Reinforcement Learning in Automotive Plants
Reinforcement Learning in Automotive Plants represents a groundbreaking approach within the Automotive sector, utilizing AI to enhance operational efficiency and decision-making processes. This concept involves training algorithms through trial and error, enabling systems to learn optimal strategies for production workflows, quality control, and resource management. As the industry pivots towards more intelligent manufacturing solutions, this practice aligns seamlessly with the broader trend of AI-led transformation, addressing the evolving needs of stakeholders who seek innovation and agility in their operations.
The significance of Reinforcement Learning in Automotive Plants is underscored by its potential to reshape competitive dynamics and innovation cycles across the ecosystem. As organizations adopt AI-driven practices, they experience enhanced efficiency and improved decision-making capabilities, ultimately steering their long-term strategic direction. However, while the opportunities for growth are substantial, challenges remain, including integration complexities and shifting expectations among stakeholders. Balancing these elements is crucial for organizations aiming to leverage AI effectively and realize its transformative potential in their operations.
Accelerate AI Adoption in Automotive Plants
Automotive companies should strategically invest in partnerships focused on Reinforcement Learning technologies and foster collaborations with AI innovators to optimize production processes. Implementing these AI solutions can lead to significant efficiency gains, reduced operational costs, and enhanced competitive advantages in the market.
How Reinforcement Learning is Transforming Automotive Manufacturing?
Implementation Framework
Begin by conducting a thorough assessment of current systems and processes to identify AI integration points. Understanding the existing landscape is vital for effective AI implementation and operational improvements in automotive plants.
Internal R&D
Design and develop reinforcement learning models that cater specifically to automotive plant operations. These models should focus on optimizing production processes, thereby enhancing efficiency and reducing operational costs significantly over time.
Technology Partners
Integrate real-time monitoring systems that collect and analyze data from production lines. This enables immediate feedback for reinforcement learning systems, enhancing decision-making and operational efficiency across automotive manufacturing processes.
Industry Standards
Provide comprehensive training programs for employees to equip them with skills necessary for utilizing AI-driven tools. Understanding AI's capabilities is essential for maximizing the benefits of reinforcement learning in automotive plants.
Cloud Platform
Regularly evaluate the performance of reinforcement learning models and make necessary adjustments based on operational feedback. Continuous optimization is critical for achieving sustained enhancements in efficiency and productivity in automotive plants.
Internal R&D
Best Practices for Automotive Manufacturers
-
Impact : Enhances decision-making speed and accuracy
Example : Example: An automotive plant uses adaptive RL models to optimize robot workflow, reducing cycle time by 20%, which translates to higher throughput and improved production efficiency.
-
Impact : Optimizes resource allocation in production
Example : Example: By leveraging adaptive learning, a factory reallocates resources dynamically based on real-time demand, resulting in a 15% reduction in waste and enhanced profitability.
-
Impact : Improves predictive maintenance capabilities
Example : Example: Predictive maintenance models prevent machinery failures by analyzing operational data, leading to a 30% decrease in unplanned downtime, thus ensuring smooth production flow.
-
Impact : Increases adaptability to market changes
Example : Example: The ability to adjust strategies in real time allows the plant to pivot quickly to emerging market trends, increasing overall competitiveness and market share.
-
Impact : Complexity in model training and tuning
Example : Example: A manufacturer struggles with training RL algorithms due to the complexity of their production environment, causing delays in implementation and potential losses in productivity during transition.
-
Impact : Requires continuous data input for accuracy
Example : Example: Continuous data input requirements lead to failures in an RL model's predictions, as outdated data caused inefficiencies and increased operational costs.
-
Impact : Potential for overfitting in models
Example : Example: Overfitting occurs when a model specialized to past production data fails to generalize, leading to poor performance during new product launches and a loss of confidence in AI systems.
-
Impact : Need for skilled personnel to manage systems
Example : Example: The lack of skilled data scientists to manage and interpret RL outputs results in underutilization of AI capabilities, hindering operational improvements and innovation.
-
Impact : Improves real-time decision-making agility
Example : Example: By utilizing real-time data analytics, a plant detects anomalies during assembly, allowing for immediate corrective actions, which reduces defect rates by 25% in the final inspection phase.
-
Impact : Enhances quality assurance processes
Example : Example: Implementing real-time quality checks through AI analytics enables early detection of defects, leading to a 40% decrease in customer returns, enhancing brand reputation.
-
Impact : Facilitates proactive problem-solving
Example : Example: Using data analytics, a plant can identify bottlenecks in the production line proactively, leading to a 15% reduction in cycle time and improved operational flow.
-
Impact : Boosts overall plant transparency
Example : Example: The transparent reporting enabled by real-time analytics fosters a culture of accountability, leading to higher employee engagement and performance optimization across all levels.
-
Impact : Dependence on stable network infrastructure
Example : Example: A plant experiences significant downtime due to network failures, which disrupts real-time data analytics, causing delays in critical decision-making processes and impacting production schedules.
-
Impact : Data overload may hinder analysis
Example : Example: Overwhelmed by vast amounts of data, a factory struggles to derive actionable insights, leading to missed opportunities for improvement and wasted resources on ineffective measures.
-
Impact : Risk of cybersecurity breaches
Example : Example: Cybersecurity breaches in the data analytics system expose sensitive production data, leading to potential loss of intellectual property and damaging the company's competitive edge.
-
Impact : Integration challenges with legacy systems
Example : Example: Legacy systems fail to integrate with new data analytics platforms, causing delays in deployment and hindering the potential benefits of real-time insights on production efficiency.
-
Impact : Enhances workforce skill and adaptability
Example : Example: A plant's initiatives to train employees on new RL systems result in a 30% increase in operational efficiency, as staff become more adept at leveraging AI tools in daily tasks.
-
Impact : Promotes a culture of continuous improvement
Example : Example: Regular training sessions create an environment of continuous improvement, leading to innovative ideas from employees that enhance production processes and reduce waste by 20%.
-
Impact : Ensures effective technology utilization
Example : Example: Employees trained on new technology quickly adapt to AI systems, ensuring maximum usage and efficiency, which results in a 15% decrease in operational costs over six months.
-
Impact : Reduces resistance to change
Example : Example: Proactive training reduces employee resistance to technological changes, resulting in smoother transitions during implementations and less disruption in production schedules.
-
Impact : High costs associated with training programs
Example : Example: A company halts AI training initiatives due to budget constraints, resulting in a skills gap that hampers the effective deployment of new technologies in the production line.
-
Impact : Time investment may slow operations
Example : Example: Extensive training sessions lead to temporary slowdowns in operations, causing missed production targets and affecting overall profitability during the transition period.
-
Impact : Potential for skill gaps in training
Example : Example: Inadequate training content results in skill gaps, where employees struggle to utilize RL systems effectively, leading to wasted investments in technology and missed opportunities for optimization.
-
Impact : Resistance from employees to new methods
Example : Example: Employees resist adopting new methods introduced in training, creating friction within teams and slowing down the integration of AI systems across the plant.
-
Impact : Aligns AI objectives with business goals
Example : Example: A plant redefines reward structures in its RL algorithms to prioritize cost reduction, resulting in a 15% decrease in production costs while maintaining quality standards.
-
Impact : Encourages desired operational behaviors
Example : Example: By aligning AI objectives with business goals, a manufacturer sees improved operational behavior, leading to faster production cycles and a 10% increase in throughput.
-
Impact : Improves model performance over time
Example : Example: Continuous adjustments to reward metrics improve model performance, allowing the RL system to adapt better to changes in production demands and market conditions, enhancing resilience.
-
Impact : Facilitates better resource management
Example : Example: Optimized reward structures encourage the efficient allocation of resources, reducing waste and ensuring optimal use of materials throughout the production process.
-
Impact : Misalignment between rewards and goals
Example : Example: A poorly defined reward structure leads to unintended behaviors in the RL model, resulting in increased defects as the system prioritizes speed over quality, damaging customer satisfaction.
-
Impact : Complexity in defining reward metrics
Example : Example: Difficulty in defining appropriate reward metrics creates confusion in the RL system, leading to inefficient operational decisions and a decline in overall productivity.
-
Impact : Risk of unintended consequences
Example : Example: Unintended consequences arise when the reward system encourages risky behaviors, causing safety concerns and increasing compliance risks on the shop floor.
-
Impact : Requires constant evaluation and adjustment
Example : Example: A company finds their reward structures require constant adjustments, leading to resource strain as teams spend more time recalibrating systems than improving operational efficiency.
-
Impact : Enhances knowledge sharing across teams
Example : Example: A cross-functional team comprising engineers and data scientists collaborates on RL projects, leading to innovative solutions that reduce production errors by 20% through shared expertise.
-
Impact : Drives innovation through diverse perspectives
Example : Example: Diverse perspectives foster innovation, resulting in new production techniques that improve efficiency by 15%, demonstrating the value of collaboration across departments.
-
Impact : Improves problem-solving capabilities
Example : Example: Cross-functional collaboration improves problem-solving capabilities, as teams tackle challenges collectively, resulting in quicker resolutions and reduced downtime during production.
-
Impact : Strengthens overall project outcomes
Example : Example: Stronger collaboration leads to comprehensive project outcomes, where integrated insights from different functions create a holistic approach to operational excellence.
-
Impact : Potential for communication breakdowns
Example : Example: Miscommunication between engineering and production teams leads to delays in RL implementation, resulting in missed deadlines and increased costs due to inefficient resource allocation.
-
Impact : Conflicting priorities among departments
Example : Example: Conflicting priorities among departments create friction, as production and engineering teams disagree on the implementation timeline, slowing down the project and delaying benefits.
-
Impact : Time investment may delay projects
Example : Example: The time invested in collaboration may delay project timelines, causing frustration among team members and impacting the overall efficiency of the production process.
-
Impact : Risk of dilution of expertise
Example : Example: In an effort to collaborate, key expertise may become diluted, leading to less effective solutions and potential setbacks in achieving operational goals.
-
Impact : Reduces risk before full deployment
Example : Example: A plant employs simulation environments to test RL algorithms, identifying potential issues that could disrupt production before actual implementation, thereby avoiding costly mistakes.
-
Impact : Facilitates safe experimentation with AI
Example : Example: Safe experimentation in simulated environments allows teams to tweak RL models without impacting real operations, resulting in a smoother transition to new technologies.
-
Impact : Improves understanding of RL dynamics
Example : Example: Improved understanding of RL dynamics through simulations enables engineers to optimize algorithms, leading to a 25% increase in production efficiency once deployed.
-
Impact : Accelerates innovation cycles
Example : Example: Accelerated innovation cycles result from using simulations, where teams iterate quickly on RL models, identifying optimal solutions faster and maintaining competitiveness in the market.
-
Impact : High costs of simulation tools
Example : Example: A manufacturer faces high costs associated with advanced simulation software, leading to budget constraints that limit their ability to fully explore RL applications in production.
-
Impact : Time-consuming setup and configuration
Example : Example: The time-consuming setup of simulation environments delays project timelines, causing frustration among stakeholders and impacting overall operational efficiency during transitions.
-
Impact : Potential for unrealistic testing scenarios
Example : Example: Unrealistic scenarios in testing environments lead to unexpected challenges during real-world implementation, resulting in a need for extensive adjustments post-deployment.
-
Impact : Requires ongoing maintenance and updates
Example : Example: Ongoing maintenance of simulation tools requires dedicated resources, diverting attention from core production activities and potentially hindering operational improvements.
Reinforcement learning is not just a tool; it's a catalyst for innovation in automotive manufacturing, enabling systems to learn and adapt in real-time.
– Bernard MarrCompliance Case Studies



Embrace AI-driven Reinforcement Learning to optimize your automotive plants. Stay ahead in the industry by transforming challenges into competitive advantages with cutting-edge solutions.

Leadership Challenges & Opportunities
Data Quality Issues
Utilize Reinforcement Learning in Automotive Plants to enhance data preprocessing and cleaning techniques. Implement adaptive algorithms that continuously learn from data inputs, ensuring high-quality datasets for training models. This leads to improved decision-making and operational efficiency, enabling more accurate predictive analytics.
Change Resistance
Foster a culture of innovation by integrating Reinforcement Learning in Automotive Plants through pilot projects that showcase quick wins. Engage employees by demonstrating tangible benefits and providing hands-on training. This approach encourages acceptance and enthusiasm for technology adoption, smoothing the transition to advanced methodologies.
Infrastructure Limitations
Address infrastructure challenges by deploying cloud-based Reinforcement Learning in Automotive Plants solutions that require minimal on-premise resources. Utilize edge computing for real-time data processing, reducing latency and enhancing system responsiveness. This strategy optimizes existing resources while enabling scalability and future growth.
Talent Acquisition Challenges
Mitigate talent acquisition issues by collaborating with educational institutions to integrate Reinforcement Learning in Automotive Plants into curricula. Offer internships and co-op programs that provide real-world experience. This proactive approach cultivates a skilled workforce tailored to the evolving needs of Automotive operations.
Assess how well your AI initiatives align with your business goals
AI Use Case vs ROI Timeline
| AI Use Case | Description | Typical ROI Timeline | Expected ROI Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Predictive Maintenance Scheduling | Using reinforcement learning, automotive plants can optimize maintenance schedules to reduce downtime. For example, a plant implemented RL algorithms to predict machine failures and adjusted maintenance schedules accordingly, leading to fewer unexpected breakdowns. | 6-12 months | High |
| Supply Chain Optimization | Reinforcement learning can enhance supply chain efficiency by predicting demand fluctuations and adjusting supply levels. For example, an automotive manufacturer utilized RL to balance inventory, reducing excess stock and improving cash flow. | 12-18 months | Medium-High |
| Quality Control Automation | AI-driven reinforcement learning can automate quality checks in production lines. For example, a plant adopted RL to adaptively learn from defects, improving inspection processes and reducing scrap rates significantly. | 6-12 months | High |
| Energy Consumption Management | Reinforcement learning algorithms can optimize energy usage in manufacturing processes. For example, an automotive plant implemented RL to adjust energy consumption dynamically, resulting in lower energy costs and a reduced carbon footprint. | 12-18 months | Medium-High |
Glossary
Work with Atomic Loops to architect your AI implementation roadmap — from PoC to enterprise scale.
Contact NowFrequently Asked Questions
- Reinforcement Learning enhances operational efficiency through automated decision-making processes.
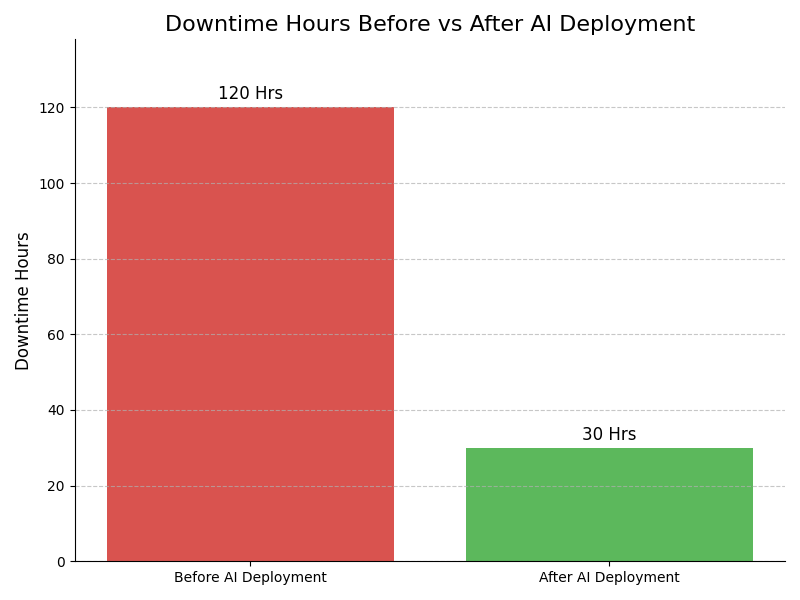
- It minimizes downtime by predicting equipment failures and optimizing maintenance schedules.
- The technology provides real-time insights, enabling data-driven decisions for production optimization.
- Companies can achieve significant cost savings through improved resource allocation and waste reduction.
- Competitive advantages arise from faster innovation cycles and improved product quality.
- Begin with a clear understanding of specific objectives and desired outcomes for implementation.
- Conduct a thorough assessment of existing systems to identify integration points and challenges.
- Engage with stakeholders to ensure alignment on goals and resource allocation for the project.
- Pilot programs can be launched to test solutions on a smaller scale before full deployment.
- Invest in training staff to build necessary skills for managing AI-driven technologies.
- Integration with legacy systems often poses significant technical challenges and requires careful planning.
- Data quality and availability issues can hinder effective model training and performance.
- Resistance to change among employees might slow down adoption and implementation speed.
- Regulatory compliance can complicate the deployment of AI technologies in production environments.
- Establishing a robust risk mitigation strategy is essential to address potential failures.
- Organizations should assess their digital maturity and readiness for AI technologies before adoption.
- Timing can coincide with major operational overhauls or shifts in production strategy.
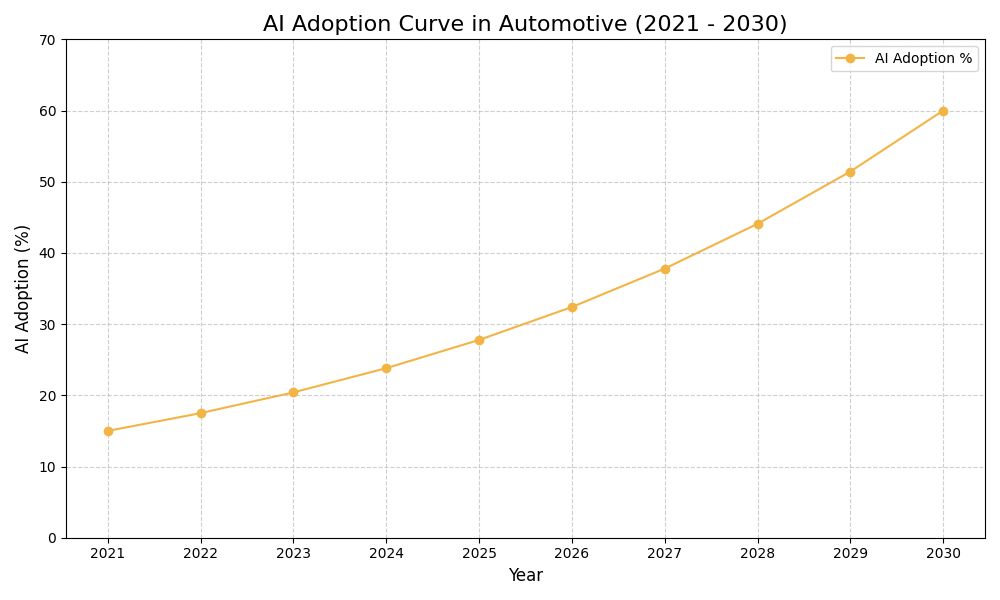
- Market competitiveness may necessitate early adoption to stay ahead of industry trends.
- Pilot projects can help gauge readiness and inform broader implementation strategies.
- Ongoing evaluation of operational challenges can signal the need for AI-driven solutions.
- Predictive maintenance applications significantly reduce downtime and maintenance costs for machinery.
- AI-driven supply chain optimization improves inventory management and reduces excess stock.
- Reinforcement Learning enhances quality control processes, leading to fewer defects in products.
- Automated assembly line adjustments based on real-time data optimize production flow.
- Companies leverage AI to personalize customer experiences through tailored vehicle options and upgrades.
- Adopting AI technologies requires adherence to industry regulations and safety standards.
- Companies must ensure data privacy and security when utilizing AI-driven systems.
- Regulatory audits may necessitate transparency in AI decision-making processes and outcomes.
- Compliance strategies should evolve alongside AI implementations to mitigate risks effectively.
- Engaging with regulatory bodies can provide guidance on acceptable AI practices in manufacturing.
- Key performance indicators should include production efficiency, downtime reduction, and cost savings.
- Monitoring quality metrics helps assess the impact of AI on product defects and customer satisfaction.
- Employee engagement and training success rates can indicate the effectiveness of implementation.
- Data-driven decision-making improvements should be tracked to measure strategic impacts.
- Return on investment calculations should encompass both tangible and intangible benefits realized.
- Investing in AI technologies positions companies for long-term competitive advantages in the market.
- Reinforcement Learning can significantly enhance operational efficiencies across various production processes.
- The technology enables proactive decision-making to address issues before they escalate.
- AI-driven insights can lead to innovative products and services that meet evolving customer demands.
- Overall, Reinforcement Learning supports a culture of continuous improvement and agility in operations.

