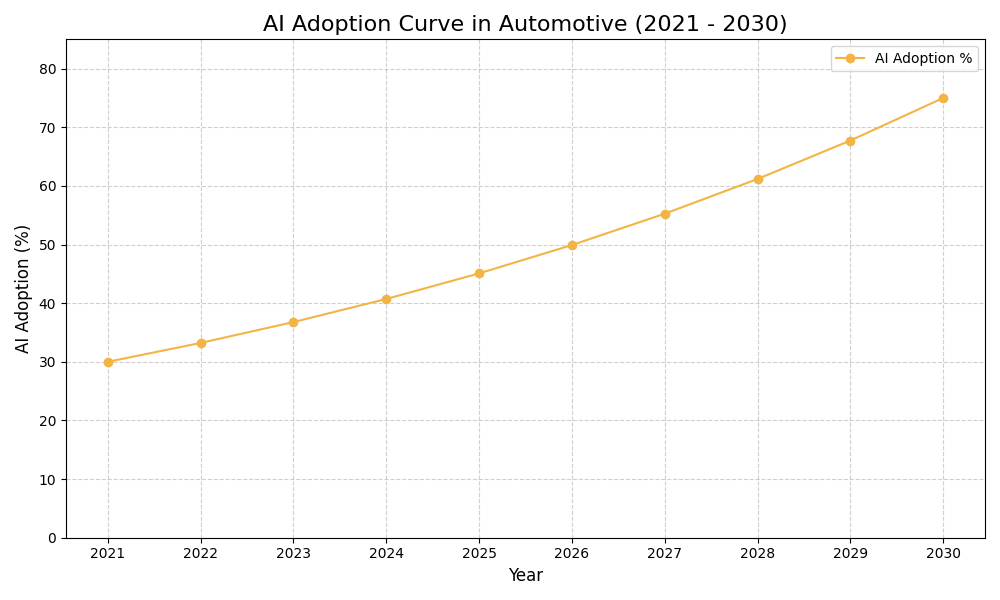
AI is revolutionizing production scheduling in the automotive industry, enabling unprecedented efficiency and adaptability through machine learning.
– RonschmelzerCompliance Case Studies




Embrace the future of production scheduling in the automotive sector. Unlock efficiency, reduce costs, and gain a competitive edge with AI-driven solutions today.

Leadership Challenges & Opportunities
Data Quality Issues
Utilize Machine Learning in Production Scheduling to enhance data preprocessing and validation techniques. Implement automated data cleaning algorithms to ensure high-quality inputs. This approach minimizes errors and optimizes scheduling decisions, ultimately improving production efficiency and reducing downtime.
Change Resistance
Foster a culture of innovation by integrating Machine Learning in Production Scheduling through user-friendly interfaces and demonstrable benefits. Conduct workshops showcasing successful case studies in the Automotive sector to alleviate fears and build enthusiasm, facilitating smoother adoption and collaboration across departments.
Integration Costs
Leverage cloud-based Machine Learning in Production Scheduling solutions that offer flexible pricing models to reduce initial integration costs. Begin with pilot projects focusing on critical areas, enabling organizations to validate effectiveness and gather support for broader implementation without overwhelming financial strain.
Talent Acquisition Challenges
Utilize Machine Learning in Production Scheduling to create intelligent talent management systems that identify skill gaps and facilitate targeted training programs. Collaborate with educational institutions to establish internships and co-op programs, ensuring a pipeline of skilled professionals ready to leverage advanced scheduling technologies.
Assess how well your AI initiatives align with your business goals
AI Use Case vs ROI Timeline
| AI Use Case | Description | Typical ROI Timeline | Expected ROI Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demand Forecasting Optimization | Using machine learning algorithms to predict future demand based on historical data. For example, an automotive manufacturer employs AI to analyze trends, leading to accurate stock adjustments and reduced inventory costs. | 6-12 months | Medium-High |
| Automated Scheduling Systems | Implementing AI-driven scheduling tools that optimize production timelines. For example, a factory uses AI to allocate resources dynamically, increasing throughput and reducing downtime during peak production hours. | 6-12 months | High |
| Predictive Maintenance Alerts | Leveraging machine learning to predict equipment failures before they occur. For example, an automotive assembly line uses AI to schedule maintenance based on usage data, minimizing unexpected breakdowns and costly repairs. | 12-18 months | Medium-High |
| Quality Control Automation | Utilizing AI to enhance quality control processes through image recognition. For example, an automotive plant employs AI cameras to identify defects in real-time, reducing waste and ensuring product quality. | 6-12 months | High},{ |
Glossary
Work with Atomic Loops to architect your AI implementation roadmap — from PoC to enterprise scale.
Contact NowFrequently Asked Questions
- Start by assessing current production processes to identify areas for improvement.
- Engage stakeholders to understand their needs and align AI objectives with business goals.
- Invest in training and resources to build a skilled team for AI implementation.
- Utilize pilot projects to test concepts and gather valuable insights before full-scale deployment.
- Ensure continuous monitoring and adjustment to enhance AI model performance over time.
- AI can significantly enhance operational efficiency by automating scheduling tasks.
- It enables real-time data analysis, improving decision-making and responsiveness.
- Companies can achieve higher accuracy in demand forecasting through machine learning algorithms.
- AI-driven scheduling optimizes resource utilization, leading to cost savings and reduced waste.
- Implementing AI can provide a competitive edge by accelerating production cycles and improving quality.
- Data quality issues can hinder effective machine learning model development and outcome accuracy.
- Resistance to change among employees may pose challenges during implementation phases.
- Integration with legacy systems can complicate the deployment of new AI technologies.
- Ensuring compliance with industry regulations requires careful planning and execution.
- Lack of clear objectives may lead to disjointed AI initiatives that fail to deliver value.
- Establish clear metrics to evaluate productivity and efficiency before implementation.
- Monitor changes in operational costs to assess financial impacts of AI initiatives.
- Evaluate improvements in lead times and customer satisfaction as key performance indicators.
- Analyze data-driven insights to understand the long-term value generated from AI solutions.
- Regularly review and adjust strategies to ensure continued alignment with business objectives.
- Start with a clear strategy that outlines goals, scope, and expected outcomes.
- Involve cross-functional teams to gather diverse insights and foster collaboration.
- Invest in continual training to keep teams updated on AI and machine learning advancements.
- Leverage existing data while ensuring it is clean and relevant for model training.
- Regularly assess and refine AI models to adapt to changing operational needs.
- Evaluate current operational challenges to determine if AI can address them effectively.
- Consider market demands and competitive pressures that necessitate quicker decision-making.
- Assess organizational readiness in terms of technology and employee skills for AI adoption.
- Look for opportunities to improve efficiency and reduce costs through data-driven insights.
- Timing also depends on available resources and support from leadership for AI initiatives.
- Understand industry-specific regulations that govern data usage and AI deployment.
- Ensure compliance with privacy laws that protect customer and employee information.
- Stay informed about evolving standards related to AI ethics and accountability.
- Implement data security measures to safeguard sensitive information during AI processing.
- Regular audits can help ensure ongoing compliance and mitigate legal risks associated with AI.
- AI can optimize assembly line scheduling to reduce downtime and improve throughput.
- Predictive maintenance powered by AI helps in minimizing equipment failures and delays.
- Real-time inventory management can be enhanced through AI-driven analytics and forecasting.
- AI can assist in dynamic scheduling to adapt to sudden changes in demand or supply chain disruptions.
- Customized production planning can improve customer satisfaction by aligning output with preferences.

