Unsupervised Learning in Automotive Quality
Unsupervised Learning in Automotive Quality refers to the application of machine learning techniques that analyze automotive data without predefined labels. In the automotive sector, this approach enables manufacturers to identify patterns and anomalies in quality data, enhancing product reliability and customer satisfaction. As the industry leans towards AI-led transformation, the integration of unsupervised learning becomes crucial, aligning with the evolving operational priorities focused on data-driven decision-making and continuous improvement.
The significance of the automotive ecosystem is underscored by how AI-driven practices, particularly unsupervised learning, are redefining competitive dynamics and fostering innovation. This technology enhances efficiency in quality control processes, facilitates informed decision-making, and shapes long-term strategic directions for automotive stakeholders. While the adoption of AI presents substantial growth opportunities, realistic challenges such as integration complexity and shifting expectations must be navigated carefully to ensure successful implementation and sustained value creation.
Harness AI for Unmatched Quality in Automotive Production
Automotive companies should strategically invest in partnerships focused on Unsupervised Learning technologies to enhance quality control mechanisms and predictive maintenance. Implementing these AI-driven strategies can lead to significant cost savings, improved product reliability, and a stronger competitive edge in the market.
How Unsupervised Learning is Revolutionizing Automotive Quality?
Implementation Framework
Assessing current data quality is crucial for implementing unsupervised learning. Identify and address gaps in data collection, ensuring comprehensive datasets enhance AI accuracy, leading to improved automotive quality control and performance.
Industry Standards
Developing robust AI models using unsupervised learning techniques allows for the identification of patterns in automotive quality data. These models enhance predictive maintenance and reduce defect rates, ultimately improving overall product quality.
Technology Partners
Setting up continuous monitoring systems for quality metrics ensures that AI-driven insights remain relevant. This process facilitates real-time adjustments based on evolving data trends, enhancing automotive quality and operational efficiency.
Internal R&D
Integrating feedback loops into quality processes enables the refinement of AI models. Real-time feedback from users and systems enhances the adaptability of unsupervised learning applications, driving further improvements in automotive quality standards.
Cloud Platform
Scaling AI solutions across various automotive operations maximizes the benefits of unsupervised learning. This approach allows for comprehensive quality improvements, ensuring consistency and reducing costs while enhancing overall supply chain resilience.
Industry Standards
Best Practices for Automotive Manufacturers
-
Impact : Improves defect identification accuracy
Example : Example: In a car manufacturing plant, clustering algorithms analyze sensor data to identify patterns in engine defects, allowing engineers to address issues proactively and significantly reduce warranty claims.
-
Impact : Facilitates real-time quality monitoring
Example : Example: A tire production facility uses unsupervised learning to monitor anomalies in rubber quality, catching potential defects before they affect production rates and customer satisfaction.
-
Impact : Enhances predictive maintenance capabilities
Example : Example: AI models cluster historical maintenance data, predicting when machines will fail. This foresight enables timely repairs, reducing unplanned downtime by 30% in high-demand periods.
-
Impact : Optimizes resource allocation effectively
Example : Example: By clustering production line data, a manufacturer reallocates workforce during peak hours, ensuring quality checks are performed without delays, improving throughput by 20%.
-
Impact : Data quality issues may arise
Example : Example: A vehicle assembly line suffers from inaccurate defect predictions due to poor data quality inputs, leading to false positives and unnecessary rework, frustrating operators and increasing costs.
-
Impact : High complexity in model training
Example : Example: Engineers struggle with complex clustering algorithms, leading to extended project timelines and resource wastage as they attempt to fine-tune models without adequate expertise.
-
Impact : Potential resistance from staff
Example : Example: Production staff resist AI integration, fearing it may replace jobs. This resistance delays the adoption of the technology, hindering potential quality improvements and operational efficiencies.
-
Impact : Difficulty in interpreting results
Example : Example: A manufacturer finds it challenging to interpret clustering results, leading to confusion in decision-making processes and ultimately impacting quality assurance protocols.
-
Impact : Reduces human error in inspections
Example : Example: An automotive plant implements AI-driven anomaly detection, enabling machines to flag deviations in assembly quality faster than human inspectors, thereby reducing error rates by over 25%.
-
Impact : Enhances speed of quality assessments
Example : Example: During a production run, AI systems automatically detect minute deviations in weld strength, allowing immediate adjustments that prevent costly recalls and maintain safety standards.
-
Impact : Increases detection of subtle defects
Example : Example: AI identifies subtle patterns in paint application anomalies that human eyes often miss, reducing aesthetic defects in finished vehicles and enhancing brand reputation.
-
Impact : Supports continuous process improvement
Example : Example: Continuous monitoring systems provide ongoing feedback, enabling engineers to make iterative improvements in production processes that lead to a 15% reduction in defect rates.
-
Impact : Requires significant technical expertise
Example : Example: A manufacturer faced challenges integrating AI with legacy inspection systems, incurring delays and added costs as engineers struggled to create compatible interfaces for data sharing.
-
Impact : Integration with legacy systems
Example : Example: An automotive company becomes overly dependent on AI, leading to a decline in manual inspection skills among staff, which creates vulnerability during system downtimes or failures.
-
Impact : Overreliance on automated systems
Example : Example: Automated systems frequently flag false positives, causing unnecessary production halts. This leads to frustration among staff and potential loss of confidence in AI technologies.
-
Impact : False positives in detection processes
Example : Example: During initial testing, an AI fails to detect certain defects due to insufficient training data, resulting in a batch of faulty vehicles reaching customers, damaging brand trust.
-
Impact : Boosts model performance significantly
Example : Example: By enhancing feature engineering, a manufacturer identifies overlooked variables influencing quality, leading to substantial improvements in defect detection accuracy during assembly processes.
-
Impact : Facilitates deeper insights into quality
Example : Example: AI models trained with diverse features provide insights into emerging trends, helping engineers adapt processes proactively and maintain high quality standards in competitive markets.
-
Impact : Improves adaptability to changing conditions
Example : Example: Continuous improvements in feature selection allow models to adapt to different production conditions, ensuring consistent quality outputs even during material changes or process adjustments.
-
Impact : Enables identification of new defect types
Example : Example: The identification of new defect types through enhanced features allows for targeted training of quality control personnel, resulting in a 40% increase in defect resolution speed.
-
Impact : Time-consuming feature selection process
Example : Example: A team spends excessive time on feature selection, delaying the deployment of AI solutions and causing lost opportunities for quality improvements in a competitive market.
-
Impact : Potential for overfitting models
Example : Example: In their haste to improve models, engineers inadvertently create overly complex models that overfit training data, resulting in poor performance during real-world applications.
-
Impact : Inadequate data representation issues
Example : Example: A failure to represent certain defect types adequately leads to AI models missing critical quality issues, causing higher rates of customer complaints and product returns.
-
Impact : Complexity in maintaining feature sets
Example : Example: Constantly evolving production requirements complicate the maintenance of feature sets, resulting in outdated models that fail to deliver accurate quality assessments over time.
-
Impact : Encourages knowledge sharing across teams
Example : Example: By fostering collaboration between engineering and quality assurance teams, an automotive manufacturer successfully aligns AI initiatives with practical operational needs, improving overall quality metrics by 15%.
-
Impact : Drives holistic quality improvement strategies
Example : Example: Joint workshops among departments enable sharing of insights that refine AI models, leading to a 20% reduction in defects during production and improved team morale.
-
Impact : Improves AI model relevance
Example : Example: Cross-department initiatives create a culture where all employees feel responsible for quality, leading to enhanced engagement and significant contributions to continuous improvement projects.
-
Impact : Enhances employee engagement and ownership
Example : Example: Regular interdepartmental meetings ensure AI models remain relevant to evolving quality standards, preventing costly oversights and improving product reliability.
-
Impact : Communication barriers may persist
Example : Example: Communication barriers between IT and production teams delay the implementation of AI solutions, resulting in missed opportunities for quality enhancements in the automotive manufacturing process.
-
Impact : Resource allocation conflicts
Example : Example: Conflicts arise over resource allocation for AI projects, leading to delays that hinder progress in quality improvements across departments and frustration among team leaders.
-
Impact : Diverse priorities among departments
Example : Example: Differing departmental priorities lead to misalignment in AI objectives, causing inefficiencies and preventing the realization of expected quality improvements from new initiatives.
-
Impact : Resistance to change from teams
Example : Example: Some teams resist changes brought about by AI integration, fearing a loss of control over quality processes, which stalls necessary advancements in operational excellence.
-
Impact : Enables immediate quality feedback
Example : Example: An automotive assembly line employs real-time monitoring systems to track quality metrics. When a deviation is detected, engineers are alerted immediately, enabling quick adjustments that prevent further defects and enhance product reliability.
-
Impact : Enhances decision-making speed
Example : Example: In a vehicle manufacturing facility, real-time monitoring of paint application allows for immediate feedback on thickness. This prevents non-compliance with standards and reduces the need for costly rework.
-
Impact : Supports proactive issue resolution
Example : Example: AI-powered dashboards display live quality data, enabling managers to make informed decisions quickly, reducing downtime by 20% during peak production times due to timely interventions.
-
Impact : Reduces waste in production
Example : Example: A real-time system identifies a recurring fault in engine assembly, allowing the team to address the root cause swiftly, reducing scrap rates and improving overall production efficiency by 15%.
-
Impact : Requires constant system updates
Example : Example: A manufacturer struggles with constant updates to their monitoring system, leading to downtime during critical production periods as IT works to implement necessary changes and patches.
-
Impact : Potential for data overload
Example : Example: A real-time monitoring system generates excessive data, overwhelming staff and making it difficult to identify actionable insights, ultimately delaying timely quality interventions.
-
Impact : Initial setup can be complex
Example : Example: Initial setup of the monitoring system proves complex, requiring extensive training and causing delays in implementation, which hampers expected timelines for quality improvements.
-
Impact : Dependence on system reliability
Example : Example: A factory’s reliance on monitoring systems leads to concerns when a system failure occurs, resulting in unmonitored production lines and potential quality control failures during peak hours.
Unsupervised learning is revolutionizing automotive quality by enabling systems to identify defects without prior labeling, thus enhancing efficiency and accuracy in production.
– Internal R&DCompliance Case Studies



Harness the power of AI-driven Unsupervised Learning to enhance quality control and gain a competitive edge. Transform your operations and lead the market today!
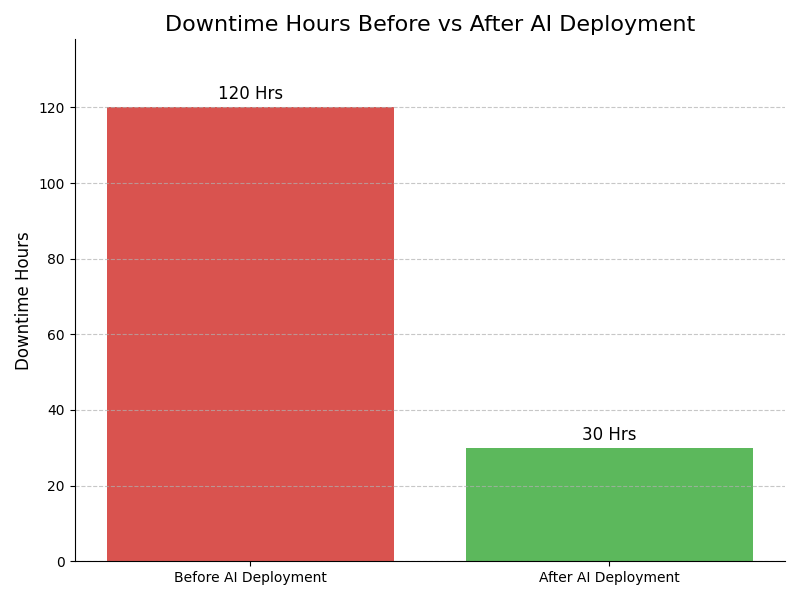
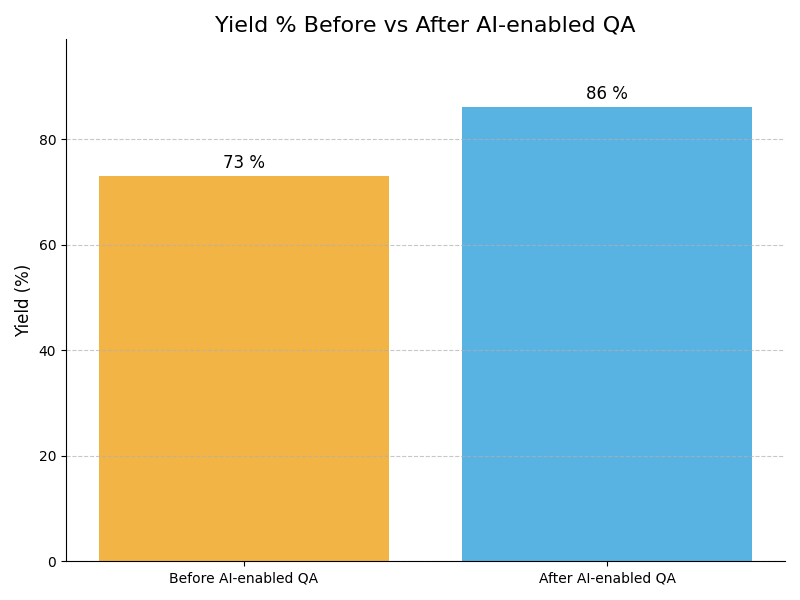
Leadership Challenges & Opportunities
Data Quality Issues
Utilize Unsupervised Learning in Automotive Quality to automate data cleansing and anomaly detection. By continuously monitoring data streams, this technology identifies inconsistencies and errors, enhancing data integrity. Improved data quality leads to more accurate insights and better decision-making across the automotive production process.
Integration of IoT Sensors
Implement Unsupervised Learning in Automotive Quality to analyze data from IoT sensors seamlessly. Utilize clustering algorithms to identify patterns in real-time sensor data, enabling proactive quality management. This integration enhances process efficiency and reduces defects by addressing issues before they escalate.
Change Resistance
Foster a culture of innovation by showcasing the benefits of Unsupervised Learning in Automotive Quality through pilot projects. Encourage cross-departmental collaboration and training sessions to demonstrate successful use cases. This approach mitigates resistance, aligning organizational values with technological advancements for quality improvement.
Talent Acquisition Challenges
Address talent shortages by leveraging Unsupervised Learning in Automotive Quality for automated insights that enhance recruitment processes. Use predictive analytics to identify candidate success factors, streamlining hiring. This technology not only improves talent acquisition efficiency but also ensures alignment with the organization's quality objectives.
Assess how well your AI initiatives align with your business goals
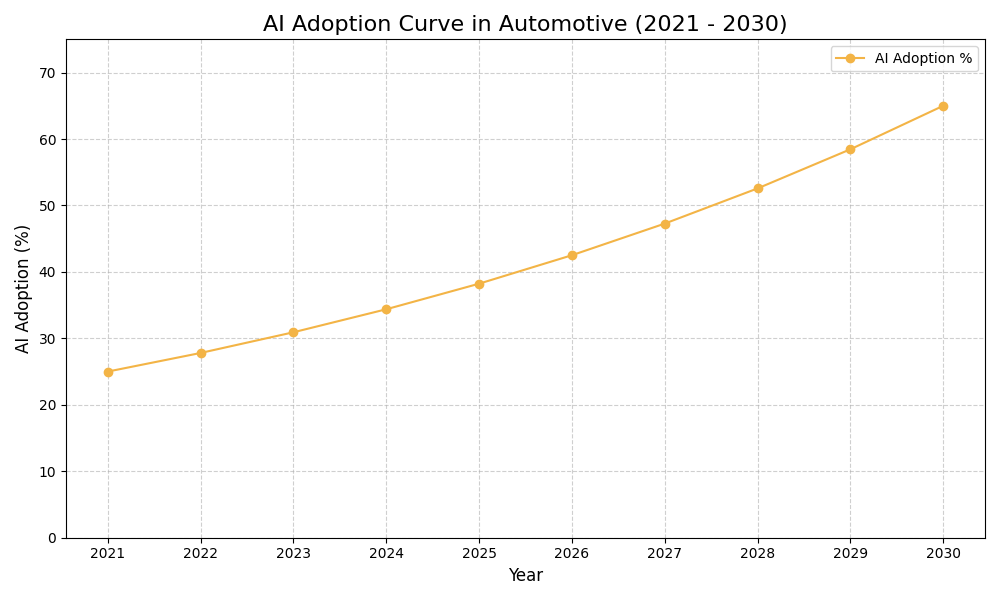
AI Use Case vs ROI Timeline
| AI Use Case | Description | Typical ROI Timeline | Expected ROI Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anomaly Detection in Manufacturing | Unsupervised learning can identify anomalies in production processes. For example, a car manufacturer uses clustering to detect defects in assembly lines, allowing for real-time adjustments. This leads to reduced waste and improved quality control. | 6-12 months | High |
| Predictive Maintenance for Equipment | Applying unsupervised algorithms can help in predictive maintenance by analyzing operational data. For example, an automotive plant uses this to forecast equipment failures, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs. | 12-18 months | Medium-High |
| Quality Assessment through Image Analysis | AI can analyze images of vehicles for quality assurance. For example, unsupervised models identify surface imperfections in painted cars, ensuring only high-quality products reach customers. | 6-12 months | High |
| Customer Feedback Analysis | Unsupervised learning can analyze customer feedback to identify trends and issues. For example, an automotive company uses clustering to group similar feedback, improving product features based on real user data. | 6-12 months | Medium-High},{ |
Glossary
Work with Atomic Loops to architect your AI implementation roadmap — from PoC to enterprise scale.
Contact NowFrequently Asked Questions
- Unsupervised Learning identifies patterns in data without labeled examples, enhancing quality control.
- It optimizes processes by uncovering hidden insights that traditional methods may miss.
- This technology fosters innovation by enabling data-driven decision-making in automotive design.
- Companies can improve product quality and reduce defects through predictive modeling techniques.
- By leveraging AI, organizations can gain a competitive edge in the automotive market.
- Begin by evaluating your current data landscape and existing technology infrastructure.
- Identify key stakeholders and create a cross-functional team to drive the initiative.
- Select appropriate algorithms based on your specific quality challenges and data types.
- Pilot projects can demonstrate value and refine approaches before broader implementation.
- Continuous training and support are essential to ensure successful adoption across teams.
- Businesses can achieve significant cost savings by reducing defect rates and waste.
- Enhanced insights lead to better product quality, increasing customer satisfaction.
- The technology enables faster identification of quality issues, improving response times.
- Organizations can streamline operations, resulting in improved supply chain efficiency.
- Overall, AI-driven processes contribute to sustained competitive advantages in the market.
- Data quality issues can hinder successful implementation, requiring thorough cleansing.
- Resistance to change from staff can impact project adoption and success rates.
- Integration with legacy systems may pose technical difficulties and require planning.
- Regulatory compliance and industry standards must be carefully navigated during deployment.
- Continuous monitoring and adjustment are key to overcoming these challenges effectively.
- The best time is when you have a clear understanding of your data capabilities.
- Implementing during a product development cycle can enhance quality outcomes.
- Timing aligns well with digital transformation initiatives within your organization.
- Early-stage pilot projects can provide insights to refine broader implementation plans.
- Regular reviews of industry trends can guide timely adoption for competitive advantage.
- Predictive maintenance models help reduce downtime and enhance vehicle reliability.
- Quality assurance processes utilize clustering techniques to identify defect patterns.
- Anomaly detection systems can spot irregularities in manufacturing processes quickly.
- Customer feedback analysis enables better understanding of consumer preferences and needs.
- Supply chain optimization can be achieved through data-driven inventory management.
- AI provides advanced analytical capabilities that traditional methods cannot match.
- It automates complex data processing, freeing up valuable human resources.
- AI-driven insights enhance decision-making speed and accuracy across operations.
- Investing in AI can future-proof your organization against industry disruptions.
- Ultimately, AI creates significant strategic advantages in quality management and innovation.

