Predictive Maintenance Automotive
Predictive Maintenance Automotive refers to a proactive approach in the Automotive sector that leverages advanced analytics and AI technologies to anticipate vehicle maintenance needs before failures occur. This concept is critical for stakeholders, as it not only minimizes operational disruptions but also optimizes maintenance schedules, ultimately enhancing vehicle reliability and reducing costs. In the context of ongoing AI-led transformations, predictive maintenance aligns with shifting operational priorities aimed at increased efficiency and improved customer satisfaction.
In the rapidly evolving automotive ecosystem, the implementation of AI-driven practices in predictive maintenance is reshaping competitive dynamics and fostering innovation. By harnessing real-time data and machine learning algorithms, companies can enhance decision-making processes and streamline operations, leading to improved performance outcomes. While the adoption of these technologies presents significant growth opportunities, stakeholders must navigate challenges such as integration complexity and evolving expectations from consumers and regulatory bodies. Balancing these factors will be essential for leveraging the full potential of predictive maintenance in the automotive landscape.
Unlock Competitive Advantage with Predictive Maintenance in Automotive
Automotive leaders should forge strategic partnerships with AI technology providers to enhance predictive maintenance capabilities, ensuring a proactive approach to vehicle upkeep. Implementing AI-driven analytics not only reduces operational costs but also significantly improves vehicle reliability and customer satisfaction, delivering substantial ROI.
How is Predictive Maintenance Transforming the Automotive Sector?
Implementation Framework
Begin by integrating IoT sensors into vehicles to collect real-time data. This enables predictive analytics by creating a continuous feedback loop, enhancing maintenance schedules, and reducing unexpected failures, which boosts operational efficiency.
Industry Standards
Deploy AI algorithms to analyze collected data for actionable insights. This analysis helps predict potential failures based on patterns, significantly reducing downtime and ensuring timely maintenance, ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Technology Partners
Develop machine learning models that utilize historical data and real-time analytics to predict maintenance needs. These models aid in scheduling the right maintenance at the right time, optimizing costs and resources effectively.
Internal R&D
Integrate predictive maintenance systems with existing enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. This ensures seamless communication and workflow, enabling timely interventions and enhancing strategic decision-making throughout the organization.
Cloud Platform
Establish a framework for continuous monitoring and optimization of predictive maintenance strategies. Regularly assess system performance and adjust models based on new data, ensuring enhanced efficiency and reduced operational risks over time.
Industry Standards
Best Practices for Automotive Manufacturers
-
Impact : Increases maintenance schedule accuracy
Example : Example: A leading automotive manufacturer uses AI-driven analytics to predict maintenance needs, leading to a 25% increase in maintenance schedule accuracy, thereby minimizing unexpected equipment failures and maximizing uptime.
-
Impact : Enhances equipment lifespan and reliability
Example : Example: An automotive parts supplier adopts predictive analytics to monitor machinery health, extending the lifespan of key equipment by 30%, which translates to significant cost savings in replacements.
-
Impact : Reduces unexpected breakdowns significantly
Example : Example: AI algorithms analyze historical data, allowing an automotive plant to anticipate breakdowns. This proactive approach reduces unplanned downtime by 40%, boosting overall production efficiency.
-
Impact : Optimizes resource allocation effectively
Example : Example: By utilizing advanced analytics, a car manufacturer optimizes resource allocation, ensuring that spare parts are available when needed, resulting in a 20% reduction in inventory costs.
-
Impact : Requires skilled personnel for analysis
Example : Example: An automotive company discovers that its staff lacks the necessary skills to interpret AI-driven insights, resulting in underutilization of predictive analytics tools and missed opportunities for improvement.
-
Impact : Data integration may pose challenges
Example : Example: During an AI implementation, a major automotive firm faces data integration challenges, as legacy systems fail to communicate, leading to delays and additional costs in the predictive maintenance rollout.
-
Impact : Over-reliance on AI predictions
Example : Example: A vehicle manufacturer becomes overly reliant on AI predictions, neglecting human expertise. When the AI mispredicts a maintenance need, it results in costly downtime and repairs.
-
Impact : Initial setup can be time-consuming
Example : Example: The initial setup of AI predictive tools takes longer than expected at a manufacturing plant, leading to delays in realizing the expected benefits and pushing back ROI timelines.
-
Impact : Enables immediate issue detection
Example : Example: An automotive assembly line uses real-time monitoring systems to detect anomalies instantly. This allows technicians to address issues within minutes, preventing major production halts and maintaining flow.
-
Impact : Reduces response time to failures
Example : Example: A car manufacturer implements real-time monitoring to track equipment performance. This reduces the average response time to failures by 50%, significantly enhancing productivity.
-
Impact : Improves operational decision-making
Example : Example: Real-time data analytics at a vehicle production plant leads to faster operational decisions. With immediate access to performance metrics, managers can make informed adjustments in real time, enhancing output.
-
Impact : Increases overall equipment effectiveness
Example : Example: An automotive supplier employs 24/7 monitoring of equipment, resulting in a noticeable increase in overall equipment effectiveness by 15%, as unplanned downtimes are drastically reduced.
-
Impact : High costs associated with technology
Example : Example: An automotive company faces high costs when implementing advanced monitoring technologies. Initial hardware and software expenditures exceed budget estimates, causing financial strains.
-
Impact : Data overload can occur
Example : Example: A vehicle manufacturer experiences data overload from excessive real-time monitoring. This leads to analysis paralysis, where staff struggle to prioritize actionable insights, resulting in delayed responses.
-
Impact : Requires constant system updates
Example : Example: Maintaining constant updates for real-time systems becomes a challenge for an automotive plant, causing interruptions in production when updates are not synchronized properly, affecting reliability.
-
Impact : Potential for system vulnerabilities
Example : Example: A new real-time monitoring system introduces vulnerabilities that hackers exploit, leading to unauthorized access to sensitive operational data and causing significant security concerns.
-
Impact : Enhances employee skill sets
Example : Example: An automotive manufacturer invests in regular AI training for technicians, significantly enhancing their skill sets. This results in a 30% improvement in productivity as employees adapt to new technologies more efficiently.
-
Impact : Fosters a culture of innovation
Example : Example: Regular training sessions foster a culture of innovation at a car assembly plant. Employees feel empowered to suggest improvements, leading to process enhancements that reduce costs by 15%.
-
Impact : Reduces resistance to change
Example : Example: A company introducing predictive maintenance faces initial resistance. However, regular training mitigates concerns, fostering acceptance and leading to smoother implementation of new technologies across the workforce.
-
Impact : Improves overall productivity
Example : Example: Automakers see a notable increase in overall productivity after implementing continuous training programs, which enhance employees' capabilities to leverage AI tools effectively, boosting output by 20%.
-
Impact : Training costs can be substantial
Example : Example: An automotive firm faces substantial training costs during AI implementation, straining budgets. The financial burden delays other operational improvements, impacting overall efficiency during the transition.
-
Impact : Employee turnover may hinder progress
Example : Example: High employee turnover at an automotive plant disrupts training initiatives. New hires struggle to catch up, resulting in inconsistent application of predictive maintenance practices and lost productivity.
-
Impact : Resistance to new methods may arise
Example : Example: Resistance to new AI methods arises among employees who are accustomed to traditional practices, causing delays in adopting predictive maintenance strategies and hindering progress.
-
Impact : Skill gaps may still exist
Example : Example: Despite training efforts, some employees still lack necessary skills to manage new predictive tools effectively, leading to ongoing skill gaps that affect operational performance in certain areas.
-
Impact : Improves forecasting accuracy
Example : Example: An automotive company leverages data analytics to improve forecasting accuracy for parts demand. This results in better inventory management and a 25% reduction in storage costs.
-
Impact : Identifies trends and patterns
Example : Example: By identifying trends through data analytics, a car manufacturer anticipates maintenance needs, reducing unplanned downtime by 40%, thus lowering operational costs significantly.
-
Impact : Enhances decision-making processes
Example : Example: Data analytics enhances decision-making at an automotive plant, allowing managers to base their strategies on concrete data rather than intuition, leading to improved operational performance.
-
Impact : Drives cost-saving initiatives
Example : Example: An automotive supplier uses data analytics to identify inefficiencies in production. Implementing improvements based on these insights drives significant cost-saving initiatives, cutting expenses by 15%.
-
Impact : Data quality may vary significantly
Example : Example: An automotive manufacturer discovers that poor data quality undermines the effectiveness of its predictive analytics tools, leading to inaccurate forecasts and operational inefficiencies.
-
Impact : Integration with existing systems is complex
Example : Example: During implementation, an automotive company faces complexities with integrating data analytics into legacy systems. The process becomes time-consuming, causing delays in realizing expected benefits.
-
Impact : Requires ongoing data management
Example : Example: An automotive assembly plant struggles with ongoing data management issues, as inconsistent data entry practices lead to discrepancies that complicate analysis and hinder decision-making.
-
Impact : Potential for misinterpretation of data
Example : Example: Employees misinterpret data insights from analytics tools, leading to flawed decisions in maintenance scheduling. This results in unexpected downtimes that could have been avoided with clearer interpretations.
-
Impact : Facilitates seamless data access
Example : Example: An automotive company adopts cloud-based solutions for predictive maintenance, facilitating seamless data access for teams worldwide. This leads to faster decision-making and immediate responses to equipment issues.
-
Impact : Enhances collaboration across teams
Example : Example: With cloud-based systems, an automotive plant enhances collaboration between maintenance and production teams. This results in improved communication and a 20% increase in overall efficiency due to coordinated efforts.
-
Impact : Supports scalability of operations
Example : Example: An automotive supplier benefits from scalable cloud solutions, allowing them to easily adjust resources according to demand fluctuations, significantly improving operational flexibility and responsiveness.
-
Impact : Reduces hardware costs significantly
Example : Example: By opting for cloud solutions, an automotive manufacturer reduces hardware costs associated with on-premises servers, reallocating those funds to enhance other operational efficiencies.
-
Impact : Security concerns with cloud data
Example : Example: An automotive firm faces security concerns when migrating sensitive maintenance data to the cloud, raising alarms about potential breaches and data loss, which could damage reputation.
-
Impact : Dependency on internet connectivity
Example : Example: A vehicle manufacturer experiences disruptions in service due to dependency on internet connectivity. Outages lead to temporary lapses in data access, impacting operations significantly.
-
Impact : Migration challenges from legacy systems
Example : Example: Migrating from legacy systems to cloud-based solutions proves challenging for one automotive company, resulting in unexpected delays and costs as they struggle to ensure data integrity during the transition.
-
Impact : Potential hidden costs of services
Example : Example: An automotive supplier discovers hidden costs associated with cloud services, such as data storage fees, which were not initially budgeted, leading to financial strain on the operational budget.
AI-driven predictive maintenance is not just about reducing costs; it's about redefining the future of automotive reliability and efficiency.
– Anan BisharaCompliance Case Studies



Harness AI-driven predictive maintenance to enhance operational efficiency and outperform competitors. Transform your automotive business for a future of unparalleled reliability and performance.

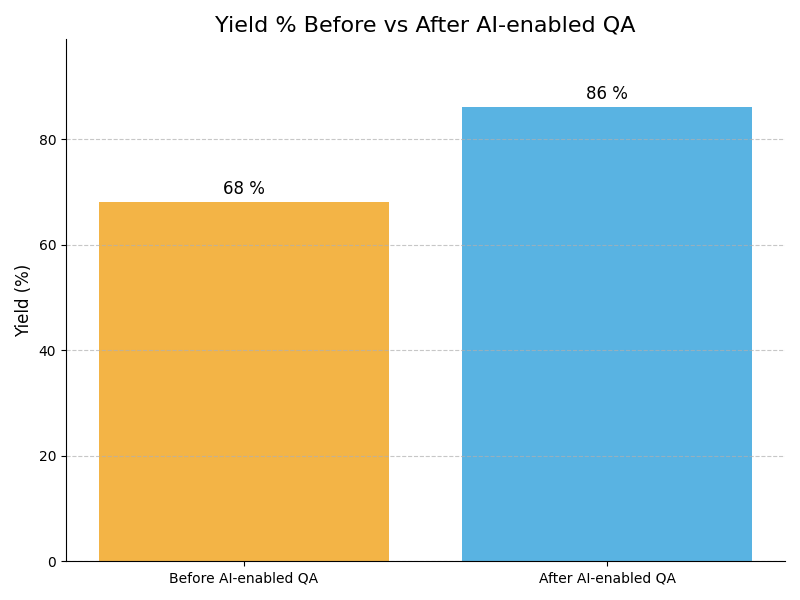
Leadership Challenges & Opportunities
Data Integration Challenges
Utilize Predictive Maintenance Automotive to unify disparate data sources through a centralized platform, enhancing data visibility and reliability. Implement IoT sensors for real-time data collection and analytics, allowing seamless integration with existing systems, ultimately improving operational efficiency and decision-making.
Change Management Resistance
Employ Predictive Maintenance Automotive to foster a culture of innovation by demonstrating quick wins in efficiency and cost savings. Initiate change management programs that include stakeholder engagement and training sessions, ensuring teams understand the benefits and empowering them to embrace new technologies.
Cost of Implementation
Mitigate initial costs by adopting a phased implementation of Predictive Maintenance Automotive, starting with critical assets to showcase ROI. Use cloud-based solutions to reduce infrastructure costs, allowing for incremental scaling that aligns with the organization's budget while maximizing long-term operational benefits.
Skill Shortages in Analytics
Address skill gaps by integrating Predictive Maintenance Automotive with user-friendly analytical tools that require less technical expertise. Provide comprehensive training programs and partner with educational institutions to develop talent pipelines, enabling employees to effectively utilize predictive analytics for maintenance decision-making.
Assess how well your AI initiatives align with your business goals
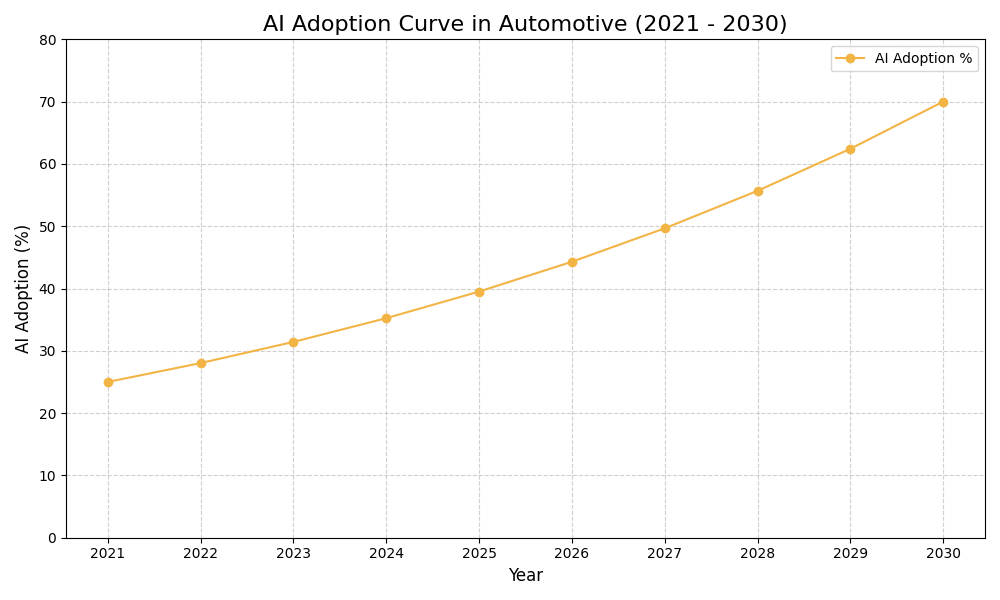
AI Use Case vs ROI Timeline
| AI Use Case | Description | Typical ROI Timeline | Expected ROI Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sensor Data Analysis for Fleet | AI analyzes sensor data from vehicles to predict maintenance needs, preventing breakdowns. For example, a fleet management company uses AI to monitor tire pressure and alerts drivers before a failure occurs, optimizing safety and reducing costs. | 6-12 months | High |
| Predictive Analytics for Engine Health | Utilizing predictive analytics, AI forecasts engine failures based on historical performance data. For example, an automotive manufacturer implements AI to analyze vibration data, predicting when components need servicing, thus minimizing downtime and repair costs. | 12-18 months | Medium-High |
| Maintenance Scheduling Optimization | AI optimizes maintenance schedules by analyzing vehicle usage patterns and wear rates. For example, a logistics company uses AI to adjust maintenance intervals based on usage, leading to increased vehicle availability and lower operational costs. | 6-12 months | Medium-High |
| Real-Time Diagnostics and Alerts | AI systems provide real-time diagnostics and alerts for vehicle maintenance issues. For example, a ride-sharing service implements AI to notify drivers of engine issues immediately, enhancing customer satisfaction and reducing service disruptions. | 3-6 months | High |
Glossary
Work with Atomic Loops to architect your AI implementation roadmap — from PoC to enterprise scale.
Contact NowFrequently Asked Questions
- Predictive Maintenance Automotive uses data analytics to foresee potential equipment failures.
- AI algorithms analyze historical data for accurate predictions and actionable insights.
- This technology minimizes downtime by scheduling maintenance before issues arise.
- It improves vehicle reliability and customer satisfaction through timely interventions.
- Adopting AI-driven approaches offers a significant competitive advantage in the market.
- Begin by assessing your current maintenance practices and identifying gaps.
- Invest in data collection technologies to gather real-time performance metrics.
- Choose AI tools that integrate seamlessly with your existing systems and processes.
- Develop a pilot project to test and validate your predictive maintenance approach.
- Engage stakeholders to ensure alignment and support throughout the implementation.
- AI enhances operational efficiency by streamlining maintenance schedules and workflows.
- It provides real-time monitoring, reducing unexpected breakdowns and repair costs.
- Businesses enjoy improved asset longevity and reliability through proactive maintenance.
- AI-driven insights enable data-backed decision-making and strategic planning.
- Ultimately, this leads to increased customer loyalty and market competitiveness.
- Common challenges include data silos and lack of integration across systems.
- Resistance to change from staff can hinder adoption of new technologies.
- Data quality issues can affect the accuracy of predictive analytics.
- Budget constraints may limit the scope of implementation efforts.
- Establishing a clear strategy and training can mitigate many of these challenges.
- Organizations should consider implementing when they experience frequent equipment failures.
- Timing is crucial when preparing for new technology investments or upgrades.
- Before peak operational periods is ideal to ensure systems are ready.
- Evaluate organizational readiness and staff capabilities to adopt new methods.
- Continuous monitoring of performance metrics can signal the need for change.
- In automotive manufacturing, it ensures machinery operates without unexpected downtimes.
- Fleet management benefits through optimized maintenance schedules based on vehicle usage.
- Predictive analytics can enhance supply chain efficiency by anticipating needs.
- Electric vehicle manufacturers leverage predictive maintenance for battery management systems.
- Compliance with industry regulations can be improved through proactive maintenance practices.
- Start by establishing baseline performance metrics before implementation begins.
- Track reductions in unplanned downtime and associated repair costs over time.
- Evaluate improvements in asset utilization and overall operational efficiency.
- Customer satisfaction metrics can also indicate the success of predictive strategies.
- Regularly review and adjust strategies based on performance data to maximize ROI.

