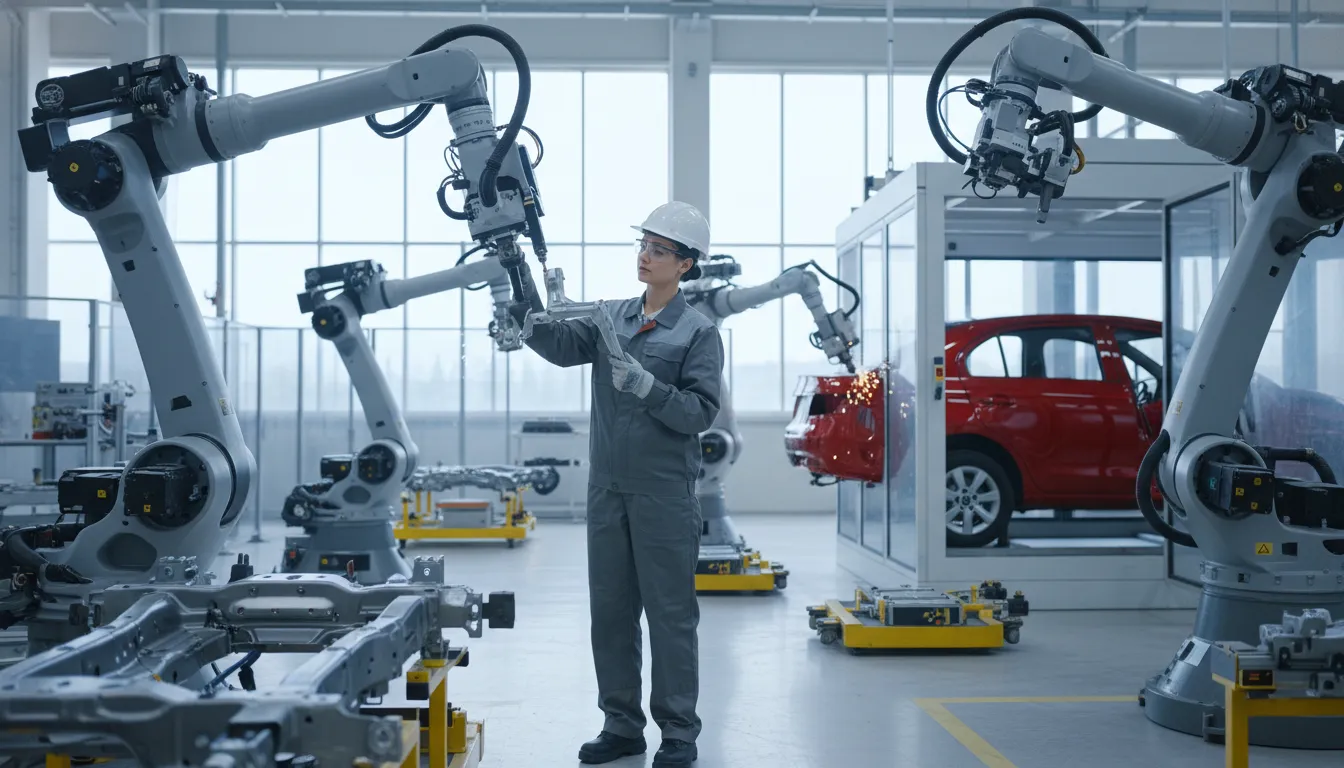
Robotics and AI in Assembly Lines
Robotics and AI in Assembly Lines represents a transformative shift within the Automotive sector, where advanced technologies are integrated to enhance production efficiency and quality. This concept encompasses the deployment of intelligent machines and algorithms that streamline assembly processes, reduce human error, and optimize resource allocation. As automotive manufacturers face increasing demands for customization and rapid production cycles, the relevance of this technological integration has never been greater, aligning seamlessly with broader trends of digital transformation and operational excellence.
The significance of Robotics and AI in Assembly Lines extends far beyond mere operational enhancements; it is reshaping the competitive landscape of the Automotive ecosystem. AI-driven practices enable organizations to innovate more rapidly, improve stakeholder collaboration, and enhance decision-making capabilities. As businesses embrace these technologies, they find new opportunities for efficiency and strategic growth. However, challenges such as integration complexity and evolving stakeholder expectations remain, necessitating a balanced approach that recognizes both the potentials and hurdles associated with this technological evolution.
Accelerate Your Automotive Production with Robotics and AI
Automotive companies must strategically invest in partnerships focused on AI technologies to enhance their assembly line processes. Implementing AI-driven solutions is expected to yield significant improvements in efficiency, quality control, and overall competitiveness in the market.
How Robotics and AI are Transforming Automotive Assembly Lines
Implementation Framework
Conduct a thorough assessment of existing assembly line processes to identify areas where AI can enhance efficiency, reduce downtime, and optimize resource allocation, paving the way for informed automation investments.
Industry Standards
Implement AI-driven solutions such as predictive maintenance and robotics integration to enhance production accuracy and speed, ensuring seamless collaboration between human workers and machines in assembly operations.
Technology Partners
Establish a robust framework for monitoring key performance indicators that measure AI's impact on assembly line operations, focusing on productivity, quality, and cost-effectiveness to ensure continuous improvement and adaptation.
Internal R&D
Develop a comprehensive training program for the workforce to enhance their AI-related skills, ensuring they can effectively collaborate with automated systems and contribute to a culture of innovation and continuous improvement.
Industry Standards
Utilize AI-driven analytics to optimize supply chain logistics, enhancing forecasting, inventory management, and supplier collaboration, which will improve overall assembly line efficiency and responsiveness to market changes.
Cloud Platform
Best Practices for Automotive Manufacturers
-
Impact : Reduces unexpected equipment failures
Example : Example: An automotive plant utilized AI to predict when robotic arms would require servicing, reducing unplanned downtime by 30%, thereby significantly enhancing production efficiency.
-
Impact : Extends machinery lifespan significantly
Example : Example: By analyzing vibration data from machines, a factory extended the life of critical components by 20%, delaying costly replacements and ensuring smoother operations.
-
Impact : Optimizes maintenance scheduling effectively
Example : Example: AI-driven analytics allowed a car manufacturer to optimize their maintenance schedule, decreasing maintenance costs by 15% while improving overall equipment effectiveness.
-
Impact : Lowers overall operational costs
Example : Example: Real-time monitoring systems enabled a major assembly line to reduce maintenance-related downtime by 25%, leading to increased throughput and overall productivity.
-
Impact : High initial investment for setup
Example : Example: A large automotive manufacturer faced budget overruns when implementing predictive maintenance, as the investment in sensors and software exceeded initial projections, delaying ROI.
-
Impact : Difficulty integrating with legacy systems
Example : Example: Legacy equipment in a plant could not integrate with new predictive maintenance software, forcing the team to spend additional resources on retrofitting, impacting project timelines.
-
Impact : Potential over-reliance on AI systems
Example : Example: An over-reliance on AI predictions led an automotive assembly line to overlook manual checks, resulting in undetected equipment issues that caused costly production breaks.
-
Impact : Risk of data inaccuracies affecting outcomes
Example : Example: A company found that inaccurate data input into their predictive maintenance system led to false positives, resulting in unnecessary service interventions and increased costs.
-
Impact : Boosts human-robot interaction efficiency
Example : Example: A leading automotive assembly line implemented collaborative robots (cobots) that worked alongside human workers, increasing assembly speed by 40% while improving safety and job satisfaction.
-
Impact : Improves task allocation between machines
Example : Example: By employing a smart task allocation system, an automotive plant optimized its robotic and human workforce, effectively reducing labor costs by 25% during peak production.
-
Impact : Enhances safety in assembly operations
Example : Example: Enhanced communication protocols between robots and humans allowed for real-time adjustments in assembly tasks, improving overall workflow efficiency by 30% in a busy manufacturing environment.
-
Impact : Reduces labor costs significantly
Example : Example: Safety features in collaborative robots minimized workplace accidents, contributing to a 50% reduction in reportable injuries over a year in a major automotive facility.
-
Impact : Potential job displacement concerns
Example : Example: An automotive manufacturer faced backlash from employees fearing job loss due to new robotics implementation, prompting the need for an extensive communication strategy to address concerns.
-
Impact : Need for extensive employee retraining
Example : Example: A company launched a retraining program for assembly line workers after introducing robots, but the complexity of new skills required led to initial productivity drops during the transition.
-
Impact : Technical malfunctions interrupt production
Example : Example: A malfunction in a robotic arm during a production run caused significant downtime, highlighting the need for reliable backup systems to prevent losses in output.
-
Impact : Integration complexity with existing workflows
Example : Example: Integrating new robotics into existing workflows proved more complex than anticipated, resulting in a delayed production schedule and requiring additional resources for troubleshooting.
-
Impact : Enhances decision-making speed and accuracy
Example : Example: An automotive assembly line harnessed real-time data analytics to identify bottlenecks immediately, allowing managers to adjust workflows and boost productivity by 15% within days.
-
Impact : Improves production quality control
Example : Example: By employing AI for quality control, a car manufacturer reduced defects in the final product by 20%, leading to higher customer satisfaction and lower returns.
-
Impact : Increases operational transparency
Example : Example: Real-time dashboards provided managers with immediate insights into production metrics, enabling quicker corrective actions and improving overall transparency in operations.
-
Impact : Facilitates proactive issue resolution
Example : Example: Proactive alerts from data analytics systems allowed an automotive plant to resolve issues before they escalated, reducing downtime by 40% and maintaining steady production flow.
-
Impact : Data overload complicates decision-making
Example : Example: An automotive plant struggled with data overload from multiple sensors, complicating decision-making processes and leading to confusion among staff regarding priorities during peak hours.
-
Impact : Dependence on continuous data streams
Example : Example: An automotive manufacturer faced challenges ensuring continuous quality data streams, resulting in occasional lapses in production insights that caused delays and inefficiencies.
-
Impact : Cybersecurity threats to data integrity
Example : Example: Cybersecurity breaches in a data-heavy environment raised concerns about data integrity, forcing a major car manufacturer to invest heavily in cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive information.
-
Impact : High costs of data management tools
Example : Example: The costs associated with advanced data management tools exceeded budget expectations for an automotive manufacturer, prompting a reassessment of priorities and resource allocation.
-
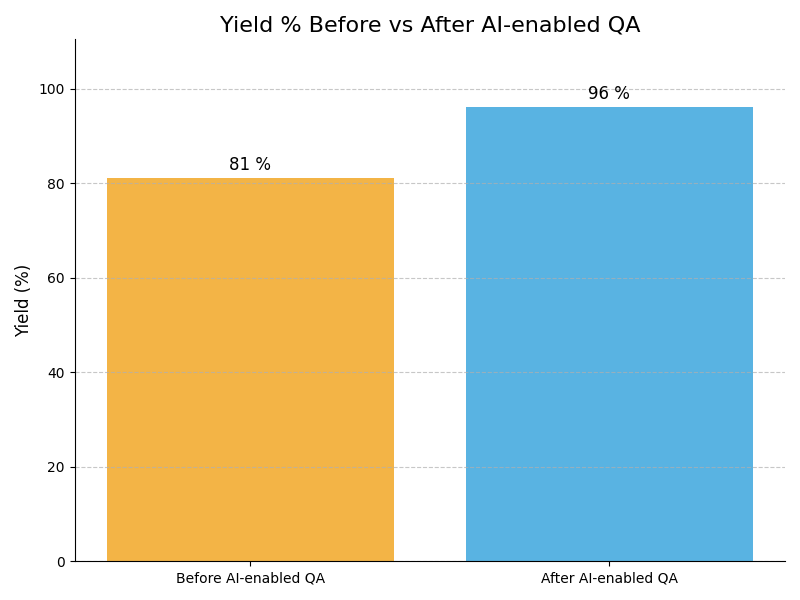
Impact : Enhances defect detection accuracy significantly
Example : Example: In an automotive assembly line, a vision-based AI system flags microscopic paint defects in real time as car bodies pass under cameras, catching flaws human inspectors previously missed during night shifts.
-
Impact : Reduces production downtime and costs
Example : Example: A semiconductor factory uses AI to detect early soldering anomalies. The system stops the line immediately, preventing a full batch failure that would have caused hours of rework and shutdown.
-
Impact : Improves quality control standards
Example : Example: A food packaging plant uses AI image recognition to verify seal integrity on every packet, ensuring non-compliant packages are rejected instantly before shipping.
-
Impact : Boosts overall operational efficiency
Example : Example: AI dynamically adjusts inspection thresholds based on production speed, allowing the factory to increase output during peak demand without sacrificing quality.
-
Impact : High initial investment for implementation
Example : Example: A mid-sized electronics manufacturer delays AI rollout after realizing camera hardware, GPUs, and system integration push upfront costs beyond budget approvals.
-
Impact : Potential data privacy concerns
Example : Example: AI quality systems capturing worker activity unintentionally store employee facial data, triggering compliance issues with internal privacy policies.
-
Impact : Integration challenges with existing systems
Example : Example: AI software cannot communicate with a 15-year-old PLC controller, forcing engineers to manually export data and slowing decision-making.
-
Impact : Dependence on continuous data quality
Example : Example: Dust accumulation on camera lenses causes the AI to misclassify normal products as defective, leading to unnecessary scrap until recalibration.
-
Impact : Improves employee skill sets continuously
Example : Example: A major automotive manufacturer implemented a continuous training program for assembly line workers, resulting in a 25% reduction in errors and higher overall productivity.
-
Impact : Boosts engagement and job satisfaction
Example : Example: Regular training sessions on new technologies increased employee engagement levels significantly, leading to a more motivated workforce and lower turnover rates in the factory.
-
Impact : Reduces errors in production processes
Example : Example: By focusing on continuous learning, an automotive assembly line adapted more quickly to new robotic technologies, reducing transition times and maintaining production levels.
-
Impact : Enhances adaptability to new technologies
Example : Example: Employees who received regular training were more adept at troubleshooting issues, leading to faster resolution times and minimized production disruptions on the assembly line.
-
Impact : Time-consuming training schedules
Example : Example: A large automotive company faced delays in production due to lengthy training schedules that took workers away from their roles for extended periods, impacting output.
-
Impact : Potential resistance to learning new skills
Example : Example: Some employees resisted adapting to new training methods, causing friction within teams and slowing down the integration of robotics in the assembly process.
-
Impact : Costs associated with training programs
Example : Example: High costs associated with hiring external trainers for advanced technologies raised concerns among management regarding the return on investment in training programs.
-
Impact : Inconsistent training quality across teams
Example : Example: Inconsistent training quality across different teams led to varied skill levels, creating gaps in knowledge that resulted in inefficiencies on the production floor.
-
Impact : Increases responsiveness to market changes
Example : Example: An automotive manufacturer adopted agile methodologies, allowing teams to respond quickly to market feedback and adjust production schedules, leading to a 20% increase in customer satisfaction.
-
Impact : Facilitates rapid prototyping of solutions
Example : Example: Rapid prototyping enabled an automotive assembly line to test new AI applications quickly, reducing the time to market for innovative solutions by 30%.
-
Impact : Enhances collaboration across teams
Example : Example: Enhanced collaboration among engineering and production teams under agile practices improved communication, leading to a 15% reduction in project delays across the board.
-
Impact : Improves project visibility and accountability
Example : Example: Agile project management tools provided better visibility into ongoing projects, increasing accountability and ensuring timely completion of tasks in the automotive factory.
-
Impact : Requires cultural shift within organization
Example : Example: A traditional automotive manufacturer struggled to adapt to agile methodologies, facing cultural resistance that slowed down the adoption process and impacted overall efficiency.
-
Impact : Potential for scope creep in projects
Example : Example: The flexibility of agile practices led to scope creep in projects, resulting in delays and budget overruns for an automotive assembly line initiative.
-
Impact : Inconsistent application of agile practices
Example : Example: Teams applying agile methodologies inconsistently created confusion and inefficiencies, leading to mismatched expectations and communication breakdowns on the production floor.
-
Impact : High initial training investment for teams
Example : Example: Initial training investments for agile practices raised concerns among management, as they weighed the immediate costs against the potential long-term benefits of agility.
The future of manufacturing won’t be written by machines alone. It will be written by people, using AI to extend what they can do, not replace them.
– Natan LinderCompliance Case Studies


Embrace AI-driven solutions and elevate your automotive manufacturing. Stay ahead of the competition by transforming your assembly lines today for unmatched efficiency and productivity.

Leadership Challenges & Opportunities
Data Integration Challenges
Utilize Robotics and AI in Assembly Lines to create a unified data ecosystem that integrates disparate sources. Implement real-time data analytics and machine learning models to enhance operational visibility. This strategy improves decision-making and drives efficiency by enabling seamless information flow across the production process.
Resistance to Change
Address resistance to adopting Robotics and AI in Assembly Lines by fostering a culture of innovation through workshops and pilot programs. Involve employees in the transition process to build trust. Highlight success stories and tangible benefits to encourage acceptance and commitment to new technologies.
Supply Chain Disruptions
Employ Robotics and AI in Assembly Lines to enhance supply chain resilience by utilizing predictive analytics and automated inventory management. This approach allows for real-time adjustments to production schedules, minimizing downtime and ensuring continuity. Accurate forecasting improves resource allocation and strengthens supplier relationships.
High Implementation Costs
Mitigate high implementation costs of Robotics and AI in Assembly Lines by leveraging government grants and subsidies targeted at technology adoption in the Automotive sector. Implement modular systems that allow for gradual investment, focusing on high-impact areas first. This phased approach reduces financial risk while maximizing ROI.
Assess how well your AI initiatives align with your business goals

AI Use Case vs ROI Timeline
| AI Use Case | Description | Typical ROI Timeline | Expected ROI Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Predictive Maintenance for Robotics | AI predicts when robotic systems need maintenance, reducing downtime. For example, a manufacturer uses sensors and AI algorithms to monitor robotic arms, identifying potential failures before they occur, minimizing production halts. | 6-12 months | High |
| Quality Control Automation | AI-driven systems enhance quality assurance by inspecting products in real-time. For example, an automotive assembly line employs AI vision systems to identify defects in car parts, ensuring only quality products proceed. | 6-12 months | Medium-High |
| Optimized Workflow Scheduling | AI algorithms optimize assembly line schedules for efficiency. For example, an automotive plant uses AI to dynamically adjust the workflow based on real-time data, improving output and reducing idle time. | 12-18 months | Medium-High |
| Robotic Process Automation | Automate repetitive tasks with AI-driven robots. For example, an automotive manufacturer implements collaborative robots (cobots) to assist human workers in assembling components, enhancing productivity and consistency. | 6-12 months | High |
Glossary
Work with Atomic Loops to architect your AI implementation roadmap — from PoC to enterprise scale.
Contact NowFrequently Asked Questions
- Robotics and AI automate repetitive tasks, enhancing efficiency in assembly lines.
- They improve quality control by minimizing human error during manufacturing.
- These technologies facilitate real-time data analysis for informed decision-making.
- Automotive companies can respond faster to market changes with agile operations.
- Overall, they lead to significant cost reductions and increased productivity.
- Start with a clear strategy that outlines specific goals and objectives.
- Conduct a thorough assessment of your existing systems and capabilities.
- Identify suitable technologies that align with your operational needs.
- Engage with experienced vendors for guidance and support during integration.
- Pilot projects can help test concepts before full-scale implementation.
- These technologies lead to increased efficiency and reduced production times.
- Companies experience improved product quality and consistency through automation.
- AI can optimize supply chain management and inventory control processes.
- Businesses gain a competitive edge by enhancing responsiveness to customer demands.
- Overall, these advancements contribute to substantial cost savings over time.
- Integration with legacy systems often poses significant technical challenges.
- Employee resistance to change can hinder successful implementation efforts.
- Data security and privacy concerns must be addressed to mitigate risks.
- High initial investment costs can deter smaller firms from adopting technologies.
- Continuous training and skill development are essential for workforce adaptation.
- Companies should assess readiness during periods of operational inefficiency.
- Market competition may trigger the need for technological advancements.
- New product lines or shifts in consumer preferences can indicate readiness.
- Economic downturns may motivate firms to seek cost-saving solutions.
- Strategic planning should align technology adoption with business growth goals.
- Compliance with safety regulations is essential for machinery and robotics.
- Data privacy laws must be adhered to, especially regarding customer information.
- Staying updated with industry standards can prevent legal complications.
- Environmental regulations may impact robotic operations and waste management.
- Engaging legal experts can help navigate complex regulatory landscapes.
- Evaluate production efficiency improvements in terms of time and costs.
- Track the reduction in error rates and product defects over time.
- Monitor employee productivity and satisfaction following technology adoption.
- Assess customer feedback and satisfaction levels regarding product quality.
- Review return on investment (ROI) to measure overall financial benefits.

